Bubble Blasters And Beyond: Analyzing The Impact Of Trade Disputes On Chinese Goods

Table of Contents
The US-China Trade War and its Fallout
The US-China trade war, initiated in 2018, stands as a pivotal moment in understanding the impact of trade disputes on Chinese goods. The imposition of tariffs on hundreds of billions of dollars worth of imports from China significantly altered the landscape of global commerce.
Impact on Specific Industries
The trade war had a profound impact on several key sectors.
- Chinese Electronics: Tariffs on Chinese electronics, including smartphones, laptops, and consumer electronics components, led to price increases for consumers in the US and a decrease in the import volume of these goods. Companies like Apple, heavily reliant on Chinese manufacturing, felt the pressure to diversify their supply chains.
- Textile Imports: The textile industry, a cornerstone of Chinese exports, faced significant challenges. Increased tariffs on textiles and apparel resulted in higher prices for consumers and prompted some US retailers to explore alternative sourcing options.
- Manufacturing in China: The trade war disrupted manufacturing supply chains globally. Many companies, particularly those relying on just-in-time manufacturing, faced delays and increased costs. This led to a reassessment of reliance on Chinese manufacturing hubs.
Shifting Global Supply Chains
The trade war accelerated the trend of relocating manufacturing away from China.
- Global Supply Chain Diversification: Companies began actively diversifying their supply chains, moving production to countries like Vietnam, India, and Mexico – a process known as nearshoring or offshoring.
- Impact on Developing Economies: This shift had a significant impact on developing economies, creating new manufacturing jobs in some regions while potentially slowing growth in others.
- Reshored Manufacturing: In some cases, companies opted for reshored manufacturing, bringing production back to their home countries, often driven by a desire for greater control and reduced reliance on global supply chains. This often involved increased automation.
Consumer Impact
The trade war’s effects were ultimately felt by consumers worldwide.
- Consumer Prices: Tariffs led to higher prices for many consumer goods, impacting household budgets.
- Product Availability: In some cases, product availability was reduced due to supply chain disruptions.
- Impact on Consumer Choice: Consumers faced less choice as some products became unavailable or significantly more expensive. The availability of substitute products became a crucial factor.
Beyond the US-China Trade War: Other Trade Disputes Affecting Chinese Goods
The impact of trade disputes on Chinese goods extends beyond the US-China trade war.
EU-China Trade Relations
The European Union has also engaged in trade disputes with China, focusing on issues such as intellectual property rights, market access, and unfair trade practices.
- Chinese Exports to EU: These disputes have resulted in tariffs and trade restrictions on specific Chinese exports to the EU, impacting sectors such as steel, solar panels, and telecommunications equipment.
- Trade Barriers: The EU has implemented various trade barriers to address concerns about Chinese state subsidies and dumping practices. These measures have created uncertainty and challenges for Chinese exporters.
Trade Disputes with Other Countries
China has also faced trade disputes with other significant trading partners, including Australia, Canada, and Japan. These disputes often involve accusations of unfair trade practices, intellectual property theft, and market access restrictions.
- China Trade Relations: The complexities of China's trade relations underscore the global nature of these challenges and the intricate web of interconnected economic interests.
- Bilateral Trade Agreements: The frequency of these disputes highlights the ongoing need for robust bilateral and multilateral trade agreements to establish fair and predictable trading environments.
The Future of Chinese Goods in a Globalized World
Despite the challenges posed by trade disputes, Chinese businesses are adapting and innovating.
Adaptability and Innovation
Chinese companies are responding to trade pressures by diversifying their product lines, investing in technological advancements, and exploring new markets.
- Chinese Innovation: Increased investment in research and development is leading to the development of more sophisticated and competitive products.
- Technological Advancements: Advancements in automation and artificial intelligence are helping to enhance efficiency and reduce reliance on low-cost labor.
- Business Adaptation: Companies are increasingly adopting strategies to mitigate trade risks, including diversifying their supply chains and exploring alternative export markets.
Geopolitical Implications
Trade disputes have significant geopolitical implications, affecting the global economic order.
- Global Trade: The rise of protectionist sentiment and trade disputes threatens the stability of the global trading system.
