Canadian Dollar Overvalued: Economists Urge Swift Action

Table of Contents
Factors Contributing to a CAD Overvaluation
Several intertwined factors contribute to the current debate surrounding a potentially overvalued CAD. Understanding these elements is crucial to developing effective strategies.
High Commodity Prices
Canada's economy is heavily reliant on its resource sector. High global prices for commodities like oil and natural gas significantly boost the Canadian dollar. The surge in demand following the pandemic, coupled with ongoing supply chain disruptions, has led to unprecedented price increases.
- Impact of Global Demand: Robust global demand for energy resources, particularly from Asia and Europe, strengthens the CAD.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Geopolitical instability and logistical challenges continue to constrain supply, further driving up prices and strengthening the Canadian dollar.
- Effect on the CAD Exchange Rate: Higher commodity prices increase the inflow of foreign currency, leading to a stronger CAD relative to other currencies. This impacts Canadian exports, making them less competitive in the global market.
Related keywords: Commodity markets, Canadian exports, resource-based economy, energy prices, global demand for resources.
Interest Rate Differentials
The Bank of Canada's monetary policy plays a significant role in influencing the CAD's value. Higher interest rates in Canada compared to other major economies attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the Canadian dollar.
- Bank of Canada Policy: The Bank of Canada's aggressive interest rate hikes aimed at controlling inflation have made Canadian assets more attractive to international investors.
- Inflation Control: While interest rate hikes combat inflation, they also strengthen the currency, creating a double-edged sword.
- Impact of Global Interest Rates: The relative difference between Canadian interest rates and those in other countries influences capital flows and the CAD's exchange rate.
Related keywords: Bank of Canada monetary policy, interest rate hikes, foreign exchange market, interest rate differentials, capital flows.
Safe Haven Status
During periods of global economic uncertainty or geopolitical instability, the Canadian dollar is often perceived as a safe haven currency. This "flight to safety" phenomenon increases demand for the CAD, further contributing to its strength.
- Geopolitical Instability: Ongoing conflicts and tensions around the world often lead investors to seek refuge in stable currencies like the CAD.
- Global Economic Downturns: Concerns about global economic slowdowns or recessions can drive capital flows towards perceived safe havens.
- Flight to Safety Phenomenon: This phenomenon increases demand for the CAD, pushing its value higher.
Related keywords: Currency hedging, safe haven assets, global economic outlook, geopolitical risk, flight to safety.
Economic Consequences of an Overvalued CAD
An overvalued Canadian dollar presents several significant economic challenges.
Impact on Exports
A strong CAD makes Canadian goods and services more expensive for international buyers, reducing their competitiveness in global markets.
- Reduced Competitiveness: Canadian exporters face difficulties competing with producers from countries with weaker currencies.
- Lower Export Volumes: Reduced competitiveness leads to lower export volumes and negatively impacts export-oriented industries.
- Impact on Specific Industries: Industries heavily reliant on exports, such as manufacturing and agriculture, are particularly vulnerable.
Related keywords: Canadian exports, trade balance, global competitiveness, export-oriented industries, trade deficit.
Effects on Inflation
While a strong CAD can suppress import prices, potentially lowering inflation, it can also negatively impact domestic producers.
- Reduced Import Prices: Cheaper imports can help keep consumer prices down, but this benefit may be offset by other factors.
- Impact on Domestic Producers: Domestic producers face increased competition from cheaper imports, potentially impacting their profitability and ability to invest.
- Potential for Deflation: In extreme cases, a sustained strong CAD could contribute to deflation, which can have harmful consequences for the economy.
Related keywords: Canadian inflation rate, consumer price index, import prices, deflation, domestic producers, price competitiveness.
Job Market Implications
The negative impacts on exports and domestic producers can translate into job losses, particularly in export-oriented sectors.
- Job Losses: Reduced competitiveness and lower export volumes can lead to layoffs and decreased employment opportunities.
- Reduced Investment: Uncertainty about future profitability can discourage businesses from investing, further hindering job creation.
- Impact on Regional Economies: Regions heavily reliant on specific export-oriented industries are particularly susceptible to negative impacts.
Related keywords: Canadian unemployment rate, employment growth, economic diversification, job creation, regional economies.
Potential Solutions and Policy Recommendations
Addressing the potential overvaluation of the CAD requires a multi-pronged approach involving monetary policy, fiscal policy, and strategic economic diversification.
