Can Algorithms Drive Individuals To Mass Violence? Exploring The Legal And Ethical Implications
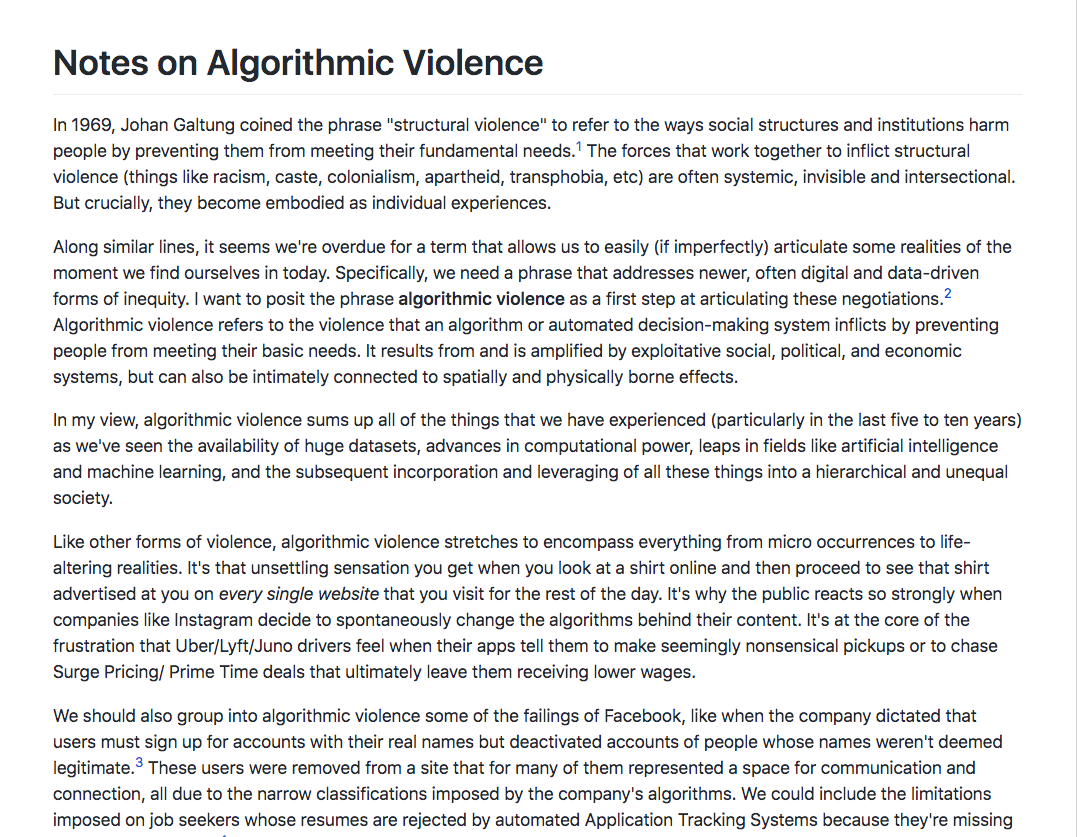
Table of Contents
The rise of social media and sophisticated algorithms has profoundly impacted our lives, but a chilling question emerges: can these algorithms contribute to mass violence? Recent events, such as the spread of extremist ideologies online, highlight a disturbing potential link between algorithms and mass violence. This article explores this complex relationship, examining how algorithms can facilitate online radicalization and analyzing the ensuing legal and ethical implications for tech companies and society as a whole. We will delve into the role of echo chambers, targeted propaganda, and algorithmic amplification of hate speech, while also considering strategies for prevention and intervention.
H2: The Role of Algorithms in Online Radicalization
Algorithms, the invisible engines driving much of our online experience, play a significant, albeit complex, role in shaping online narratives and potentially contributing to radicalization. Their influence manifests in several key ways:
H3: Echo Chambers and Filter Bubbles:
Algorithmic curation, designed to personalize our online experience, can inadvertently create echo chambers and filter bubbles. This means users are primarily exposed to information and viewpoints that confirm their pre-existing beliefs, often leading to polarization and the reinforcement of extremist ideologies.
