Google And The Competition Bureau: A Constitutional Showdown?

Table of Contents
Google's Antitrust Allegations and the Competition Bureau's Case
The Competition Bureau, along with other global regulators, has leveled significant antitrust allegations against Google, accusing the tech giant of engaging in monopolistic practices that stifle competition and harm consumers. These allegations center on Google's dominance in several key digital markets, including search, advertising, and mobile operating systems. The keywords here are Google antitrust, Competition Bureau investigation, monopolistic practices, and digital market dominance.
-
Key Allegations:
- Search Manipulation: The Competition Bureau alleges that Google manipulates its search algorithm to favor its own products and services over competitors, effectively burying rivals in search results. This includes preferential placement of Google Shopping results and Google Maps listings.
- Preferential Treatment of Own Products: Google is accused of giving preferential treatment to its own products within its ecosystem, creating barriers to entry for competitors. For instance, pre-installing Google apps on Android devices makes it harder for competing apps to gain traction.
- Anti-competitive Acquisitions: The bureau argues that Google has used acquisitions to eliminate potential competitors rather than fostering innovation. The acquisition of smaller, innovative companies could be seen as a strategy to stifle competition before it can gain significant market share.
-
Examples of Google's Actions Cited as Evidence: The Competition Bureau points to specific instances where Google's actions appear to favor its own services, such as the prioritization of Google Maps over other map providers in its search results or the integration of Google Assistant into its Android ecosystem.
-
Google's Defense Strategies: Google typically defends its actions by arguing that its practices benefit consumers by providing them with high-quality, integrated services. They claim their actions are driven by innovation and a desire to provide the best possible user experience, not anti-competitive behavior.
Constitutional Challenges to Regulatory Overreach
Google may raise several constitutional challenges against the Competition Bureau's actions, arguing that regulatory overreach infringes upon its fundamental rights. The keywords here are Constitutional rights, due process, regulatory overreach, freedom of speech, and government intervention.
-
Due Process Violations: Google might argue that the Competition Bureau's investigation and enforcement actions violate its due process rights, particularly if the procedures are deemed unfair or lacking transparency.
-
Infringement on Freedom of Speech: The algorithm used to rank search results could be argued as a form of expression protected by freedom of speech. Government interference with the algorithm, therefore, could be seen as censorship.
-
Inappropriate Government Intervention: Google might contend that government intervention in a rapidly evolving technological market is unwarranted and hampers innovation. The argument is that the market itself is dynamic enough to handle issues of competition without heavy-handed regulation.
-
Potential Constitutional Arguments: Google's legal team could cite the Fifth Amendment (due process), the First Amendment (freedom of speech), and potentially other relevant clauses depending on the specifics of the case. They would likely draw on relevant legal precedents involving government regulation of private companies.
The Role of Innovation and Consumer Welfare
A central question in this "Google Competition Bureau Constitutional Showdown" is the impact of Google's actions on innovation and consumer welfare. Keywords here include Innovation, consumer welfare, competition, market efficiency, and technological advancement.
-
Does Google's Dominance Stifle Competition and Innovation? Critics argue that Google's market power discourages innovation by creating significant barriers to entry for smaller companies. The lack of meaningful competition, they claim, leads to stagnation.
-
Benefits vs. Harms: Google offers many free services, arguably benefiting consumers. However, this dominance also limits consumer choice and potentially leads to higher prices in related markets. The net effect on consumer welfare is a complex issue requiring careful analysis.
-
Examples of Pro- and Anti-Competitive Behaviors: The debate hinges on identifying and weighing instances of pro-competitive behavior (e.g., development of new technologies) against anti-competitive behaviors (e.g., manipulation of search results).
International Implications and Comparative Law
The Competition Bureau's case against Google is not isolated. Similar antitrust cases are playing out in other jurisdictions, particularly within the European Union. Understanding these international implications is crucial. Keywords here are International antitrust law, EU competition law, global regulation, and cross-border enforcement.
-
Comparison of Regulatory Approaches: Different countries employ varying approaches to regulating tech giants. The EU, for example, has been more assertive in its enforcement actions against Google than some other jurisdictions.
-
Effectiveness of Enforcement Mechanisms: The effectiveness of different enforcement mechanisms (fines, structural remedies, behavioral remedies) varies across countries. The ongoing legal battles help in determining the effectiveness of each approach.
-
Challenges of Regulating a Global Tech Giant: Regulating a global company like Google presents significant challenges for national regulators due to differences in legal frameworks, enforcement powers, and jurisdictional issues. This global nature of the issue requires international collaboration.
-
Key Differences and Similarities: The international landscape demonstrates a global trend towards regulating tech monopolies, but the approaches and effectiveness vary significantly based on specific legal traditions and political environments.
Conclusion
The conflict between Google and the Competition Bureau highlights the complexities of regulating powerful tech companies in the digital age. The alleged anti-competitive practices of Google, the Competition Bureau's efforts to enforce antitrust laws, and the potential constitutional challenges raised by Google create a complex legal and economic landscape. The "Google Competition Bureau Constitutional Showdown" is not just about a single company; it’s about the future of technological innovation, the balance between competition and consumer welfare, and the proper role of government in regulating the digital sphere. This case will set significant precedents for the future of antitrust law and technological regulation globally.
The Google and Competition Bureau conflict presents a crucial moment in the evolution of antitrust law and technological regulation. Stay informed about the developments in this "Google Competition Bureau Constitutional Showdown" by following reputable news sources and legal analyses. Further research into the specifics of the case and relevant legal precedents is encouraged to gain a deeper understanding of the potential constitutional ramifications.

