High Temperatures Claim 311 Lives In England: Analysis Of Heatwave Impact
Table of Contents
The Scale of the Tragedy: Understanding the 311 Fatalities
The 311 heatwave fatalities represent a significant increase compared to previous years, highlighting the severity of this event. A detailed breakdown reveals crucial insights:
- Age Groups: The elderly (over 65) were disproportionately affected, accounting for the majority of deaths. Infants and young children also experienced a higher mortality rate during the peak heat.
- Geographical Distribution: While heat-related deaths occurred across England, certain regions with limited access to cooling infrastructure and higher concentrations of vulnerable populations experienced higher mortality rates. Data visualizations, including maps and charts, clearly illustrate this geographical disparity.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Pre-existing cardiovascular and respiratory conditions significantly increased the risk of heat-related death. This underscores the importance of managing chronic illnesses during periods of extreme heat. Keywords: heatwave fatalities, mortality rate, age demographics, geographical distribution, underlying health conditions.
A comparison with previous heatwaves in England reveals a concerning upward trend in mortality rates, directly correlating with the rising frequency and intensity of heatwaves linked to climate change.
Vulnerable Populations: Identifying Those Most at Risk During Extreme Heat
Certain groups are inherently more vulnerable to extreme heat, experiencing significantly higher risks of heatstroke and heat-related mortality:
- Elderly: Reduced thermoregulation, chronic health conditions, and social isolation place the elderly at heightened risk.
- Infants and Young Children: Their immature thermoregulatory systems make them especially susceptible to heat stress.
- Individuals with Pre-existing Conditions: Those with cardiovascular, respiratory, renal, or other chronic diseases face a dramatically increased risk during heatwaves.
- Socially Disadvantaged Groups: Poverty, lack of access to cooling (air conditioning, shaded areas), and inadequate housing contribute significantly to heat vulnerability.
Specific case studies highlighting the challenges faced by vulnerable populations during the recent heatwave will further illuminate the impact of extreme temperatures on these communities. Keywords: vulnerable groups, elderly, infants, pre-existing conditions, social determinants of health, heat vulnerability.
The Role of Public Health Infrastructure: Assessing England's Preparedness for Extreme Heat
The effectiveness of England's public health response during the recent heatwave requires careful evaluation:
- Heatwave Warning System: The accuracy, timeliness, and reach of the UK's heatwave warning system need review. Improvements in dissemination and public understanding of these warnings are crucial.
- Resource Allocation: The adequacy of resources allocated to heatwave preparedness and mitigation measures, including public awareness campaigns and support for vulnerable individuals, must be assessed.
- Public Health Campaigns: An evaluation of the effectiveness of public health campaigns and communication strategies in reaching and informing vulnerable populations is essential.
Recommendations for improvement include enhancing the heatwave warning system, increasing resource allocation for heatwave preparedness, and implementing targeted public health campaigns tailored to specific vulnerable groups. Keywords: heatwave warning system, public health response, resource allocation, public health campaigns, heatwave preparedness, heat mitigation.
Long-Term Implications: Climate Change and the Future of Heatwave Management in England
The increasing frequency and intensity of heatwaves are directly linked to climate change, demanding long-term strategies for adaptation and mitigation:
- Climate Change Adaptation: England needs to develop robust strategies for adapting to a changing climate, including infrastructure improvements and strengthened public health responses.
- Heatwave Mitigation Strategies: Implementing measures to reduce urban heat island effects, promote green spaces, and ensure access to cooling for vulnerable populations are crucial.
- Government Policy: Government policies must prioritize climate change adaptation and investment in heatwave preparedness to protect public health.
Proactive measures are essential to safeguarding public health and reducing heatwave-related mortality in the face of a warming climate. Keywords: climate change, heatwave frequency, heatwave intensity, climate change adaptation, heatwave mitigation strategies, government policy.
Conclusion: Learning from Tragedy: Preventing Future Heatwave Deaths in England
The 311 deaths during the recent heatwave highlight England's vulnerability to extreme heat and the urgent need for improved preparedness. This tragedy underscores the disproportionate impact on vulnerable populations and the need for enhanced public health infrastructure. Improving the heatwave warning system, increasing resource allocation, and implementing targeted public health campaigns are crucial steps. Understanding the impact of extreme heat is crucial to saving lives. Learn more about heatwave safety and how you can contribute to a better-prepared England by visiting [link to relevant government website] and [link to public health organization]. Let's work together to mitigate the effects of future heatwaves and protect the most vulnerable members of our society.

