Analysis: China's Monetary Policy Response To Trade Tensions
Table of Contents
China's economic growth has been significantly impacted by escalating trade tensions, most notably the protracted trade war with the United States. This analysis delves into the complex ways China's monetary policy has adapted and responded to these challenges, examining the effectiveness of various strategies implemented to mitigate negative economic consequences. We will explore the impact on key economic indicators like GDP growth and the RMB exchange rate, analyze the role of interest rates and quantitative easing, and project the future trajectory of China's monetary policy in a globally uncertain environment. Understanding China's monetary policy response is crucial for comprehending the broader global economic landscape and the intricate interplay between trade and monetary tools.
H2: The Impact of Trade Tensions on the Chinese Economy:
The China-US trade war, along with other global trade tensions, inflicted considerable damage on the Chinese economy. The imposition of tariffs and trade restrictions led to a decline in key economic indicators. This negative impact manifested in several ways:
- Decreased export demand: Tariffs imposed by the US significantly reduced Chinese export demand, leading to factory closures, particularly in sectors heavily reliant on US markets. This resulted in substantial job losses and a slowdown in manufacturing activity. Data from [cite source showing decline in exports] highlights this decline.
- Reduced foreign direct investment (FDI): The uncertainty surrounding the trade war discouraged foreign investment. Businesses hesitated to commit capital to a market perceived as unstable and subject to unpredictable policy changes. This impacted overall investment growth and economic expansion. Statistics from [cite source showing FDI decline] corroborate this observation.
- Weakening consumer confidence: The trade war's negative effects on employment and economic growth dampened consumer confidence, impacting domestic consumption. Consumers were less inclined to spend, leading to a slowdown in retail sales and overall economic activity. Reports from [cite source on consumer confidence] illustrate this decline.
- Supply chain disruptions: The trade war disrupted global supply chains, affecting various industries in China. Companies faced difficulties sourcing raw materials and intermediate goods, increasing production costs and hindering output. Case studies of [cite affected industries] clearly demonstrate the impact.
These combined factors contributed to a slowdown in China's GDP growth rate, necessitating a swift and decisive monetary policy response.
H2: China's Monetary Policy Response: Easing Measures:
Faced with slowing economic growth, the People's Bank of China (PBOC) implemented a series of monetary easing measures aimed at stimulating the economy. These included:
- Reduction of the reserve requirement ratio (RRR): The PBOC lowered the RRR, the percentage of deposits banks are required to hold in reserve. This injection of liquidity into the banking system increased the lending capacity of banks, making credit more readily available to businesses and consumers.
- Cuts in interest rates: The PBOC reduced both the policy rate (the benchmark interest rate) and benchmark lending rates. Lower interest rates aimed to encourage borrowing and investment, stimulating economic activity.
- Targeted lending programs: The PBOC implemented targeted lending programs to support specific sectors, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which are often more vulnerable to economic shocks. These programs provided preferential lending terms and financial assistance to SMEs.
- Increased use of quantitative easing (QE) tools: The PBOC employed QE tools, including open market operations, to inject liquidity directly into the market and lower long-term interest rates.
These measures were intended to increase investment, bolster consumption, and ultimately mitigate the negative impact of trade tensions on economic growth.
H2: Managing the RMB Exchange Rate:
Managing the RMB exchange rate amidst trade tensions presented a significant challenge for the PBOC. The strategies employed included:
- Maintaining a relatively stable RMB against the US dollar: Despite downward pressure on the RMB, the PBOC sought to maintain a relatively stable exchange rate to avoid further uncertainty and volatility in the market.
- Using foreign exchange reserves: The PBOC utilized its substantial foreign exchange reserves to intervene in the foreign exchange market, buying RMB and selling foreign currencies to control volatility and prevent sharp depreciations.
- Balancing stability with export competitiveness: While stability was a priority, a slightly weaker RMB could have boosted exports by making Chinese goods more competitive internationally. The PBOC attempted to carefully balance these competing objectives.
Maintaining exchange rate stability in a volatile global market proved challenging, requiring constant monitoring and skillful intervention by the PBOC.