Featured Posts
-
 Des Moines Car Crash Police Investigation Underway
May 30, 2025
Des Moines Car Crash Police Investigation Underway
May 30, 2025 -
 Autoroute A69 La Justice Contournee Le Projet Reprend Vie
May 30, 2025
Autoroute A69 La Justice Contournee Le Projet Reprend Vie
May 30, 2025 -
 Ticketmaster Y Setlist Fm Se Unen Una Experiencia De Fan Mejorada
May 30, 2025
Ticketmaster Y Setlist Fm Se Unen Una Experiencia De Fan Mejorada
May 30, 2025 -
 Measles Virus Found In Sacramento County Wastewater Public Health Alert
May 30, 2025
Measles Virus Found In Sacramento County Wastewater Public Health Alert
May 30, 2025 -
 Best San Diego County Beaches Weekend Trip Ideas
May 30, 2025
Best San Diego County Beaches Weekend Trip Ideas
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Manitoba Wildfires Crews Fight Deadly Spreading Blazes
May 31, 2025
Manitoba Wildfires Crews Fight Deadly Spreading Blazes
May 31, 2025 -
 Canadian Wildfires Minnesota Air Quality Plummets
May 31, 2025
Canadian Wildfires Minnesota Air Quality Plummets
May 31, 2025 -
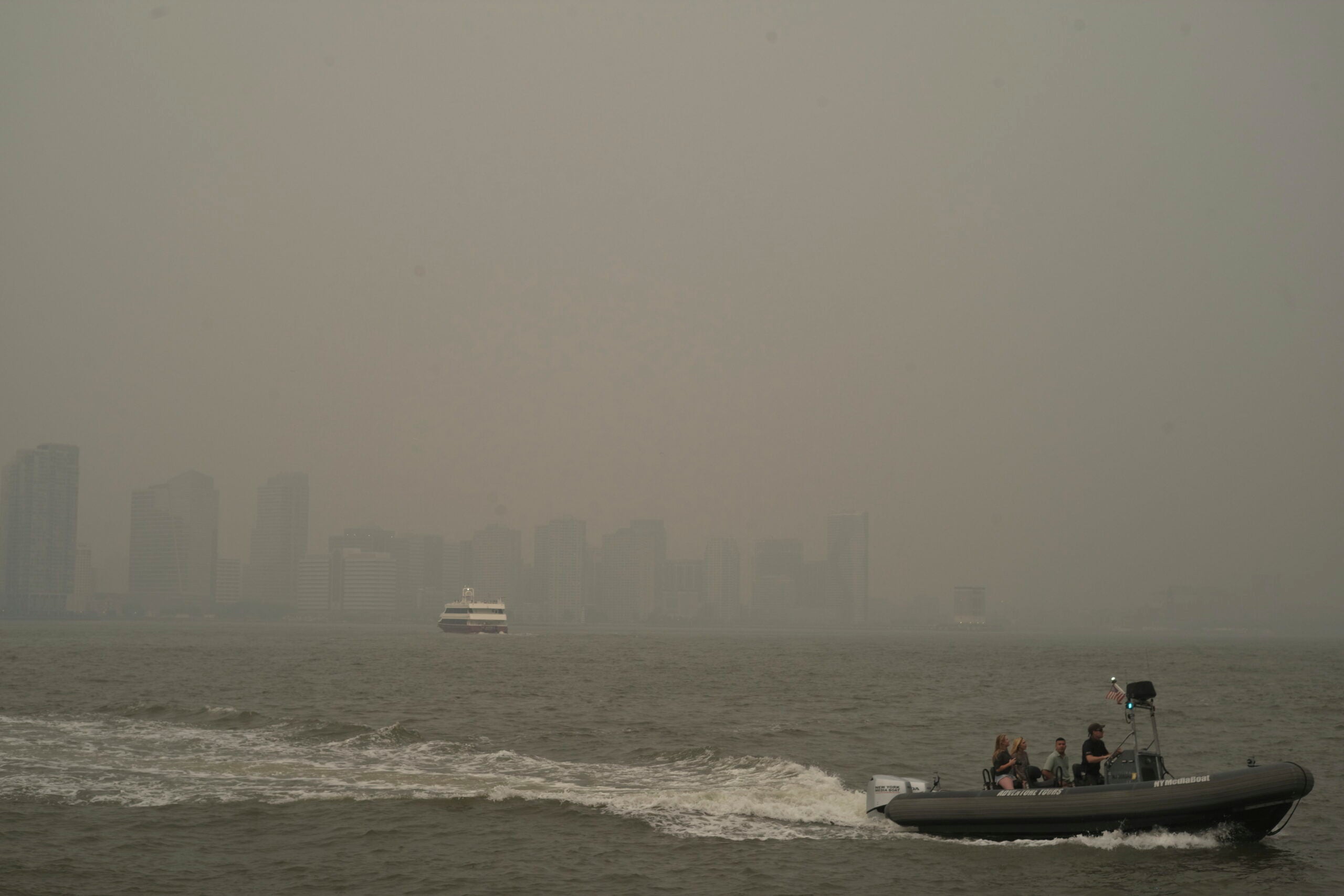 Canadian Wildfires New York Citys 3 C Temperature Drop And Elevated Air Toxicants
May 31, 2025
Canadian Wildfires New York Citys 3 C Temperature Drop And Elevated Air Toxicants
May 31, 2025 -
 Cyclings Team Victorious Targets Tour Of The Alps Victory
May 31, 2025
Cyclings Team Victorious Targets Tour Of The Alps Victory
May 31, 2025 -
 Helping Manitoba Wildfire Evacuees A Guide To Canadian Red Cross Support
May 31, 2025
Helping Manitoba Wildfire Evacuees A Guide To Canadian Red Cross Support
May 31, 2025
