Economic Uncertainty: Inflation, Unemployment, And The Outlook For The Future
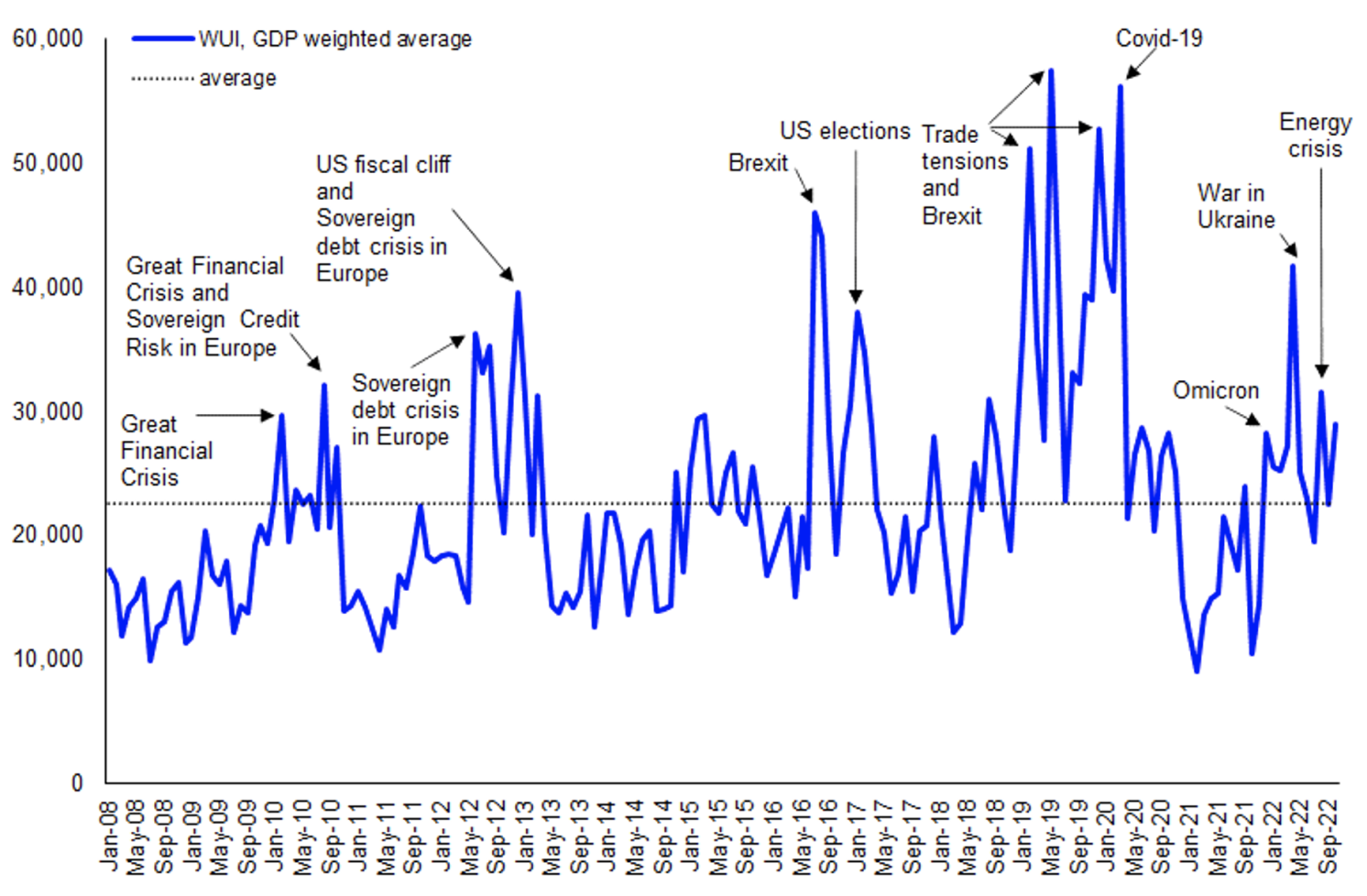
Table of Contents
Understanding Inflation's Impact on Economic Uncertainty
Defining Inflation and its Measurement
Inflation, a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time, is a key driver of current economic uncertainty. It's measured primarily using the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which tracks changes in the prices paid by urban consumers for a basket of goods and services, and the Producer Price Index (PPI), which measures the average change over time in the selling prices received by domestic producers for their output. Inflation can manifest in various forms:
- Demand-pull inflation: Occurs when aggregate demand exceeds aggregate supply, driving prices upward.