H3: Coordination with Fiscal Policy:
China's response to trade tensions was not solely reliant on monetary policy. Fiscal policy played a crucial complementary role. The government implemented various fiscal stimulus measures to support economic growth, including:
- Increased infrastructure spending: Significant investments in infrastructure projects, such as roads, railways, and other public works, created jobs and stimulated economic activity.
- Tax cuts: Tax reductions for businesses and individuals aimed to boost investment and consumption.
- Subsidies: Targeted subsidies were provided to specific industries and businesses to offset the negative impacts of the trade war.
The coordinated use of monetary and fiscal policies aimed to provide a comprehensive and effective response to the economic challenges posed by trade tensions.
H2: Effectiveness and Future Outlook of China's Monetary Policy:
Assessing the effectiveness of China's monetary policy response is complex. While the easing measures helped to prevent a sharper economic downturn, they also presented limitations and potential side effects:
- Limited effectiveness in boosting exports: The trade war's impact extended beyond price adjustments, making it difficult for monetary policy alone to fully restore export growth.
- Increased debt levels: The expansionary monetary policy led to an increase in overall debt levels in the economy, posing potential long-term risks.
- Inflationary pressures: While inflation remained relatively contained, there were concerns about potential inflationary pressures arising from the increased money supply.
Looking ahead, China's monetary policy will need to navigate a challenging environment. The ongoing global economic uncertainty and evolving trade relations require a flexible and adaptable approach. Potential future policy adjustments might include a more cautious approach to monetary easing, a greater focus on structural reforms to enhance long-term growth, and a continued emphasis on managing the RMB exchange rate effectively.
