2% Decline In U.S. Economic Growth: Analysis Of Spending And Tariff Effects
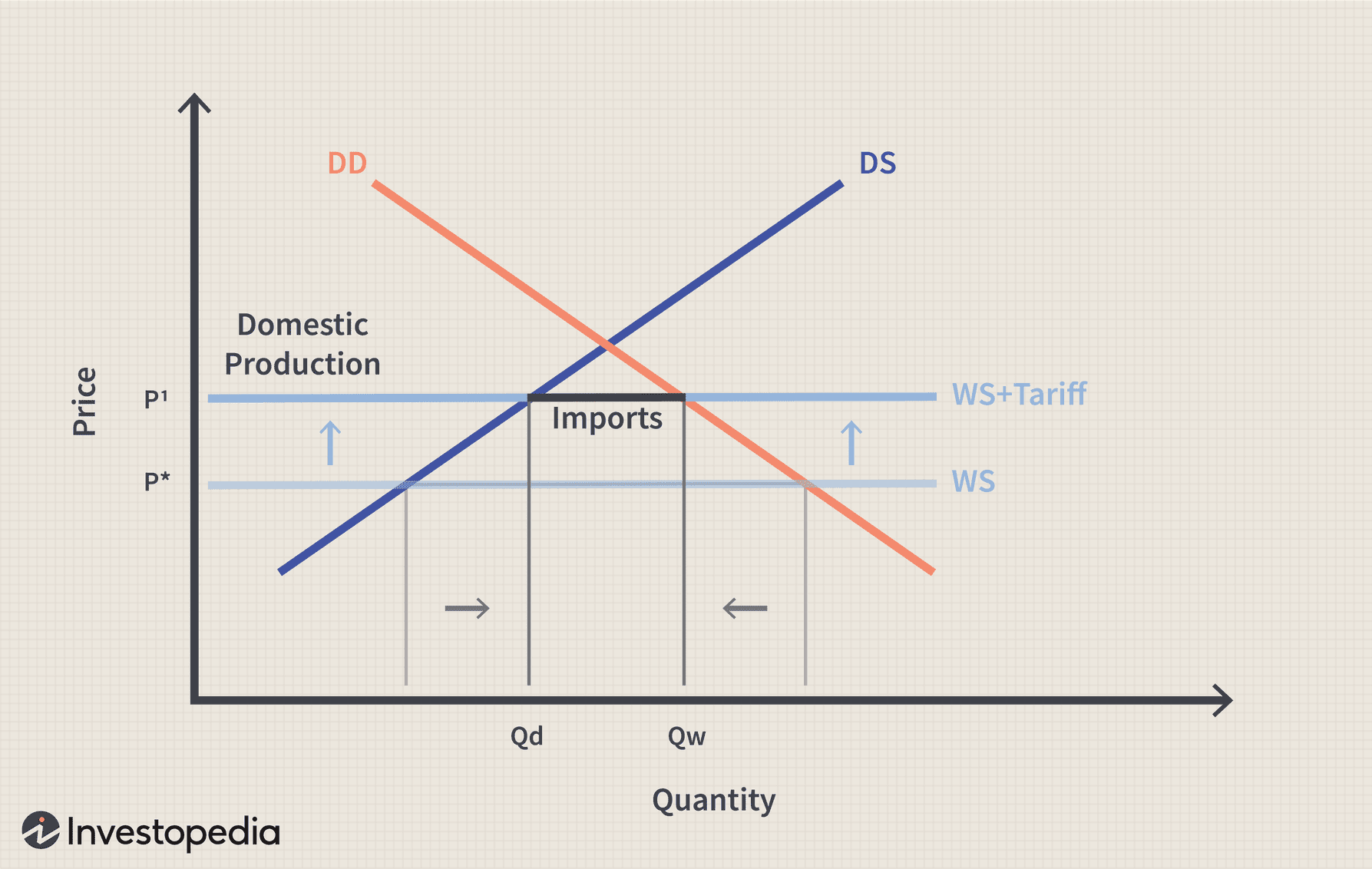
Table of Contents
The Role of Reduced Consumer Spending in Economic Slowdown
The slowdown in U.S. economic growth is inextricably linked to a decrease in consumer spending. This decline isn't merely a dip; it's a significant shift in consumer behavior with far-reaching consequences.
Decreased Disposable Income and its Impact
Several factors contributed to the decrease in disposable income, directly impacting consumer spending. High inflation, fueled by factors like supply chain disruptions and increased energy prices, eroded purchasing power. Simultaneously, rising interest rates increased the cost of borrowing, making large purchases like homes and cars less accessible.
This resulted in a noticeable drop in consumer spending across various sectors. Data reveals a significant decline in retail sales, particularly in the durable goods sector (e.g., appliances, furniture).
- Impact on specific industries: The automotive industry felt the pinch, with car sales slowing down due to higher interest rates and prices. The housing market also experienced a slowdown, with fewer new home purchases and construction projects.