- Geopolitical Risks: These disputes contribute to geopolitical instability and uncertainty, making it harder for businesses to plan and invest.
- International Trade Agreements: The future of multilateral trade agreements like the WTO remains uncertain, further complicating the landscape for Chinese goods.
Navigating the Shifting Sands of Trade: The Future of Chinese Goods
The impact of trade disputes on Chinese goods is multifaceted and far-reaching. We’ve seen how these disputes have affected specific industries, reshaped global supply chains, and influenced consumer prices and choices. Chinese businesses are responding with innovation and adaptation, but the long-term consequences remain to be seen. The future of Chinese goods in a globalized world hinges on the ability of countries to navigate geopolitical complexities and foster a more stable and predictable trade environment.
Key Takeaways: Trade disputes significantly impact various sectors reliant on Chinese goods; global supply chains are shifting; and Chinese businesses are adapting through innovation. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for businesses and policymakers alike.
Call to Action: To make informed decisions in this evolving landscape, further research on the multifaceted impact of trade disputes on Chinese goods is essential. Explore resources from organizations like the World Trade Organization (WTO) and reputable economic research institutions to deepen your understanding of this crucial aspect of global trade.

Featured Posts
-
 Instagram Vs Tik Tok Ceos Testimony On Growth And Survival
May 10, 2025
Instagram Vs Tik Tok Ceos Testimony On Growth And Survival
May 10, 2025 -
 Blue Origin Faces Launch Setback Subsystem Issue Delays Flight
May 10, 2025
Blue Origin Faces Launch Setback Subsystem Issue Delays Flight
May 10, 2025 -
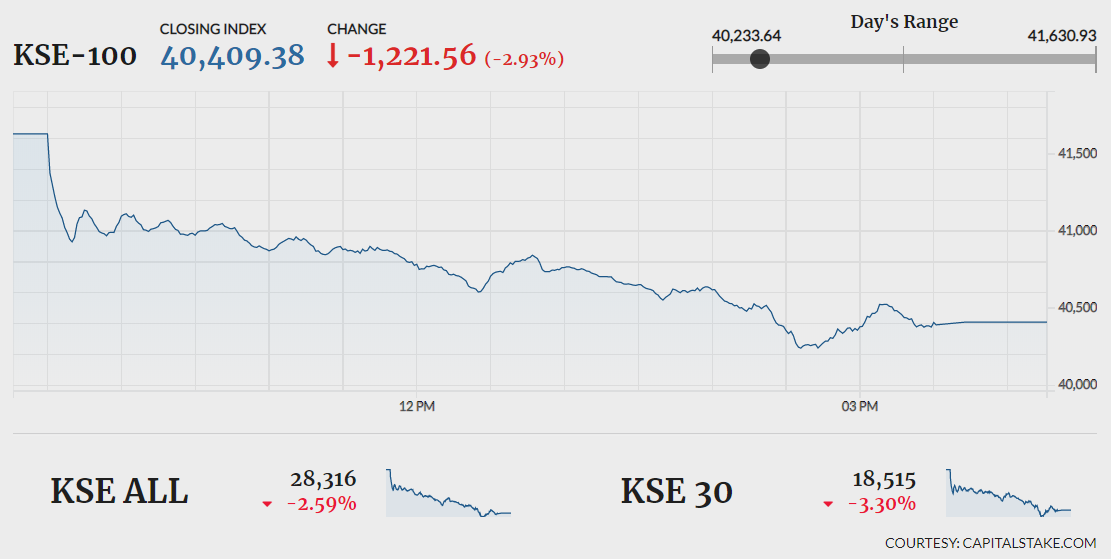 Operation Sindoor Pakistan Stock Market Plunges Kse 100 Trading Halted
May 10, 2025
Operation Sindoor Pakistan Stock Market Plunges Kse 100 Trading Halted
May 10, 2025 -
 Investigation Into Nottingham Attacks Leads To Police Misconduct Meeting
May 10, 2025
Investigation Into Nottingham Attacks Leads To Police Misconduct Meeting
May 10, 2025 -
 How To Find Cheap Elizabeth Arden Skincare At Walmart
May 10, 2025
How To Find Cheap Elizabeth Arden Skincare At Walmart
May 10, 2025
