Country Diary: Identifying And Cooking A Carrot's Edible Root Relative
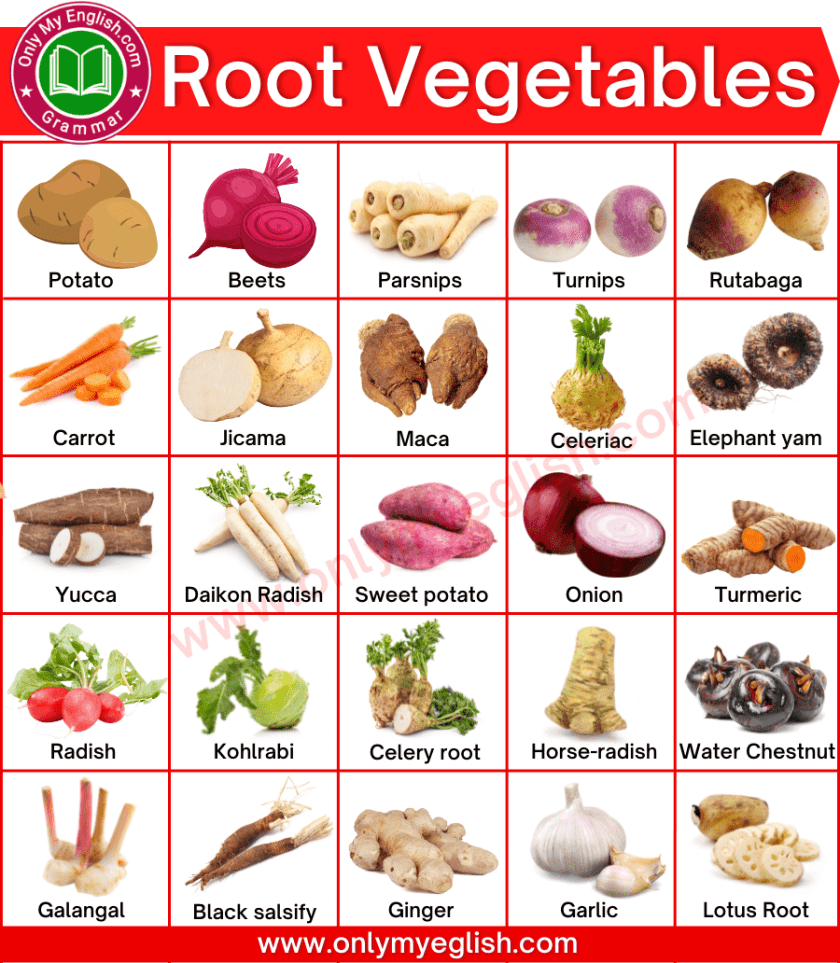
Table of Contents
Identifying Carrot's Edible Root Relatives
Understanding the Daucus carota Family
The Daucus carota species boasts incredible genetic diversity, resulting in the array of carrots and their relatives we see today. The familiar orange carrot is a cultivated variety, selectively bred for its size, sweetness, and vibrant color. However, its wild ancestor, Queen Anne's Lace (Daucus carota subsp. carota), provides a glimpse into the broader family. This wild carrot, with its delicate white flowers and small, often woody root, showcases the remarkable variation within the species. This genetic diversity has led to different root shapes – from long and slender to short and stubby – colors ranging from pale yellow to deep purple, and flavor profiles that span from sweet to subtly spicy.
!
Key Characteristics of Edible Relatives
While the common carrot reigns supreme in many gardens, several other Daucus carota relatives offer delicious edible roots. Let's explore some key examples:
-
Parsnips: Parsnips (Pastinaca sativa) are often considered the most prominent and readily available carrot relative. They boast a long, tapered root, typically creamy white to pale yellow, with a slightly sweet and earthy flavor, far more intense than the carrot. Search online for "parsnip recipes" to discover their versatility. Excellent sources of fiber and nutrients, parsnips offer significant "parsnip nutrition" benefits.
-
Other Potential Relatives: While caution is always advised with wild foraging, certain types of wild carrots may offer edible roots, though their size and flavor can vary dramatically. Always consult with foraging experts and utilize reliable identification resources before consuming any wild plants. Resources such as field guides or online databases specializing in edible plants are recommended.
| Feature | Carrot | Parsnip | Wild Carrot (Caution!) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Root Shape | Tapered, various | Long, tapered | Small, often woody |
| Color | Orange, Yellow, Purple | Pale Yellow, White | Pale Yellow, White |
| Flavor | Sweet | Sweet & Earthy | Variable, often bitter |
| Ease of ID | Easy | Easy | Difficult, requires expertise |
For safe identification, consider consulting reputable field guides on edible plants or seeking advice from experienced foragers. [Link to reputable online resource 1] [Link to reputable online resource 2]
Cooking with Carrot's Edible Root Relatives
Preparing Parsnips and Other Relatives
Preparing parsnips for cooking is straightforward:
- Scrubbing: Thoroughly scrub the parsnips under cold running water to remove any soil or debris. A vegetable brush is helpful. Search for "how to clean parsnips" for more detailed instructions.