Bank of Canada Intervention
The Bank of Canada could potentially intervene in the foreign exchange market to manage the CAD's value. However, such interventions are complex and have limitations.
- Potential Tools: The Bank of Canada could adjust interest rates or directly intervene in the foreign exchange market, but such actions carry risks and can have unintended consequences.
- Limitations of Intervention: Market forces can often overwhelm central bank interventions, making their effectiveness uncertain.
Related keywords: Monetary policy tools, central bank intervention, currency manipulation, foreign exchange reserves.
Fiscal Policy Measures
Government policies can play a role in mitigating the negative consequences of an overvalued CAD.
- Examples of Fiscal Policies: Targeted support for export-oriented industries, investments in infrastructure, and tax incentives can help improve competitiveness.
- Their Impact on the Economy: Well-designed fiscal policies can boost economic activity and offset some of the negative effects of a strong CAD.
- Potential Challenges: Fiscal policies can be politically challenging and may face constraints due to budget limitations.
Related keywords: Government spending, fiscal stimulus, economic diversification, infrastructure investment, tax incentives.
Diversification Strategies
Reducing Canada's reliance on commodity exports is crucial for long-term economic resilience.
- Investing in New Industries: Diversifying the economy into high-growth sectors such as technology, clean energy, and advanced manufacturing can reduce vulnerability to fluctuations in commodity prices.
- Fostering Innovation: Investing in research and development and promoting innovation can create new industries and opportunities.
- Supporting Small Businesses: Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are crucial for economic diversification and job creation.