Conclusion:
China's response to trade tensions involved a multifaceted monetary policy strategy incorporating interest rate adjustments, RRR cuts, targeted lending, and QE. While these measures helped mitigate the negative impact on GDP growth and other economic indicators, the interplay between trade, monetary policy, and fiscal policy remains complex. The effectiveness of the strategy is subject to ongoing debate, with challenges like increased debt levels and the need for structural reforms remaining key considerations. For a deeper understanding of the intricate dynamics between international trade and China's monetary policy, further research into specific economic indicators and policy decisions is essential. Continue your exploration of China's monetary policy and its responses to global trade tensions by exploring [link to related resources/further reading].

Featured Posts
-
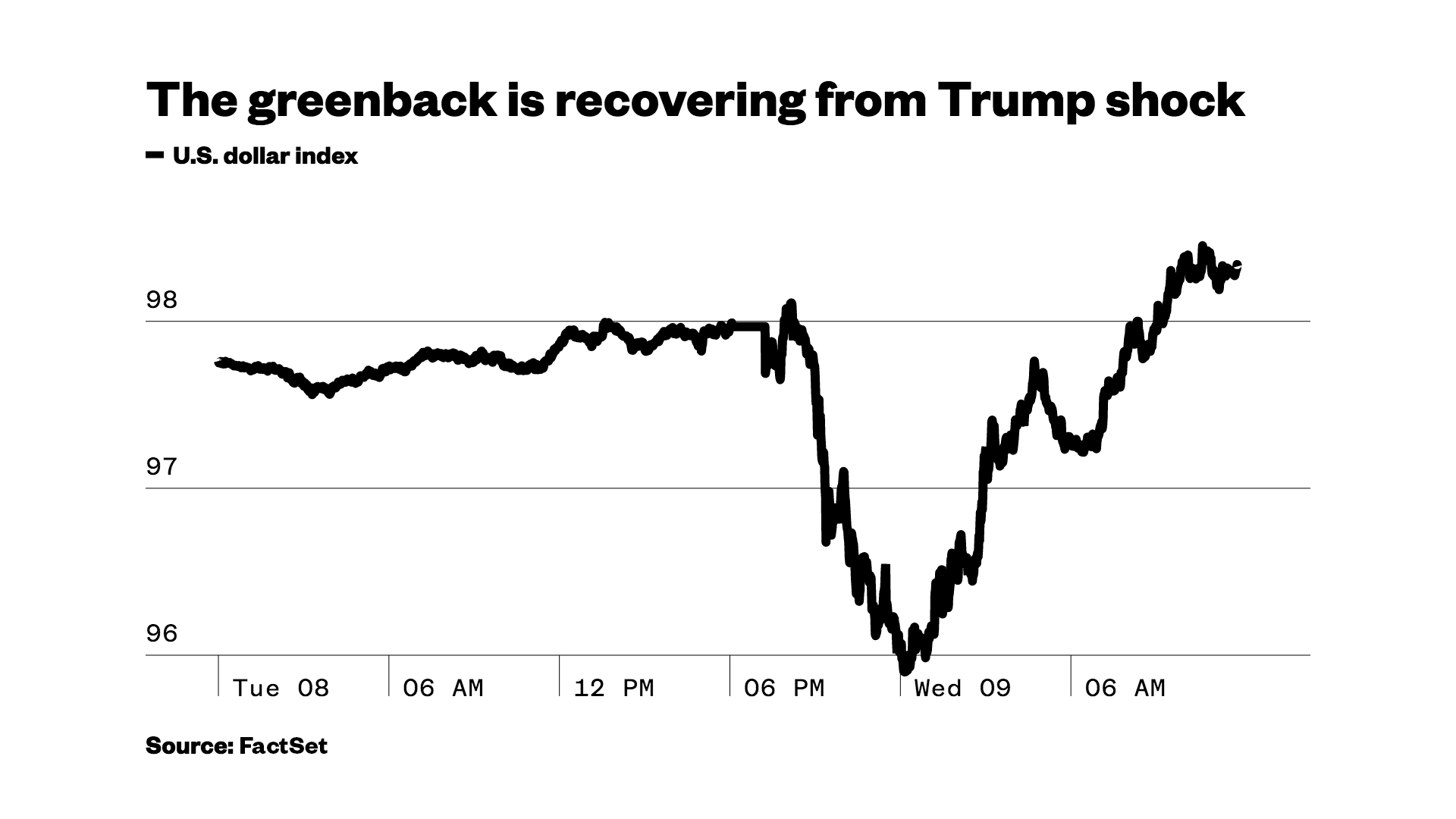 Understanding Xrps Price Movement The Role Of President Trump And Market Sentiment
May 08, 2025
Understanding Xrps Price Movement The Role Of President Trump And Market Sentiment
May 08, 2025 -
 Arsenal Vs Psg Champions League Final Hargreaves Expert Prediction
May 08, 2025
Arsenal Vs Psg Champions League Final Hargreaves Expert Prediction
May 08, 2025 -
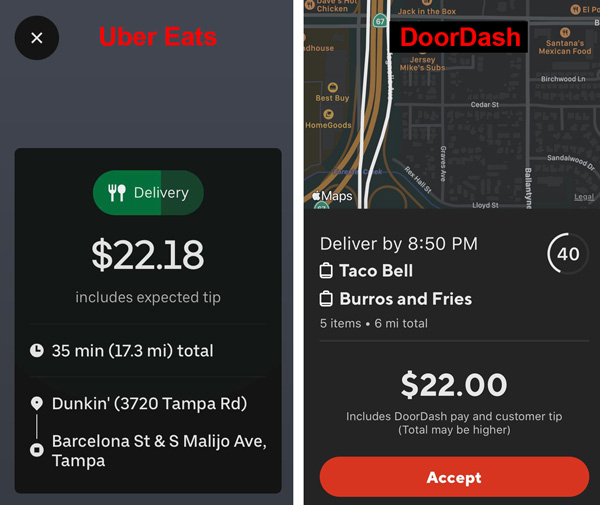 Uber Vs Door Dash A Legal Battle Over Food Delivery Dominance
May 08, 2025
Uber Vs Door Dash A Legal Battle Over Food Delivery Dominance
May 08, 2025 -
 Ethereum Price Forecast 1 11 Million Eth Accumulated Bullish Momentum Builds
May 08, 2025
Ethereum Price Forecast 1 11 Million Eth Accumulated Bullish Momentum Builds
May 08, 2025 -
 Antisemitism Investigation At Boeings Seattle Campus
May 08, 2025
Antisemitism Investigation At Boeings Seattle Campus
May 08, 2025