- Cost-push inflation: Results from increased production costs, such as rising wages or raw material prices.
Several factors contribute to inflationary pressures today:
- Soaring energy costs, exacerbated by geopolitical instability and supply chain disruptions.
- Global supply chain bottlenecks, leading to shortages and higher prices for goods.
- Increased consumer demand following the pandemic, coupled with robust government spending in some regions.
The impact of inflation extends far beyond headline numbers:
- It erodes purchasing power, reducing the value of consumers' savings and disposable income.
- It makes investment decisions more complex, as the real return on investments is diminished by inflation.
Inflation's Effects on Businesses and Consumers
Inflation presents significant challenges for both businesses and consumers. Businesses face:
- Increased production costs, squeezing profit margins and forcing difficult pricing decisions.
- The need to implement cost-cutting measures to maintain profitability in a high-inflation environment. This can lead to job losses or reduced investment in growth.
Examples of business adaptations include:
- Implementing price increases to offset higher input costs.
- Streamlining operations and reducing overhead expenses.
- Investing in automation and technology to improve efficiency.
Consumers, meanwhile, are forced to adapt their spending habits:
- Reduced disposable income necessitates careful budgeting and potentially reduced consumption.
- A shift towards cheaper alternatives and a reevaluation of spending priorities.
Examples of consumer adaptations include:
- Cutting back on discretionary spending and prioritizing essential goods and services.
- Seeking out discounts and promotions to mitigate the impact of higher prices.
- Increasing savings rates to protect against future inflationary pressures.
The Unemployment Landscape and its Contribution to Economic Uncertainty
Current Unemployment Trends and Statistics
Unemployment, the percentage of the labor force that is actively seeking employment but unable to find it, is another critical component of economic uncertainty. While unemployment rates may vary significantly by region and sector, [Insert current unemployment statistics from a reputable source, e.g., the Bureau of Labor Statistics]. This data reveals:
- Job losses concentrated in specific sectors (e.g., manufacturing, retail).
- Regional disparities in unemployment rates, reflecting variations in economic activity.
Different types of unemployment exist:
- Frictional unemployment: Short-term unemployment due to job searching.
- Structural unemployment: Long-term unemployment caused by mismatches between skills and available jobs.
- Cyclical unemployment: Unemployment related to economic downturns.
The relationship between inflation and unemployment is complex and often debated, illustrated by the Phillips Curve, which suggests an inverse relationship between the two. However, this relationship is not always consistent.
Unemployment's Social and Economic Consequences
High unemployment rates have profound social and economic consequences:
- Increased poverty and income inequality, potentially leading to social unrest and instability.
- Strain on government budgets due to increased spending on welfare programs and social safety nets.
The economic impact includes:
- Reduced economic growth, as a significant portion of the labor force remains underutilized.
- Lower productivity and reduced tax revenue, hindering government's ability to fund essential services.
- Increased pressure on social security systems.
Governments employ various policies to combat unemployment, including:
- Fiscal stimulus measures to boost aggregate demand and create jobs.
- Investment in education and training programs to improve worker skills.
- Support for small and medium-sized enterprises to stimulate job creation.
