Creatine: Benefits, Side Effects, And How To Use It

Table of Contents
The Benefits of Creatine
Creatine supplementation offers a range of potential benefits for athletes and fitness enthusiasts, impacting strength, muscle growth, and even cognitive function. Let's explore these advantages in detail.
Increased Strength and Power
Creatine's primary benefit lies in its ability to significantly increase strength and power output, particularly during high-intensity activities. This is primarily due to its role in ATP (adenosine triphosphate) production.
- Increased ATP Production: Creatine helps replenish ATP, the body's primary energy source for muscle contractions. Higher ATP levels translate directly into improved performance during short bursts of intense exercise.
- Improved Performance: You'll likely experience enhanced performance in activities like weightlifting, sprinting, and other high-intensity interval training (HIIT) exercises. This improvement stems from the increased availability of energy for muscle cells.
- Enhanced Muscle Recovery: By aiding in ATP replenishment, creatine contributes to faster muscle recovery after intense workouts, allowing you to train harder and more frequently.
Muscle Growth and Hypertrophy
Creatine plays a crucial role in promoting muscle growth (hypertrophy) through several mechanisms. It's not just about strength; creatine contributes to a visibly larger and more defined physique.
- Improved Protein Synthesis: Creatine enhances muscle protein synthesis, the process by which your body builds and repairs muscle tissue. This leads to greater muscle mass over time.
- Increased Cell Hydration: Creatine draws water into muscle cells, leading to increased cell volume and a fuller, more defined appearance. This is often referred to as "cell volumization."
- Enhanced Strength Gains: The strength gains facilitated by creatine directly support and amplify muscle growth. More strength means you can lift heavier weights, stimulating greater muscle development.
Improved Cognitive Function
While not as extensively studied as its effects on physical performance, some research suggests creatine may offer cognitive benefits. It's important to note that this is an area requiring further research and isn't a primary reason to take creatine.
- Potential Benefits for Memory and Learning: Some studies indicate potential improvements in memory and learning abilities, particularly in individuals with specific cognitive impairments.
- May be Beneficial for Neurological Conditions: Preliminary research suggests potential benefits for individuals with certain neurological conditions. However, more research is needed to confirm these findings. Always consult a healthcare professional before using creatine to treat or manage a medical condition.
- More Research Needed: The cognitive effects of creatine are not fully understood and require more extensive investigation.
Potential Side Effects of Creatine
While generally safe, creatine supplementation can lead to some side effects in certain individuals. Understanding these potential drawbacks is crucial for making informed decisions.
Water Retention
One of the most common side effects of creatine is water retention. This leads to a temporary increase in weight, which can be concerning for some individuals.
- Mechanism of Water Retention: Creatine attracts water into muscle cells, contributing to increased cell volume and a fuller appearance. However, this also leads to overall increased body weight.
- Clarification on Weight Gain: It's important to emphasize that this weight gain is primarily water weight, not fat. The weight is likely to decrease once creatine supplementation is stopped.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Some users experience mild gastrointestinal discomfort when starting creatine. These issues are usually temporary and easily managed.
- Bloating, Nausea, and Diarrhea: These are the most common gastrointestinal side effects. They're often associated with starting a high dose of creatine.
- Minimizing GI Issues: Start with a lower dose, increase gradually, and ensure adequate hydration to reduce the likelihood of these issues.
Muscle Cramps
Although rare, some individuals report an increased incidence of muscle cramps while using creatine. The exact relationship is unclear.
- Uncertain Link: The connection between creatine and muscle cramps isn't fully understood. Further research is needed to establish a definitive link.
- Mitigation Strategies: Maintaining proper hydration and electrolyte balance can help minimize this risk.
Kidney Issues
Concerns about creatine's impact on kidney function have been raised, but these are largely unfounded for healthy individuals. This is a crucial point to emphasize.
- Risk Primarily for Individuals with Pre-existing Conditions: The primary risk is for individuals who already have pre-existing kidney problems. Creatine is not typically recommended for those with kidney disease.
- Consult a Doctor: If you have any concerns about your kidney health, consult a doctor before starting creatine supplementation.
How to Use Creatine Effectively
To maximize the benefits and minimize potential side effects, follow these guidelines for effective creatine usage.
Dosage
A standard and effective dosage is typically 3-5 grams of creatine monohydrate per day.
- Loading Phase (Optional): Some individuals opt for a loading phase, taking 20 grams per day for the first week, followed by a maintenance phase of 3-5 grams daily. However, a loading phase isn't necessary for effectiveness. Consistent daily intake is more important.
- Consistent Daily Intake: Maintaining a consistent daily intake is crucial for maintaining optimal creatine levels in your muscles.
Timing
Creatine can be taken at any time of the day. However, some people prefer post-workout consumption.
- Various Timing Strategies: There is some research supporting both pre- and post-workout timing. Experiment and see what works best for your individual needs.
Cycling Creatine
Cycling creatine involves periods of use followed by periods of rest. While not strictly necessary, some athletes prefer this approach.