Related keywords: Economic diversification, innovation policy, small business support, technological innovation, sustainable economy.
Conclusion: Addressing the Overvalued Canadian Dollar – A Call to Action
The potential overvaluation of the Canadian dollar presents a complex challenge with significant economic consequences. Factors such as high commodity prices, interest rate differentials, and the CAD's safe-haven status contribute to its strength. The resulting impacts – reduced export competitiveness, potential inflationary pressures, and job market implications – necessitate urgent action. While the Bank of Canada's monetary policy plays a key role, effective solutions require a combination of monetary and fiscal measures alongside a strategic focus on economic diversification. Staying informed on the latest economic developments and advocating for policies that will address the overvalued Canadian dollar and safeguard the Canadian economy is crucial. Let's work together to ensure Canada's long-term economic prosperity.

Featured Posts
-
 Lahwr Ke Askwlwn Ka Py Ays Ayl Ke Baeth Awqat Kar Tbdyl
May 08, 2025
Lahwr Ke Askwlwn Ka Py Ays Ayl Ke Baeth Awqat Kar Tbdyl
May 08, 2025 -
 Inter Milan Vs Fc Barcelona Watch The Live Champions League Match
May 08, 2025
Inter Milan Vs Fc Barcelona Watch The Live Champions League Match
May 08, 2025 -
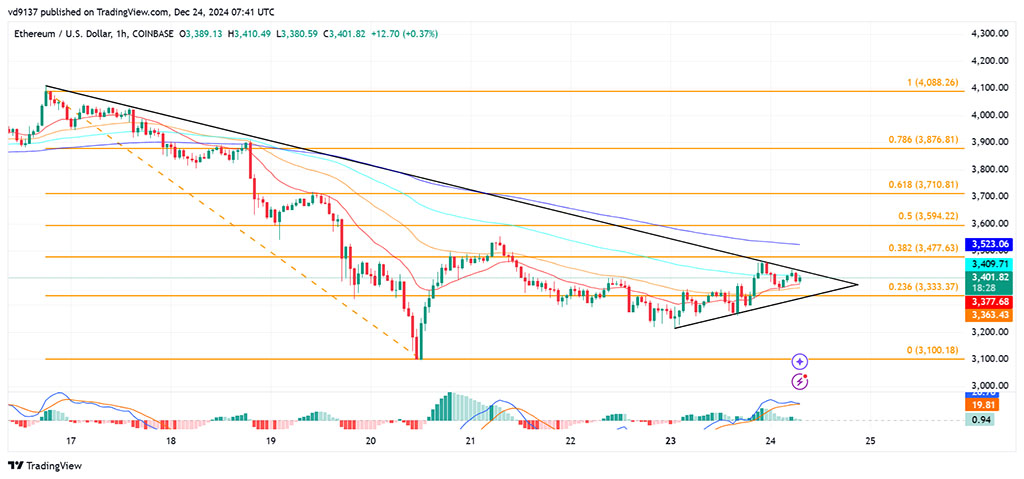 Ethereum Cross X Signals Strong Buy Analysts Predict 4 000 Price Target Amid Institutional Accumulation
May 08, 2025
Ethereum Cross X Signals Strong Buy Analysts Predict 4 000 Price Target Amid Institutional Accumulation
May 08, 2025 -
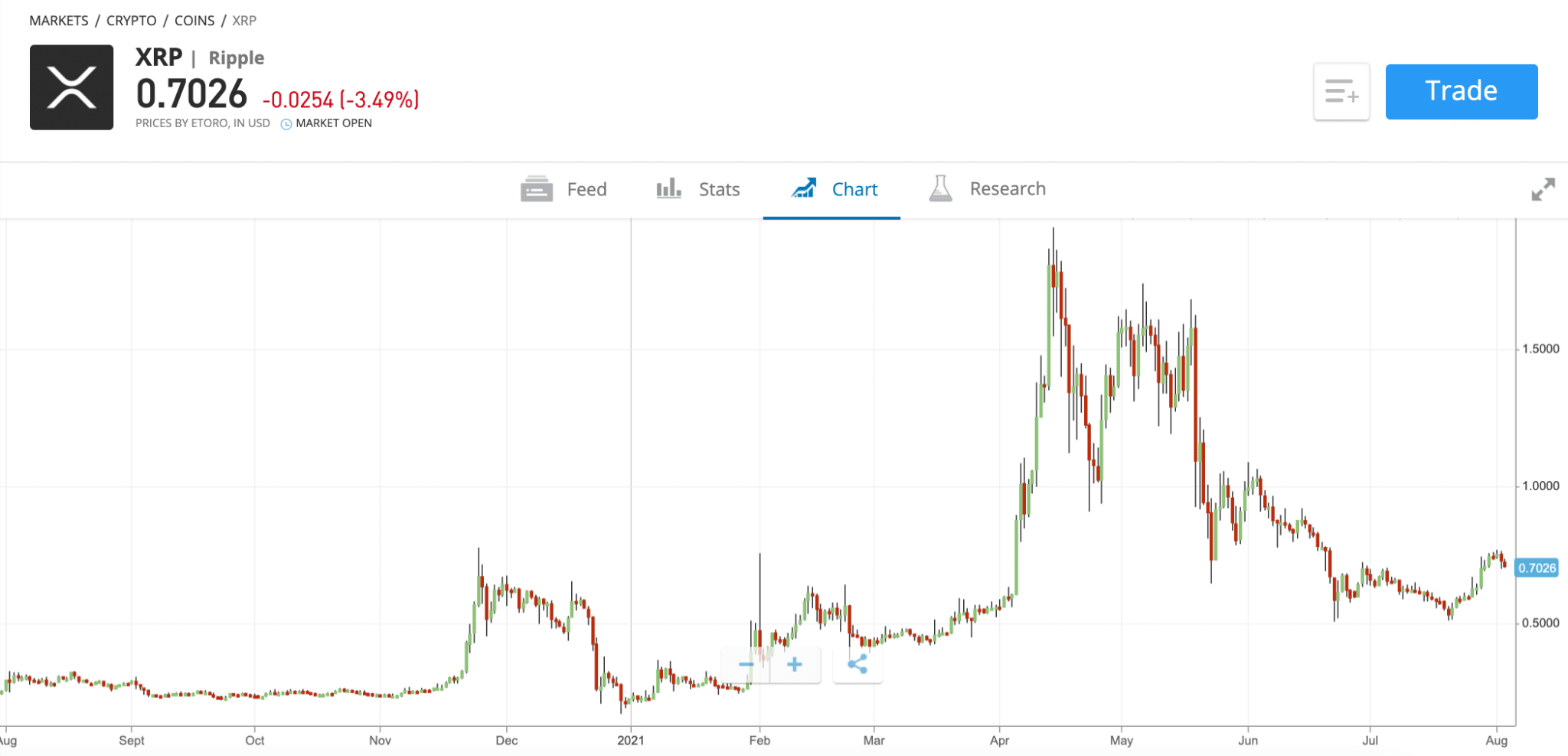 Deciphering The Xrp Price 2 Support And Future Price Predictions
May 08, 2025
Deciphering The Xrp Price 2 Support And Future Price Predictions
May 08, 2025 -
 De Andre Jordan I Nikola Jokic Objasnjenje Za Trostruki Poljubac
May 08, 2025
De Andre Jordan I Nikola Jokic Objasnjenje Za Trostruki Poljubac
May 08, 2025
