Analyzing Putin's War-Focused Economic Strategy In Russia
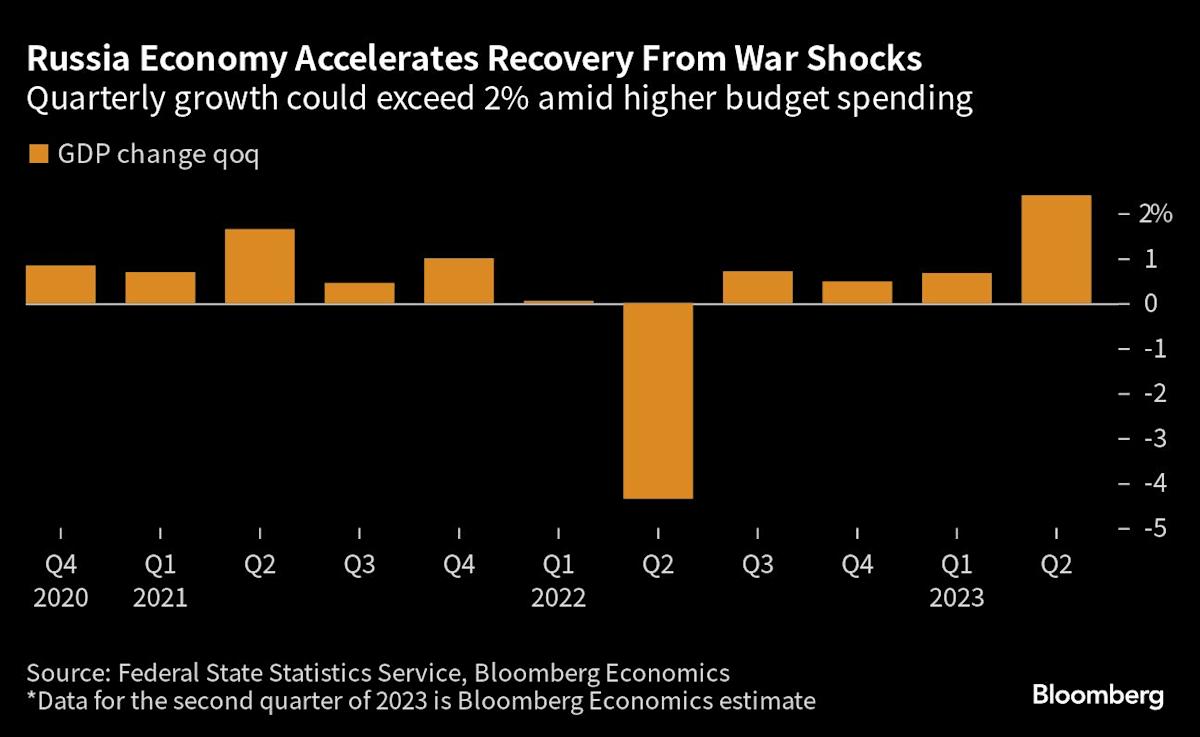
Table of Contents
The Impact of Western Sanctions on the Russian Economy
The imposition of sweeping Western sanctions following the invasion of Ukraine dealt a significant blow to the Russian economy. Keywords: Sanctions, Russia sanctions, economic sanctions, financial sanctions, oil sanctions, impact of sanctions. These sanctions targeted various sectors, aiming to cripple Russia's ability to finance its war effort and exert geopolitical influence.
-
Initial Impact: The initial impact was dramatic. The ruble plummeted, the Russian Central Bank implemented emergency measures, and access to international financial markets was severely restricted. Financial sanctions significantly hampered the ability of Russian businesses to conduct international transactions.
-
Central Bank Response: The Central Bank of Russia responded swiftly, raising interest rates, imposing capital controls, and implementing other measures to stabilize the ruble and prevent a complete collapse of the financial system. While initially effective, these measures came at a cost, restricting economic activity and contributing to inflation.
-
Sectoral Impacts: Sanctions heavily impacted specific sectors. The energy sector, a crucial source of Russian revenue, faced restrictions on oil and gas exports, although the impact was less severe than initially predicted due to ongoing demand from certain countries. The technology sector suffered from restrictions on the import of essential components and software, hindering innovation and production. Manufacturing also faced significant disruptions due to supply chain issues and the lack of access to advanced technologies.
-
Curbing Military Capabilities: The effectiveness of sanctions in directly curbing Russian military capabilities is a complex issue. While some sanctions have undoubtedly impacted the supply of advanced technologies and components for weapons systems, Russia has demonstrated resilience by relying on domestic production and exploring alternative supply chains.
-
Sanctions Circumvention: Russia has actively employed strategies to circumvent sanctions, including using shadow banking systems, engaging in barter trade, and leveraging relationships with countries less willing to fully comply with sanctions. This necessitates continued monitoring and adaptation of sanctions regimes.
Russia's Pivot Towards Import Substitution
Faced with sanctions and the disruption of global supply chains, Russia has embarked on an ambitious import substitution program, aiming to reduce its reliance on foreign goods and technologies. Keywords: Import substitution, Russia import substitution, self-sufficiency, domestic production, industrial policy, technological independence. This strategy involves boosting domestic production in crucial sectors to achieve greater self-sufficiency.
-
Push for Self-Sufficiency: The government has actively promoted domestic production of various goods, ranging from food products to high-tech components. Significant investment is directed towards supporting domestic industries.
-
Technological Limitations: However, Russia faces significant challenges in achieving true import substitution. Technological limitations, particularly in advanced industries, hinder the development of domestic alternatives to imported goods and technologies. The lack of access to advanced research and development capabilities poses a significant constraint.
-
Role of State-Owned Enterprises: State-owned enterprises (SOEs) play a central role in driving import substitution initiatives. The government often provides these SOEs with financial support and preferential treatment to ensure their success.