The Outlook for the Future: Predicting Economic Trends
Analyzing Potential Scenarios
Predicting future economic trends is inherently challenging, but analyzing current data and expert opinions allows us to explore potential scenarios:
- Recession: A significant and prolonged decline in economic activity.
- Stagflation: A combination of slow economic growth, high unemployment, and high inflation.
- Recovery: A period of economic growth following a recession or period of stagnation.
Factors influencing future economic growth include:
- Technological advancements, creating new industries and jobs.
- Geopolitical events, which can disrupt supply chains and impact global trade.
- Government policies, which can stimulate or dampen economic activity.
Each potential scenario presents unique risks and opportunities:
- A recession could lead to job losses and reduced consumer spending but might also create opportunities for businesses to acquire assets at discounted prices.
- Stagflation poses a severe challenge, requiring careful management of both inflation and unemployment.
- A strong recovery could lead to increased employment and economic growth but also might exacerbate inflationary pressures.
Strategies for Navigating Economic Uncertainty
Navigating economic uncertainty requires proactive planning and adaptation:
For individuals:
- Diversify investment portfolios to minimize risk.
- Build an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses.
- Develop a detailed budget and track spending habits carefully.
For businesses:
- Optimize costs and improve efficiency to maintain profitability.
- Invest in innovation and new technologies to stay competitive.
- Develop flexible workforce plans to adapt to changing economic conditions.
Conclusion: Preparing for the Future in a Climate of Economic Uncertainty
The current economic landscape, characterized by high inflation and fluctuating unemployment, presents significant challenges. Understanding the complex interplay between these two factors is crucial for individuals and businesses to effectively navigate this uncertainty. Proactive planning, adaptation, and a willingness to adjust strategies are key to mitigating the negative impacts and seizing emerging opportunities. Stay ahead of the curve by regularly reviewing your financial strategy in light of continuing economic uncertainty. Learn more about managing your finances during periods of high inflation and unemployment and seek professional advice when necessary to ensure you are well-prepared for whatever the future may hold.

Featured Posts
-
 Top Beaches In San Diego County For A Relaxing Weekend
May 30, 2025
Top Beaches In San Diego County For A Relaxing Weekend
May 30, 2025 -
 Ira Khans Shocking Revelation After Meeting Andre Agassi
May 30, 2025
Ira Khans Shocking Revelation After Meeting Andre Agassi
May 30, 2025 -
 Pandemic Fraud Lab Owner Pleads Guilty To Falsified Covid Tests
May 30, 2025
Pandemic Fraud Lab Owner Pleads Guilty To Falsified Covid Tests
May 30, 2025 -
 Best San Diego County Beaches Weekend Trip Ideas
May 30, 2025
Best San Diego County Beaches Weekend Trip Ideas
May 30, 2025 -
 Djokovic Gauff And Andreeva Advance At Roland Garros
May 30, 2025
Djokovic Gauff And Andreeva Advance At Roland Garros
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Tudor Pelagos Fxd Chrono Pink Release Date And Info
May 31, 2025
Tudor Pelagos Fxd Chrono Pink Release Date And Info
May 31, 2025 -
 Historic Meeting Pope Leo Xiv Greets Giro D Italia Peloton
May 31, 2025
Historic Meeting Pope Leo Xiv Greets Giro D Italia Peloton
May 31, 2025 -
 Giro D Italia 2024 Papal Audience For Cyclists In Vatican City
May 31, 2025
Giro D Italia 2024 Papal Audience For Cyclists In Vatican City
May 31, 2025 -
 Ladri Di Biciclette E Il Neorealismo L Opera Fotografica Di Arese Borromeo
May 31, 2025
Ladri Di Biciclette E Il Neorealismo L Opera Fotografica Di Arese Borromeo
May 31, 2025 -
 Giro D Italia In Diretta Risultati E Classifiche In Tempo Reale
May 31, 2025
Giro D Italia In Diretta Risultati E Classifiche In Tempo Reale
May 31, 2025