- Pros and Cons of Cycling: Cycling may prevent tolerance development in some individuals. However, consistent daily use often proves equally effective.
- Evidence-Based Recommendations: Current research doesn't strongly advocate for creatine cycling.
Creatine and Hydration
Adequate hydration is critical when using creatine. It assists with water retention and overall health.
- Importance of Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Dehydration can exacerbate potential side effects.
Conclusion
Creatine monohydrate, when used correctly, can be a valuable supplement for enhancing athletic performance, increasing muscle mass, and potentially improving cognitive function. While some mild side effects are possible, they are typically temporary and manageable. By understanding the benefits, potential side effects, and optimal usage of creatine, you can make an informed decision about whether it's right for you. Remember to always consult your doctor before starting any new supplement regimen, particularly if you have pre-existing health conditions. Start your journey to improved strength and performance with creatine today!

Featured Posts
-
 Blue Origins Rocket Launch Postponed Details On Subsystem Failure
May 15, 2025
Blue Origins Rocket Launch Postponed Details On Subsystem Failure
May 15, 2025 -
 Bangladesh Election Sheikh Hasinas Party Barred
May 15, 2025
Bangladesh Election Sheikh Hasinas Party Barred
May 15, 2025 -
 Reshaping Indias Insurance Landscape Ind As 117s Transformative Potential
May 15, 2025
Reshaping Indias Insurance Landscape Ind As 117s Transformative Potential
May 15, 2025 -
 Dissecting The Gop Mega Bill Key Details And Anticipated Conflicts
May 15, 2025
Dissecting The Gop Mega Bill Key Details And Anticipated Conflicts
May 15, 2025 -
 Padres Vs Cubs A Detailed Game Prediction And Analysis
May 15, 2025
Padres Vs Cubs A Detailed Game Prediction And Analysis
May 15, 2025
Latest Posts
-
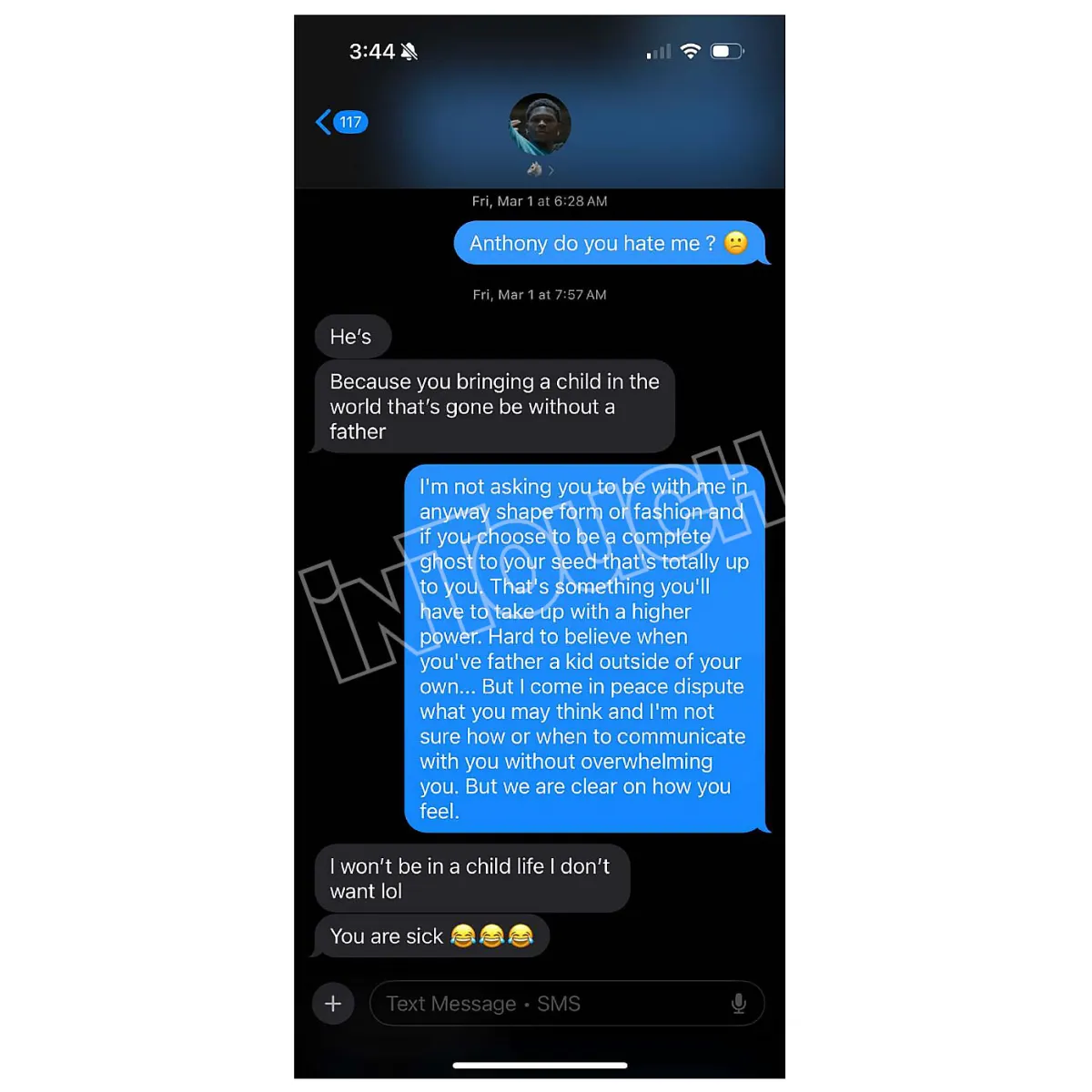 Court Awards Ayesha Howard Custody After Anthony Edwards Paternity Dispute
May 15, 2025
Court Awards Ayesha Howard Custody After Anthony Edwards Paternity Dispute
May 15, 2025 -
 Twitter Explodes Over Anthony Edwards Baby Mama Drama
May 15, 2025
Twitter Explodes Over Anthony Edwards Baby Mama Drama
May 15, 2025 -
 Dodgers Quiet Bats Lead To Defeat Against Cubs
May 15, 2025
Dodgers Quiet Bats Lead To Defeat Against Cubs
May 15, 2025 -
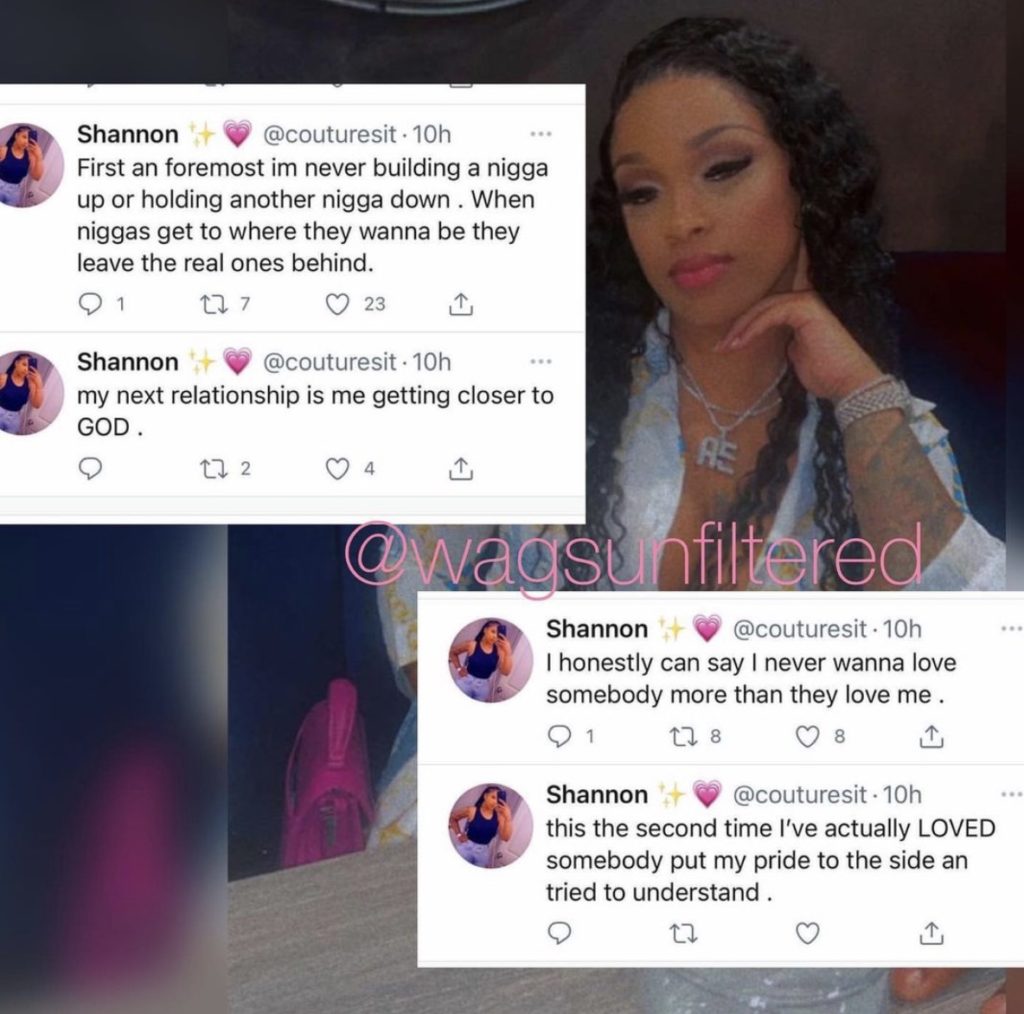 Anthony Edwards And His Baby Mama Drama A Twitter Firestorm
May 15, 2025
Anthony Edwards And His Baby Mama Drama A Twitter Firestorm
May 15, 2025 -
 Anthony Edwards Loses Paternity Case Ayesha Howard Granted Custody
May 15, 2025
Anthony Edwards Loses Paternity Case Ayesha Howard Granted Custody
May 15, 2025
