Canadian Wildfires And The Devastating Impact On Minnesota's Air
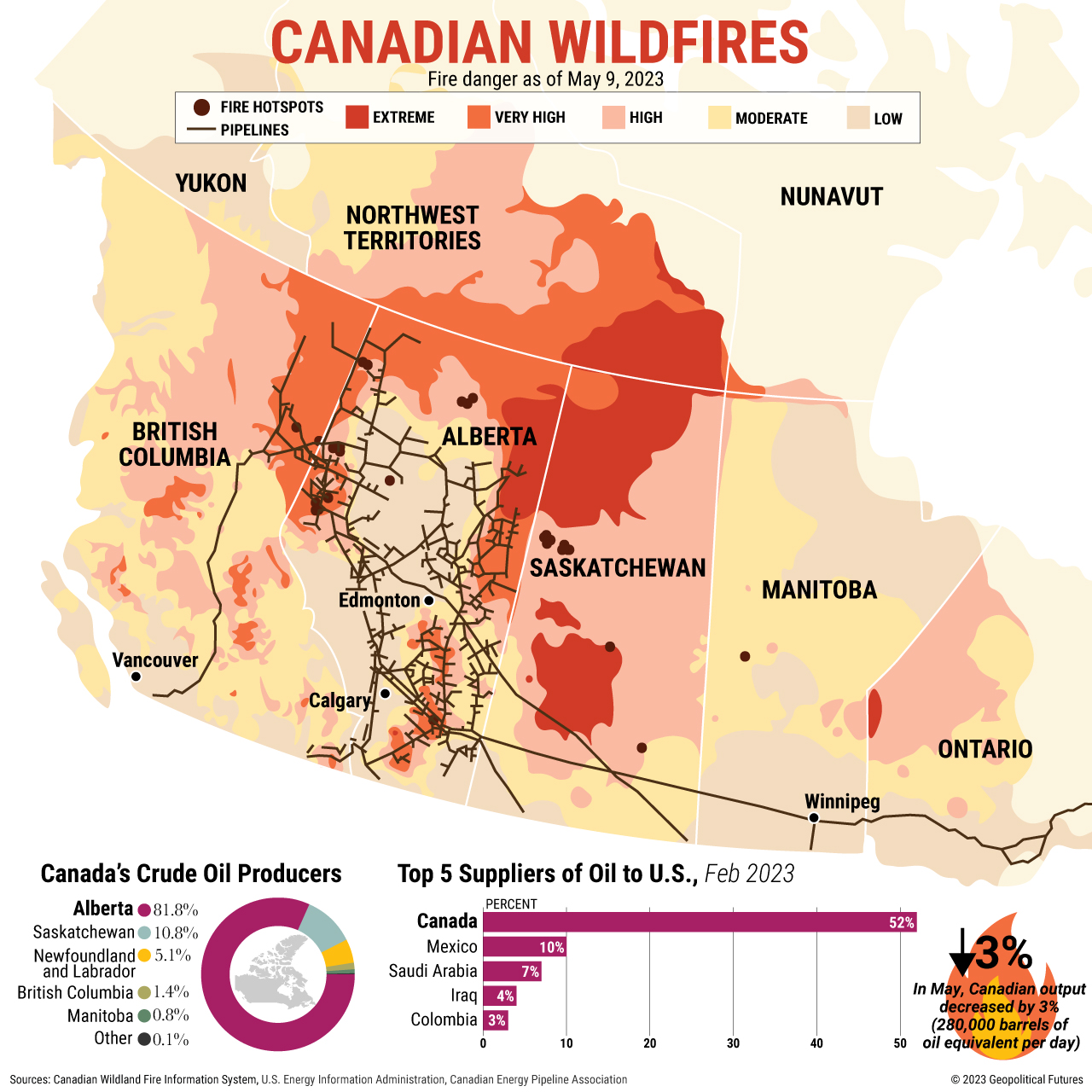
Table of Contents
The Science Behind the Smoke: How Canadian Wildfires Reach Minnesota
Wildfire smoke doesn't stay confined to its origin point. Meteorological conditions play a crucial role in transporting these pollutants vast distances. Strong prevailing winds, often westerly winds, carry smoke plumes from burning forests in Canada directly south into Minnesota. High-pressure systems can trap smoke near the surface, exacerbating air quality issues and creating dense haze. These atmospheric conditions, combined with the sheer scale of the wildfires, allow for the widespread dissemination of smoke across large geographical areas.
- Wind Patterns: Westerly winds are the primary culprit, carrying smoke from Canadian provinces like Ontario and Quebec directly into Minnesota.
- Atmospheric Pressure: High-pressure systems create stagnant air masses, trapping smoke close to the ground and increasing its concentration.