- Peeling (Optional): Peeling is optional, but many prefer to peel parsnips, especially larger ones, to remove the tough outer skin.
- Chopping: Chop the parsnips into uniform pieces for even cooking. The size will depend on your chosen cooking method.
Parsnips can be cooked in various ways: roasting brings out their sweetness; boiling makes them creamy and perfect for pureeing; frying adds a crispy exterior; and they can even be used in baking. To prevent mushiness, avoid overcooking, especially when boiling.
Delicious Recipes Featuring Carrot Relatives
Roasted Parsnips with Rosemary and Garlic:
- Toss chopped parsnips with olive oil, minced garlic, and fresh rosemary.
- Roast at 400°F (200°C) for 20-25 minutes, or until tender and slightly caramelized. Search online for "roasted parsnip recipe" for variations.
Creamy Parsnip and Carrot Soup:
- Sauté diced onions and carrots before adding chopped parsnips.
- Simmer in vegetable broth until tender.
- Blend until smooth and creamy. Season with salt, pepper, and a touch of nutmeg. Search for "parsnip soup recipe" for additional tips.
! !
Nutritional Benefits of Carrot's Edible Root Relatives
Parsnips and other carrot relatives are packed with nutrients. They're excellent sources of fiber, promoting digestive health. They also contain essential vitamins such as vitamin C and various B vitamins, as well as minerals like potassium and manganese. "Parsnip health benefits" are widely documented, highlighting their contribution to overall well-being. Furthermore, they provide antioxidants that help protect against cellular damage. Compared to regular carrots, parsnips often have a higher concentration of certain vitamins and minerals. Exploring "nutritional value of root vegetables" will reveal the impressive health benefits of this family.
Conclusion: Embrace the Diversity of Your Carrot's Edible Root Relative
Exploring the world of carrot's edible root relatives opens up exciting culinary possibilities and nutritional advantages. From the earthy sweetness of parsnips to the potential discoveries among wild varieties (always with caution), these often-overlooked vegetables add depth and flavor to your cooking. Try the recipes suggested above, experiment with different flavor pairings, and uncover the unique taste profiles each relative offers. Start exploring the world of delicious carrot relatives today! Share your culinary adventures using #carrotsrelatives #parsniprecipes

Featured Posts
-
 Roland Garros 2024 Ruuds Knee Problem Leads To Loss Against Borges
May 30, 2025
Roland Garros 2024 Ruuds Knee Problem Leads To Loss Against Borges
May 30, 2025 -
 Monte Carlo Masters Alcaraz Wins As Musetti Withdraws
May 30, 2025
Monte Carlo Masters Alcaraz Wins As Musetti Withdraws
May 30, 2025 -
 Swiss Village Evacuated Buried By Mud And Rock Following Glacier Collapse
May 30, 2025
Swiss Village Evacuated Buried By Mud And Rock Following Glacier Collapse
May 30, 2025 -
 Ticketmaster Problemas Y Caidas Reportadas El 8 De Abril
May 30, 2025
Ticketmaster Problemas Y Caidas Reportadas El 8 De Abril
May 30, 2025 -
 Retraite Accord Possible Entre Le Rn Et La Gauche
May 30, 2025
Retraite Accord Possible Entre Le Rn Et La Gauche
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Scargill Parallel Analysing Rachel Reeves Approach To Industrial Relations
May 31, 2025
The Scargill Parallel Analysing Rachel Reeves Approach To Industrial Relations
May 31, 2025 -
 Is Rachel Reeves Following In Arthur Scargills Footsteps A Look At Labours Economic Strategy
May 31, 2025
Is Rachel Reeves Following In Arthur Scargills Footsteps A Look At Labours Economic Strategy
May 31, 2025 -
 Reeves Economic Policies Echoes Of Scargills Militancy
May 31, 2025
Reeves Economic Policies Echoes Of Scargills Militancy
May 31, 2025 -
 The Elon Musk Dilemma Challenges And Opportunities
May 31, 2025
The Elon Musk Dilemma Challenges And Opportunities
May 31, 2025 -
 Are Vets Being Forced To Compromise Care For Profit A Bbc Report
May 31, 2025
Are Vets Being Forced To Compromise Care For Profit A Bbc Report
May 31, 2025