-
Success and Viability: While some progress has been made in certain sectors, the long-term viability of Russia's import substitution strategy remains questionable. The effectiveness is hindered by lingering technological gaps and the difficulty of competing with established global manufacturers.
-
Impact on Consumers: The shift towards import substitution has impacted consumer goods availability and prices. While some goods have become more readily available through domestic production, the quality and affordability often lag behind imported alternatives, leading to inflation and reduced consumer choice.
The Role of Energy Exports in Funding the War Effort
Energy exports remain a crucial pillar of the Russian economy, providing a significant source of revenue that directly funds the war effort. Keywords: Energy exports, Russian energy, oil prices, gas exports, revenue generation, energy sanctions, European dependence. Despite sanctions, energy exports continue to generate substantial income for the Russian government.
-
Revenue Generation: Russia's oil and gas exports generate vast revenues, even with reduced volumes and price caps imposed by some countries. These revenues form a significant portion of the state budget.
-
Impact of Price Caps and Reduced Demand: While price caps and reduced demand from some European countries have had an impact, Russia has successfully redirected a significant portion of its energy exports to Asia, mitigating the losses to a certain degree.
-
Shift Towards Asia: Russia is actively developing new energy export routes and partnerships with Asian countries, particularly China and India. This diversification of energy export markets helps to offset the impact of sanctions from the West.
-
Long-Term Implications: The continued heavy reliance on energy exports for economic stability presents significant long-term risks. Fluctuations in global energy prices and the potential for future sanctions could drastically impact Russia's economy.
-
Sustainability of Revenue: The long-term sustainability of this revenue stream for financing the war is questionable. The transition to renewable energy sources globally poses a significant threat to the long-term value of Russian energy exports.
Military Spending and its Economic Consequences
The invasion of Ukraine has led to a substantial increase in Russia's military spending, diverting significant resources from other sectors of the economy. Keywords: Military spending, defense budget, economic impact of military spending, military industrial complex, resource allocation, opportunity cost.
-
Scale of Increase: Military spending has risen dramatically since the start of the conflict, diverting a substantial portion of the state budget from social programs, infrastructure development, and other essential areas.
-
Opportunity Cost: The opportunity cost of this high military spending is considerable. Resources invested in the military could have been utilized for education, healthcare, technological advancement, and other sectors contributing to long-term economic growth.
-
Impact on Macroeconomic Indicators: The increased military spending has contributed to inflation, exacerbated by sanctions and supply chain disruptions. It has also put pressure on the national budget, potentially leading to fiscal imbalances.
-
Long-Term Sustainability: The long-term sustainability of this high level of military spending is questionable. The continued strain on the national budget and the potential for further economic sanctions raise concerns about Russia’s ability to maintain this level of expenditure indefinitely.
-
Impact on Future Growth: The diversion of resources towards the military sector ultimately hampers long-term economic growth, limiting investment in other sectors and potentially leading to technological stagnation.
Conclusion
Putin's war-focused economic strategy is a complex and evolving phenomenon, marked by both resilience in the face of unprecedented sanctions and significant long-term economic risks. While the initial shock of sanctions has been absorbed to some degree, the reliance on energy exports, the challenges of import substitution, and the massive investment in military spending paint a picture of an economy under strain. The long-term sustainability of this approach remains highly questionable.
Call to Action: Understanding the intricacies of Putin's war-focused economic strategy is crucial for comprehending the ongoing geopolitical landscape. Further research and analysis of this complex topic are vital for informed decision-making on international relations and economic policy related to Russia. Continue to follow the developments in Putin's economic strategy for a more comprehensive understanding of its implications.

Featured Posts
-
 Pokemon Tcg Game Stop Imposes One Per Customer Limit
May 29, 2025
Pokemon Tcg Game Stop Imposes One Per Customer Limit
May 29, 2025 -
 Brshlwnt Yufajy Aljmye Bqrarh Bshan Alteaqd Me Tah
May 29, 2025
Brshlwnt Yufajy Aljmye Bqrarh Bshan Alteaqd Me Tah
May 29, 2025 -
 Real Madrid Vs Athletic Club 1 0 Respuestas A Tres Preguntas Importantes
May 29, 2025
Real Madrid Vs Athletic Club 1 0 Respuestas A Tres Preguntas Importantes
May 29, 2025 -
 Argentinian Moto Gp Honda Targets Competitive Performance From The Outset
May 29, 2025
Argentinian Moto Gp Honda Targets Competitive Performance From The Outset
May 29, 2025 -
 Man Utd Transfer News Dominant Free Agent Joins The Race
May 29, 2025
Man Utd Transfer News Dominant Free Agent Joins The Race
May 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Exploring The Differences Between Rosemary And Thyme Flavor Profiles And Uses
May 31, 2025
Exploring The Differences Between Rosemary And Thyme Flavor Profiles And Uses
May 31, 2025 -
 Rosemary And Thyme Recipes Simple Dishes With Big Flavor
May 31, 2025
Rosemary And Thyme Recipes Simple Dishes With Big Flavor
May 31, 2025 -
 Duncan Bannatynes Support For Life Changing Childrens Charity In Morocco
May 31, 2025
Duncan Bannatynes Support For Life Changing Childrens Charity In Morocco
May 31, 2025 -
 Dragon Dens Duncan Bannatyne Supports Moroccan Childrens Charity
May 31, 2025
Dragon Dens Duncan Bannatyne Supports Moroccan Childrens Charity
May 31, 2025 -
 Achieving The Good Life A Step By Step Guide For Lasting Fulfillment
May 31, 2025
Achieving The Good Life A Step By Step Guide For Lasting Fulfillment
May 31, 2025
