Bond Market Volatility: Analyzing The Tariff Shock
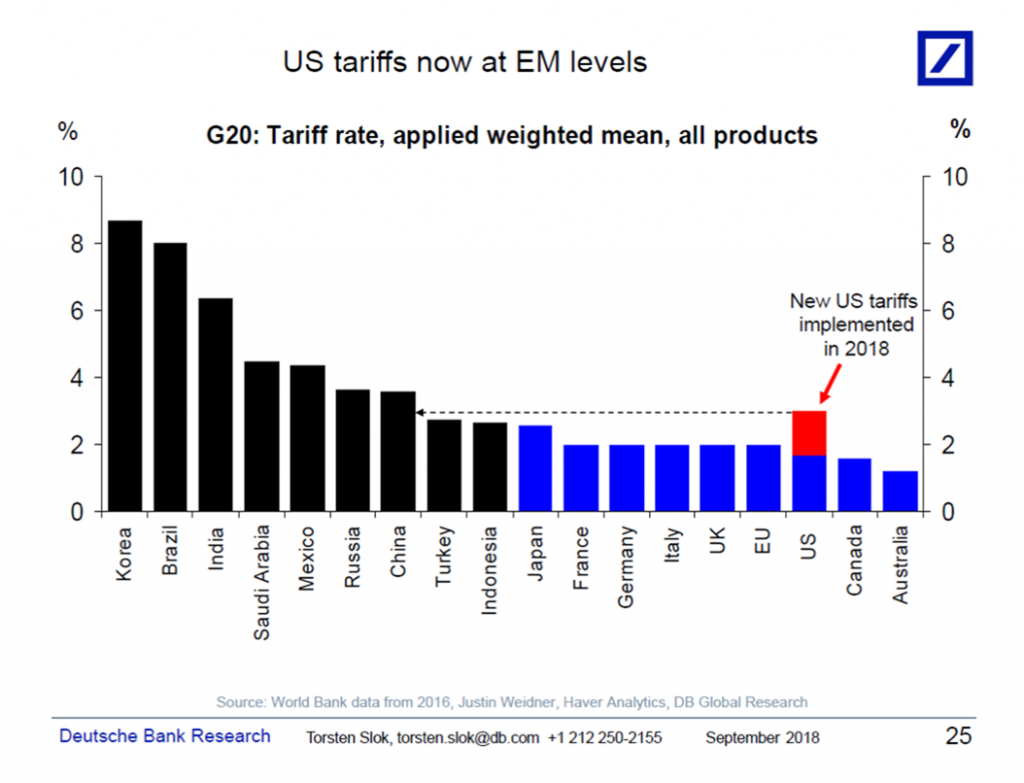
Table of Contents
The Mechanism of Tariff-Induced Volatility
Tariffs introduce significant uncertainty into the global economic system, directly impacting bond markets. This uncertainty manifests in several key ways:
Increased Uncertainty and Risk Aversion
Tariffs introduce uncertainty into the global trade landscape, leading investors to seek safer havens, driving demand for government bonds and potentially decreasing yields. This "flight to safety" is driven by several factors:
- Increased uncertainty about future economic growth: The unpredictability of trade relations makes forecasting future economic performance more difficult, increasing risk aversion.
- Reduced corporate profits due to higher input costs: Tariffs increase the cost of imported goods, squeezing profit margins for businesses reliant on global supply chains. This leads to lower corporate bond ratings and higher yields.
- Flight to safety: Investors, worried about the broader economic implications of tariffs, shift their investments towards perceived safe havens like government bonds, pushing down yields on these assets. This increased demand for lower-risk government debt can significantly reduce yields.
Inflationary Pressures and Central Bank Response
Tariffs can exert upward pressure on inflation. This occurs because tariffs increase the cost of imported goods, leading to higher consumer prices. This inflationary pressure forces central banks to react:
- Increased prices for imported goods: Tariffs directly increase the cost of imported goods, impacting consumer price indices and broader inflation measures.
- Potential for wage increases to offset higher prices: To maintain their purchasing power, workers may demand higher wages, further fueling inflation.
- Central bank response: potential interest rate hikes or quantitative easing: Central banks may respond to inflationary pressures by raising interest rates, impacting bond yields. Alternatively, they may implement quantitative easing to manage the economic fallout, influencing bond prices in different ways. Understanding the central bank's likely response is crucial in assessing bond market volatility.
Currency Fluctuations and Their Impact
Tariff disputes frequently lead to currency fluctuations, which significantly affect the value of foreign bonds held by domestic investors. These fluctuations can create considerable volatility:
- Depreciation of the domestic currency impacting returns on foreign bonds: A weaker domestic currency reduces the value of returns from foreign bonds when converted back to the domestic currency.
- Increased hedging costs for investors exposed to currency risk: Investors need to employ hedging strategies to protect against currency risk, increasing their costs and potentially reducing overall returns.
- Potential for capital flight as investors seek alternative markets: Uncertainty surrounding currency fluctuations can lead to capital flight as investors seek more stable investment environments.