Featured Posts
-
 Bts Comeback Speculation Soars After Reunion Teaser
May 30, 2025
Bts Comeback Speculation Soars After Reunion Teaser
May 30, 2025 -
 The Enduring Appeal Of Dara O Briains Voice Of Reason
May 30, 2025
The Enduring Appeal Of Dara O Briains Voice Of Reason
May 30, 2025 -
 Energy Price Increases Experts Warn Of Impacts From New Us Policy
May 30, 2025
Energy Price Increases Experts Warn Of Impacts From New Us Policy
May 30, 2025 -
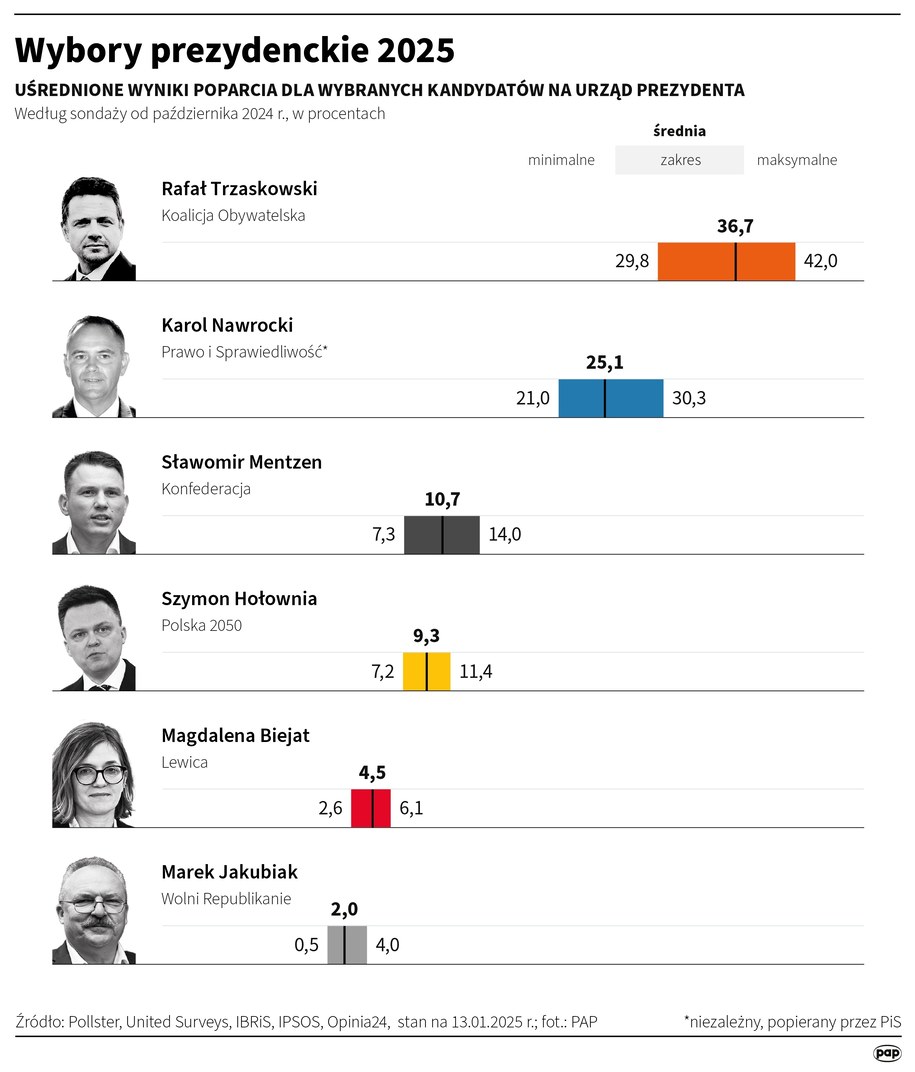 Mentzen I Wybory Prezydenckie 2025 Niezwykla Kampania
May 30, 2025
Mentzen I Wybory Prezydenckie 2025 Niezwykla Kampania
May 30, 2025 -
 Casper Ruuds Knee Injury Costs Him Roland Garros Match Against Nuno Borges
May 30, 2025
Casper Ruuds Knee Injury Costs Him Roland Garros Match Against Nuno Borges
May 30, 2025