- Consumer confidence index trends: The Consumer Confidence Index (CCI) consistently reflected declining consumer sentiment throughout the period, indicating a lack of confidence in the economy and future prospects.
- Government stimulus measures and their effectiveness: While government stimulus measures were implemented, their effectiveness in counteracting the decline in consumer spending proved limited, highlighting the depth of the economic challenges.
Shifting Consumer Priorities and Spending Habits
Consumers adapted to the economic downturn by altering their spending habits. Increased savings became a priority as consumers sought financial security in uncertain times. Discretionary spending on non-essential goods and services decreased significantly.
Inflation played a crucial role in shaping consumer choices. With prices soaring, consumers prioritized essential goods, trading down to cheaper alternatives or reducing overall consumption.
- Growth of the "experiential economy" vs. material goods: Interestingly, while spending on material goods declined, the "experiential economy" (travel, entertainment) saw some resilience, suggesting a shift in consumer priorities towards experiences over possessions.
- Impact of supply chain disruptions on consumer goods availability and prices: Continued supply chain issues contributed to both reduced availability and higher prices of consumer goods, further restricting spending.
- Changes in borrowing and credit card usage: With higher interest rates, borrowing and credit card usage decreased, reflecting consumers' increased caution and reduced reliance on debt.
The Impact of Tariffs on U.S. Economic Growth
The imposition of tariffs, particularly during trade wars, added another layer of complexity to the economic slowdown. These tariffs had a multifaceted impact, affecting businesses, consumers, and the overall economic landscape.
Trade Wars and Their Economic Consequences
Tariffs significantly impact both import and export prices. Increased tariffs on imported goods lead to higher prices for consumers, reducing demand and potentially harming domestic businesses relying on imported components. Conversely, tariffs imposed by other countries on U.S. exports negatively affect U.S. businesses involved in international trade.
- Examples of specific industries heavily impacted by tariffs: The agricultural sector and manufacturing industries were particularly vulnerable, facing retaliatory tariffs from trading partners.
- Data on trade deficits and surpluses before and after tariff implementation: Analysis of trade data reveals a significant impact on trade deficits and surpluses, illustrating the effects of tariffs on the overall balance of trade.
- Analysis of retaliatory tariffs from other countries: Retaliatory tariffs from other countries further exacerbated the negative economic consequences, creating a cycle of trade restrictions and economic damage.
Inflationary Pressures from Tariffs
Tariffs are a significant contributor to inflationary pressures. Increased import costs due to tariffs translate directly into higher prices for consumers, affecting the cost of living.
- Examples of specific goods affected by tariff-induced price increases: Numerous everyday goods, from clothing and electronics to certain food items, experienced price increases due to tariffs.
- Comparison of inflation rates before and after tariff implementation: Inflation rates generally increased following the implementation of tariffs, reflecting the direct impact on consumer prices.
- Government efforts to mitigate inflationary pressures: The government employed various measures to attempt to mitigate inflationary pressures, but their effectiveness was limited, underscoring the severity of the issue.
Conclusion: Understanding and Addressing the 2% Decline in U.S. Economic Growth
The 2% decline in U.S. economic growth is a complex issue stemming from a confluence of factors. Reduced consumer spending, driven by decreased disposable income and shifting priorities, played a significant role. Simultaneously, the lingering effects of tariffs, contributing to inflation and trade imbalances, further exacerbated the economic downturn. These two factors are interconnected, with decreased consumer spending partly fueled by tariff-induced inflation.
To address this decline, a comprehensive strategy addressing both consumer spending and the impact of tariffs is crucial. This requires a multifaceted approach, including policies aimed at bolstering consumer confidence, stimulating demand, and addressing trade imbalances through careful negotiation and trade agreements. To deepen your understanding of the intricacies of U.S. economic growth analysis and the impact of spending and tariffs on the US economy, further research into economic indicators, trade policies, and consumer behavior is recommended. Understanding economic decline and its complex causes is key to fostering a more resilient and prosperous future.

Featured Posts
-
 Le Combat Pour Les Droits Du Vivant L Exemple De L Etoile De Mer
May 31, 2025
Le Combat Pour Les Droits Du Vivant L Exemple De L Etoile De Mer
May 31, 2025 -
 Las Mejores Empanadas De Jamon Y Queso Sin Horno
May 31, 2025
Las Mejores Empanadas De Jamon Y Queso Sin Horno
May 31, 2025 -
 Early Start To Fire Season In Canada And Minnesota
May 31, 2025
Early Start To Fire Season In Canada And Minnesota
May 31, 2025 -
 Thompsons Bad Luck In Monte Carlo
May 31, 2025
Thompsons Bad Luck In Monte Carlo
May 31, 2025 -
 Estevan Street Sweeping Schedule 2024 Full Dates Released
May 31, 2025
Estevan Street Sweeping Schedule 2024 Full Dates Released
May 31, 2025