Sectoral Impacts of Tariff Shocks on Bond Markets
The impact of tariff shocks on bond market volatility isn't uniform across all sectors. Different industries and asset classes experience varying degrees of impact.
Impact on the Manufacturing Sector
Industries heavily reliant on imported goods or exports are particularly vulnerable to tariff shocks:
- Increased production costs for manufacturers: Tariffs raise input costs, reducing profitability and potentially leading to job losses.
- Reduced competitiveness in global markets: Higher production costs make domestic manufacturers less competitive internationally.
- Higher default risk for corporate bonds in affected sectors: Reduced profitability and competitiveness increase the default risk associated with corporate bonds issued by manufacturers in tariff-sensitive sectors. This increases the yield required by investors to compensate for that increased risk.
Impact on the Financial Sector
Banks and financial institutions holding assets exposed to tariff-sensitive sectors face heightened risks:
- Increased non-performing loans: Businesses struggling due to tariffs may default on their loans, increasing the number of non-performing loans on bank balance sheets.
- Lower profitability for financial institutions: Increased loan defaults and reduced economic activity translate to lower profitability for financial institutions.
- Potential for regulatory intervention and increased capital requirements: Regulatory bodies may intervene to ensure the stability of the financial system, potentially leading to increased capital requirements for banks.
Impact on the Government Bond Market
The government bond market, often considered a safe haven, is also affected by tariff shocks:
- Increased demand for safe-haven government bonds: During periods of uncertainty, investors flock to government bonds, driving down yields.
- Potential for decreased government bond yields: Increased demand leads to lower yields on government bonds, reflecting the lower perceived risk.
- Increased government borrowing costs due to higher inflation or decreased economic growth: Higher inflation or slower economic growth can increase government borrowing costs, potentially impacting government bond yields.
Forecasting Bond Market Volatility in the Face of Tariffs
Predicting the impact of tariffs on bond market volatility requires a multifaceted approach:
Utilizing Economic Models and Indicators
Sophisticated econometric models can help analyze the impact of tariffs:
- Incorporating tariff data into macroeconomic models: Integrating tariff data into macroeconomic models allows for better forecasting of economic variables, including bond yields and volatility.
- Analyzing correlations between tariff shocks and bond market movements: Studying historical data helps identify correlations between tariff implementations and subsequent market movements.
- Using leading indicators to predict future volatility: Leading economic indicators can provide early warning signs of potential volatility.
The Role of Sentiment Analysis and News Sentiment
Monitoring news sentiment provides valuable insights:
- Analyzing news articles and social media data: Analyzing news sentiment and social media discussions can reveal shifts in investor confidence.
- Tracking investor confidence indices: Investor confidence indices provide valuable information regarding market sentiment.
- Assessing the impact of policy announcements on market sentiment: Policy announcements related to tariffs can significantly impact market sentiment, triggering immediate volatility.
Importance of Diversification and Risk Management
Effective risk management is crucial during periods of heightened volatility:
- Diversification across different bond maturities and credit ratings: Diversifying across different bond maturities and credit ratings reduces the overall risk exposure.
- Utilizing hedging strategies to protect against currency risk: Hedging strategies can mitigate the impact of currency fluctuations on foreign bond investments.
- Implementing stress testing to assess potential losses under various scenarios: Stress testing helps assess potential losses under different economic scenarios, including the impact of unexpected tariff increases.
Conclusion
Tariff shocks represent a significant source of uncertainty in the global economy, directly impacting bond market volatility. Understanding the mechanisms through which tariffs influence bond yields, inflation, and currency fluctuations is critical for navigating this complex landscape. By employing sophisticated econometric models, monitoring market sentiment, and implementing effective risk management strategies, investors can better prepare for and mitigate the effects of bond market volatility arising from tariff-related events. Therefore, a thorough understanding of bond market volatility and its relationship to tariffs is essential for informed investment decisions in today's dynamic global economy. Understanding and managing bond market volatility requires constant vigilance and a proactive approach to risk management.

Featured Posts
-
 Adam Sandlers Wealth A Look At His Successful Comedy Career
May 12, 2025
Adam Sandlers Wealth A Look At His Successful Comedy Career
May 12, 2025 -
 Ludogorets Privleche Antoan Baroan Pod Naem
May 12, 2025
Ludogorets Privleche Antoan Baroan Pod Naem
May 12, 2025 -
 The Chaplin Factor Ipswich Towns Path To Victory
May 12, 2025
The Chaplin Factor Ipswich Towns Path To Victory
May 12, 2025 -
 Tariff Hikes And Their Ripple Effect On Bond Yields
May 12, 2025
Tariff Hikes And Their Ripple Effect On Bond Yields
May 12, 2025 -
 Rare Condition Bilateral Anophthalmia Information And Resources For Parents Of Affected Infants
May 12, 2025
Rare Condition Bilateral Anophthalmia Information And Resources For Parents Of Affected Infants
May 12, 2025
