Exploring Whidbey Clams: A Citizen Science Approach
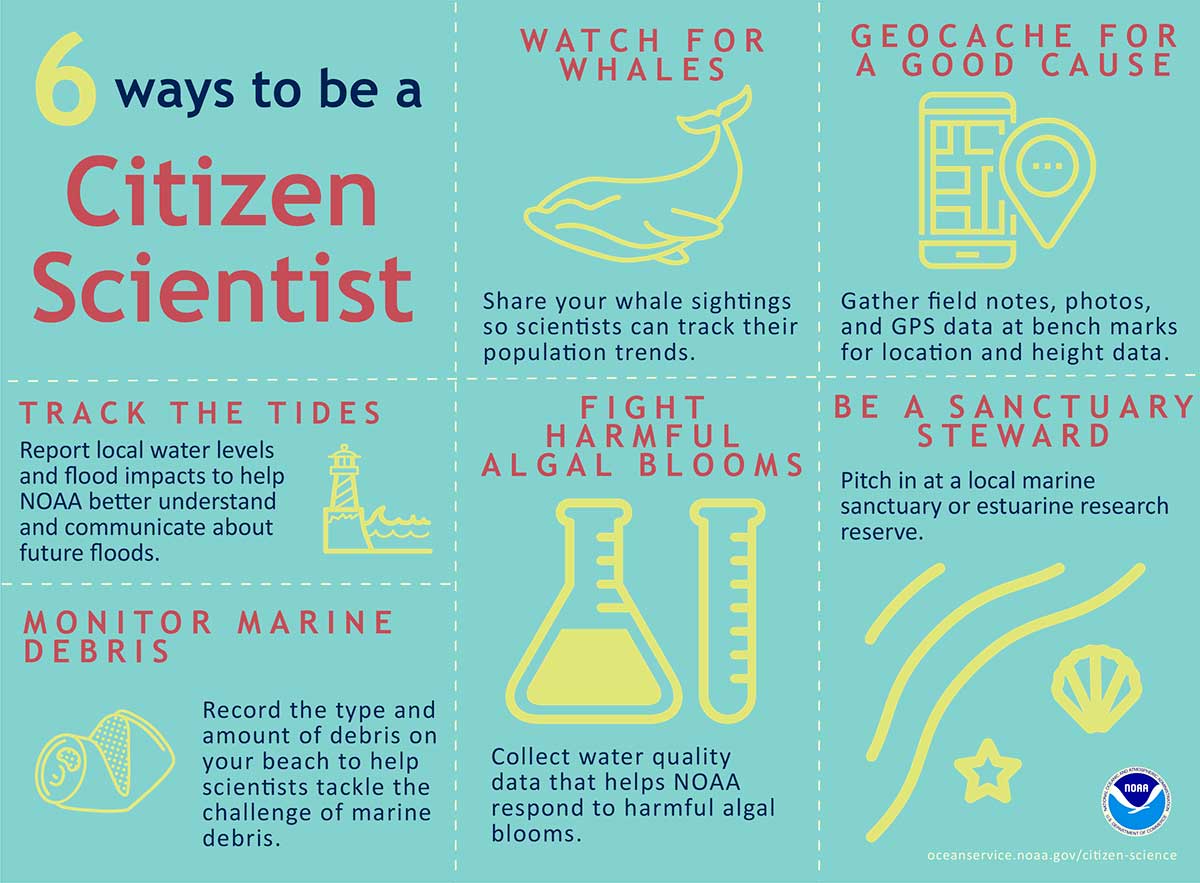
Table of Contents
Understanding Whidbey Clam Species & Habitats
Identifying Common Whidbey Clam Species
Whidbey Island's waters host a variety of clam species, each with unique characteristics and habitat preferences. Accurate identification is crucial for effective monitoring. Here are some common species found in the region:
-
Butter Clams (Saxidomus giganteus): These large, robust clams boast a thick, oval shell, often exhibiting a yellowish-brown color. They prefer sandy or muddy bottoms in the lower intertidal and shallow subtidal zones.
- Key Identifying Features: Large size (up to 6 inches), thick shell, yellowish-brown coloration.
- Unique Characteristics: Known for their sweet, buttery flavor (hence the name!), making them a popular shellfish.
-
Littleneck Clams (Leukoma staminea): Littlenecks are smaller, with a more rounded, thinner shell, varying in color from white to grayish-brown. They inhabit sandy and gravelly areas in the intertidal zone.
- Key Identifying Features: Smaller size (1-3 inches), thinner shell, varied coloration.
- Unique Characteristics: Often found clustered together in dense populations.
(Include high-quality images of Butter Clams and Littleneck Clams here)
Whidbey Clam Habitats and Ecology
Understanding the habitats where Whidbey clams thrive is essential for their conservation. These clams play a key role in the local ecosystem:
- Ideal Habitats:
- Sandy or muddy substrates in the intertidal and shallow subtidal zones.
- Areas with good water circulation and oxygen levels.