- Pollutants: Wildfire smoke contains a complex mixture of harmful pollutants. PM2.5 (fine particulate matter), notorious for its deep lung penetration, is a major concern. Other pollutants include carbon monoxide, ozone, and various volatile organic compounds, all contributing to respiratory and cardiovascular problems. Understanding the composition of wildfire smoke helps in developing effective mitigation strategies and public health interventions.
[Insert a map here illustrating the movement of smoke plumes from Canada to Minnesota]
Health Impacts of Wildfire Smoke on Minnesota Residents
The health impacts of prolonged exposure to wildfire smoke are significant and far-reaching. PM2.5, the primary culprit, can deeply penetrate the lungs, causing irritation and inflammation. This leads to a range of respiratory problems, from coughing and shortness of breath to aggravated asthma and bronchitis. Cardiovascular issues are also prevalent, with increased risk of heart attacks and strokes in vulnerable populations.
- Respiratory Issues: Increased coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, asthma attacks, and bronchitis are common.
- Cardiovascular Problems: Wildfire smoke can worsen existing heart conditions and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Vulnerable Populations: Children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory or cardiovascular conditions are particularly at risk. These groups require extra precautions and close monitoring during periods of poor air quality.
- Preventative Measures: Staying indoors with windows and doors closed, using high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters, and monitoring air quality indices are crucial preventative steps.
Economic Consequences of Degraded Air Quality
The economic consequences of degraded air quality extend beyond immediate healthcare costs. Reduced productivity due to illness forces many Minnesotans to miss work, leading to lost wages and decreased economic output. Outdoor activities, from tourism to construction, are significantly hampered, impacting various industries. The healthcare system faces increased burdens, handling a surge in respiratory and cardiovascular cases.
- Lost Productivity: Illness caused by wildfire smoke leads to absences from work and school, resulting in significant economic losses.
- Tourism Impact: Poor air quality deters tourists, negatively impacting the hospitality and tourism industries.
- Healthcare Costs: A surge in respiratory and cardiovascular-related hospitalizations and emergency room visits places a strain on the healthcare system.
- Agricultural Impacts: Exposure to wildfire smoke can also impact agricultural yields and livestock health.
Mitigation and Preparedness Strategies for Future Wildfire Events
Improving air quality monitoring and forecasting is paramount. Minnesota needs a robust system that provides timely and accurate information to residents, allowing them to take necessary precautions. Public health initiatives play a vital role in educating the public about air quality risks and promoting preventative measures. Furthermore, addressing climate change, a key driver of wildfire intensification, through emissions reduction is crucial for long-term mitigation.
- Enhanced Air Quality Monitoring: Investing in a network of air quality sensors to provide real-time data and improved forecasting capabilities is essential.
- Public Health Initiatives: Effective communication strategies, public awareness campaigns, and readily available information on health risks and protective measures are vital.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is a long-term strategy to combat climate change and lessen the frequency and intensity of wildfires.
Conclusion: Protecting Minnesota's Air from the Threat of Canadian Wildfires
The Canadian wildfires' impact on Minnesota's air quality is undeniable, posing significant health, economic, and environmental challenges. Understanding the science behind smoke transport, its health risks, and its economic consequences is crucial for effective mitigation and preparedness. By staying informed about air quality alerts, taking preventative measures, and supporting initiatives that address climate change, we can collectively work towards protecting Minnesota's air and the health of its residents. Stay informed about Canadian wildfire smoke impacts on Minnesota's air quality and take steps to protect your health and your community. Check your local air quality index regularly and consult resources like the Minnesota Department of Health for up-to-date information and recommendations.

Featured Posts
-
 Ai Doesnt Really Learn Understanding The Implications For Responsible Use
May 31, 2025
Ai Doesnt Really Learn Understanding The Implications For Responsible Use
May 31, 2025 -
 India Covid 19 Recent Case Numbers And The Role Of The Xbb 1 16 Variant
May 31, 2025
India Covid 19 Recent Case Numbers And The Role Of The Xbb 1 16 Variant
May 31, 2025 -
 Ais Learning Constraints Navigating The Ethical Challenges Of Artificial Intelligence
May 31, 2025
Ais Learning Constraints Navigating The Ethical Challenges Of Artificial Intelligence
May 31, 2025 -
 East London Shop Blaze 125 Firefighters Battle Large Fire
May 31, 2025
East London Shop Blaze 125 Firefighters Battle Large Fire
May 31, 2025 -
 Nintendo Switch A Legacy Forged In Indie Partnerships And Challenges
May 31, 2025
Nintendo Switch A Legacy Forged In Indie Partnerships And Challenges
May 31, 2025