- Examples: Facebook's News Feed algorithm, YouTube's recommendation system, and Twitter's trending topics all contribute to this phenomenon. These algorithms prioritize content that resonates with a user's past behavior, limiting exposure to diverse perspectives.
- Psychological Impact: The constant reinforcement of extreme views within echo chambers can lead to increased confidence in those beliefs, reduced empathy for opposing viewpoints, and a heightened susceptibility to manipulation and radicalization. This can be particularly potent for vulnerable individuals seeking belonging or validation.
H3: Targeted Propaganda and Disinformation:
Sophisticated algorithms are increasingly used to deliver highly targeted propaganda and disinformation campaigns. These campaigns leverage user data to identify individuals susceptible to extremist ideologies and then deliver tailored messages designed to recruit them or further radicalize them.
- Real-world Instances: The spread of extremist propaganda during elections, the use of targeted advertising to recruit members to violent groups, and the dissemination of conspiracy theories are all examples of this.
- The Role of Bots and Automated Accounts: Automated accounts and bots are frequently used to amplify the reach and impact of targeted propaganda, creating an illusion of widespread support for extremist views.
H3: Algorithmic Amplification of Hate Speech:
Algorithms can inadvertently, or even intentionally, amplify hate speech and violent content, leading to its increased exposure and normalization. This can desensitize users to violence and create a climate of intolerance conducive to real-world violence.
- Challenges of Content Moderation: The sheer volume of online content makes effective content moderation incredibly challenging. Algorithms struggle to accurately identify and remove hate speech, particularly nuanced or subtly coded messages.
- Examples: Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube have consistently faced criticism for their failure to effectively moderate hate speech and violent content, resulting in the spread of harmful ideologies and the normalization of violence.
H2: Legal and Ethical Responsibilities of Tech Companies
The potential link between algorithms and mass violence raises critical legal and ethical questions for tech companies. Their role in shaping online discourse and facilitating the spread of harmful content demands careful scrutiny.
H3: Liability for Algorithmic Harm:
Determining the legal liability of tech companies for violence potentially instigated by their algorithms poses significant challenges. The complex interplay between algorithmic design, user behavior, and real-world actions makes establishing direct causality difficult.
- Legal Frameworks and Precedents: Existing legal frameworks struggle to adequately address this novel challenge, and clear legal precedents are lacking.
- Challenges of Proving Causality: Proving a direct causal link between an algorithm's actions and a violent act is extremely difficult, requiring extensive evidence and sophisticated analysis.
H3: Ethical Obligations for Content Moderation:
Tech companies face complex ethical dilemmas in balancing free speech principles with the imperative to prevent the spread of violent extremism. Their content moderation policies and practices must be carefully considered.
- Potential for Bias in Content Moderation Algorithms: Algorithms used for content moderation can reflect and amplify existing societal biases, potentially leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- The Role of Human Oversight: Human oversight in content moderation remains crucial to ensure fairness, accuracy, and contextual understanding, mitigating the limitations of algorithms.
H3: Transparency and Accountability:
Greater transparency in algorithmic decision-making and increased accountability for tech companies are vital. Users need to understand how algorithms shape their online experiences, and companies need to take responsibility for the potential consequences of their algorithms.
- Mechanisms for Increased Transparency: Tech companies should provide greater insight into how their algorithms work and the criteria used for content moderation.
- The Role of Independent Audits and Oversight Bodies: Independent audits and oversight bodies can play a crucial role in ensuring accountability and identifying potential problems with algorithmic design and implementation.
H2: Mitigating the Risks: Strategies for Prevention and Intervention
Addressing the complex relationship between algorithms and mass violence requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing improved algorithmic design, enhanced media literacy, and collaborative efforts.