- Salinity levels appropriate for the specific clam species.
- Ecological Role:
- Clams filter feed, improving water quality by removing suspended particles.
- They serve as a food source for various birds, fish, and other marine animals.
- Their burrows aerate the sediment, enhancing habitat diversity.
Participating in Whidbey Clam Citizen Science Projects
Finding and Joining Relevant Projects
Several organizations conduct citizen science initiatives focused on Whidbey clam monitoring. Getting involved is easier than you think!
- [Link to Organization 1]: Focuses on clam population density surveys.
- [Link to Organization 2]: Conducts research on clam health and disease.
- [Link to Organization 3]: Monitors water quality in clam habitats.
These programs typically collect data on clam density, size, health, and habitat conditions.
Data Collection Methods and Techniques
Participating in Whidbey clam citizen science often involves:
- Safe Digging Techniques: Learn proper methods to minimize habitat disturbance. Use hand tools carefully and avoid unnecessary digging.
- Accurate Measurements: Use calibrated tools (e.g., rulers, calipers) to record clam size accurately.
- Data Recording: Utilize provided data sheets, mobile apps, or online platforms to record your observations systematically.
(Include a simple diagram illustrating safe digging techniques and data recording methods)
Data Submission and Contribution
Once you’ve collected data, submitting it is crucial:
- Online Forms: Most programs utilize online forms for easy data entry and submission.
- Mobile Apps: Some projects offer dedicated mobile apps for streamlined data collection and upload.
- Data Integrity: Ensure accuracy in your recordings to maintain data quality and reliability. Your contribution directly impacts scientific understanding and conservation efforts.
The Importance of Whidbey Clam Conservation
Threats to Whidbey Clam Populations
Whidbey clam populations face several significant threats:
- Pollution: Runoff from land-based activities can introduce pollutants into clam habitats.
- Habitat Loss: Development and coastal modifications can destroy or degrade critical clam habitats.
- Overharvesting: Unsustainable harvesting practices can deplete clam populations.
- Climate Change: Changes in water temperature and salinity can negatively affect clam survival and reproduction.
These threats can lead to population declines, impacting the entire ecosystem.
The Role of Citizen Science in Conservation
Citizen science is vital to Whidbey clam conservation:
- Data-Driven Management: Collected data informs management strategies, regulations, and conservation policies.
- Community Engagement: Citizen science fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility within the community.
- Early Warning System: Monitoring helps detect potential problems early, enabling timely interventions.
Your participation directly contributes to protecting these valuable shellfish.
Conclusion
Whidbey clam conservation is crucial for maintaining the health of our local ecosystem. Citizen science plays a vital role in this effort, providing valuable data that informs management decisions and ensures the long-term survival of these shellfish. By following the steps outlined above, you can become an active participant in Whidbey clams citizen science initiatives. Join a project today, and contribute to a healthier future for Whidbey Island's precious clam populations! Become a Whidbey clam citizen scientist today and help protect these vital shellfish! Explore Whidbey clam conservation opportunities near you and make a difference!

Featured Posts
-
 Alastqlal Qst Kfah Wthdy
May 30, 2025
Alastqlal Qst Kfah Wthdy
May 30, 2025 -
 Madrid Open De Minaurs Early Exit Swiateks Dominant Win Over Keys
May 30, 2025
Madrid Open De Minaurs Early Exit Swiateks Dominant Win Over Keys
May 30, 2025 -
 Mozarts Clavierkonzert Kommt Nach Augsburg Musikgeschichte Zum Anfassen
May 30, 2025
Mozarts Clavierkonzert Kommt Nach Augsburg Musikgeschichte Zum Anfassen
May 30, 2025 -
 London Gorillaz Concerts A Guide To Getting Tickets For Full Album Sets
May 30, 2025
London Gorillaz Concerts A Guide To Getting Tickets For Full Album Sets
May 30, 2025 -
 Bts 2025 Reunion Top 10 Fan Questions Answered
May 30, 2025
Bts 2025 Reunion Top 10 Fan Questions Answered
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 New Report Highlights Dangerous Climate Whiplash Impacts On Global Cities
May 31, 2025
New Report Highlights Dangerous Climate Whiplash Impacts On Global Cities
May 31, 2025 -
 Climate Whiplash A New Threat To Cities Worldwide
May 31, 2025
Climate Whiplash A New Threat To Cities Worldwide
May 31, 2025 -
 Dangerous Climate Whiplash Global Cities Face Impacts New Report Reveals
May 31, 2025
Dangerous Climate Whiplash Global Cities Face Impacts New Report Reveals
May 31, 2025 -
 Spring 2024 A Historical Echo And Its Significance For Summer Drought
May 31, 2025
Spring 2024 A Historical Echo And Its Significance For Summer Drought
May 31, 2025 -
 Wherry Vets Bungay Planning Bid Approved
May 31, 2025
Wherry Vets Bungay Planning Bid Approved
May 31, 2025