H3: Improving Algorithmic Design:
Algorithms themselves can be redesigned to minimize the risk of radicalization and the spread of violent content.
- Prioritizing Diverse Perspectives and Critical Thinking: Algorithms should be designed to promote diverse perspectives and encourage critical thinking, rather than simply reinforcing existing biases.
- Identifying and Flagging Potentially Harmful Content: Improved algorithms can be developed to more effectively identify and flag potentially harmful content, such as hate speech and extremist propaganda.
H3: Enhancing Media Literacy:
Empowering individuals with strong media literacy skills is crucial to help them critically evaluate online information and resist manipulation.
- Improving Critical Thinking Skills: Education initiatives should focus on developing critical thinking skills, enabling users to identify misinformation, propaganda, and biased content.
- Initiatives Promoting Media Literacy Education: Governments, educational institutions, and civil society organizations should collaborate to promote widespread media literacy education.
H3: Collaborative Efforts:
Addressing this issue effectively requires close collaboration between tech companies, governments, researchers, and civil society organizations.
- Increased Collaboration and Information Sharing: Increased collaboration and information sharing are essential to identify emerging threats, share best practices, and develop effective countermeasures.
- The Role of International Cooperation: International cooperation is crucial to address the global nature of online radicalization and the spread of extremist ideologies.
Conclusion:
The potential link between algorithms and mass violence is a serious concern demanding urgent attention. The evidence suggests that algorithms can contribute to online radicalization by creating echo chambers, facilitating targeted propaganda, and amplifying hate speech. This raises significant legal and ethical challenges for tech companies, demanding increased transparency, accountability, and ethical content moderation practices. Mitigating these risks requires a multifaceted approach focusing on improved algorithmic design, enhanced media literacy education, and collaborative efforts between various stakeholders. Further research into the impact of algorithms on violence and the development of effective strategies for preventing algorithmic radicalization are crucial steps toward creating a safer online environment. Let's work together to ensure that algorithms are used for good, not to drive individuals towards mass violence.

Featured Posts
-
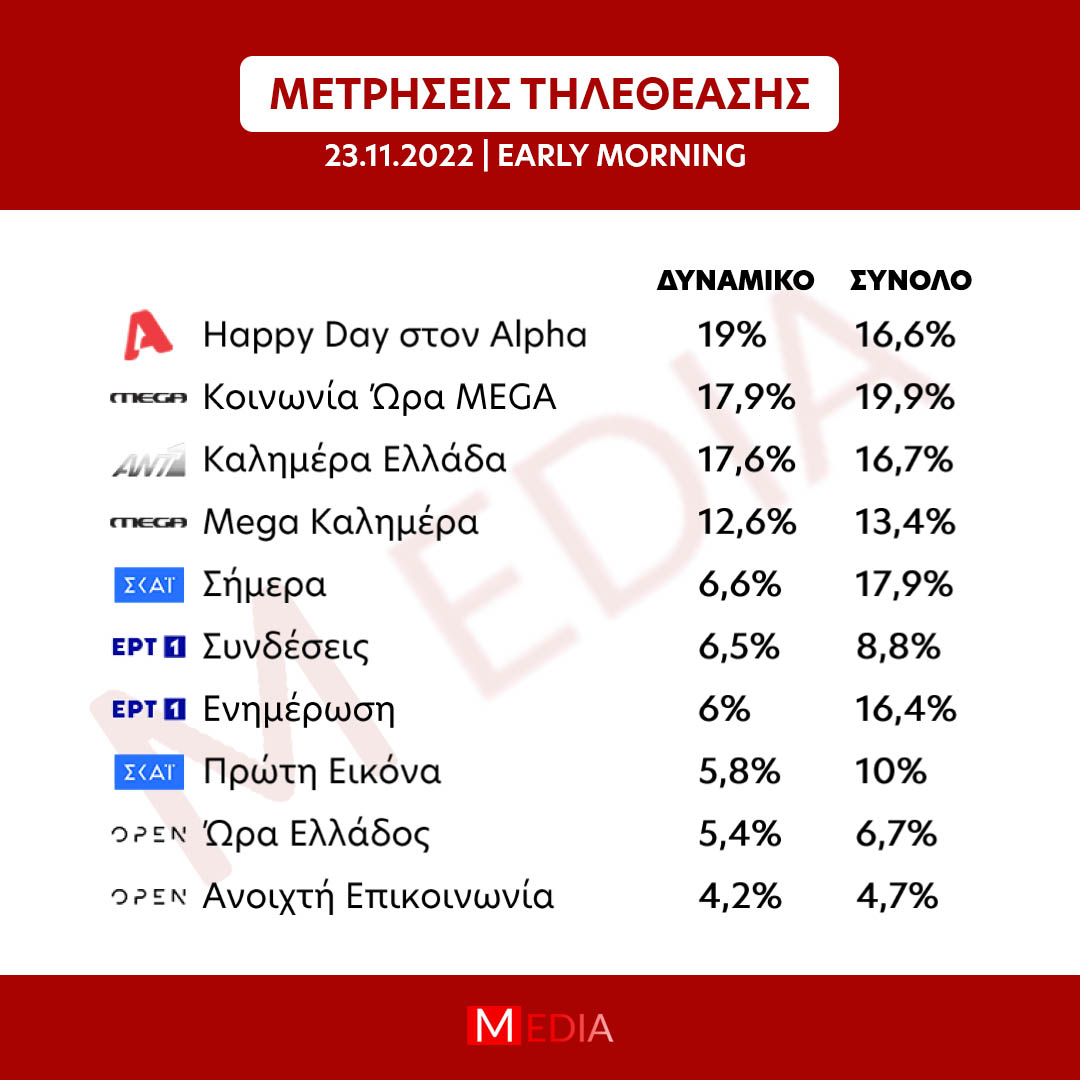 Odigos Tiletheasis Tetarti 23 Aprilioy
May 30, 2025
Odigos Tiletheasis Tetarti 23 Aprilioy
May 30, 2025 -
 How Trumps Trade War Is Already Affecting Canada 8 Economic Indicators
May 30, 2025
How Trumps Trade War Is Already Affecting Canada 8 Economic Indicators
May 30, 2025 -
 Ryujinx Emulator Development Halted Nintendos Involvement
May 30, 2025
Ryujinx Emulator Development Halted Nintendos Involvement
May 30, 2025 -
 Dansk Chef Under Beskydning Stjerne Beskylder For Mangel Pa Respekt
May 30, 2025
Dansk Chef Under Beskydning Stjerne Beskylder For Mangel Pa Respekt
May 30, 2025 -
 Is Selena Gomezs Next Top 10 Hit Already Leaked
May 30, 2025
Is Selena Gomezs Next Top 10 Hit Already Leaked
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Severe Thunderstorms Bring Power Outages To Northeast Ohio Stay Safe And Informed
May 31, 2025
Severe Thunderstorms Bring Power Outages To Northeast Ohio Stay Safe And Informed
May 31, 2025 -
 Power Outages And Weather Alerts Issued Across Northeast Ohio Due To Intense Thunderstorms
May 31, 2025
Power Outages And Weather Alerts Issued Across Northeast Ohio Due To Intense Thunderstorms
May 31, 2025 -
 April 29th Twins Guardians Game Progressive Field Weather And Potential Delays
May 31, 2025
April 29th Twins Guardians Game Progressive Field Weather And Potential Delays
May 31, 2025 -
 Rain Possible On Election Day In Northeast Ohio
May 31, 2025
Rain Possible On Election Day In Northeast Ohio
May 31, 2025 -
 Cleveland Fire Station Temporary Closure After Significant Water Leaks
May 31, 2025
Cleveland Fire Station Temporary Closure After Significant Water Leaks
May 31, 2025
