Increased Access To Birth Control: A Post-Roe Analysis
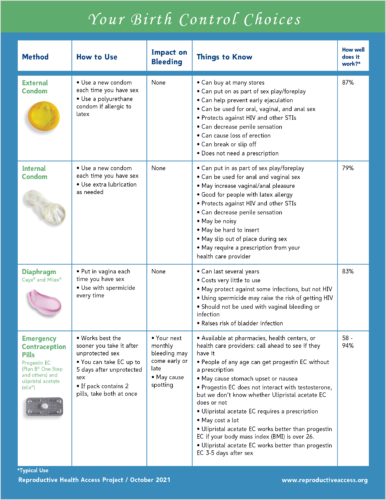
Table of Contents
The Shifting Landscape of Contraceptive Access
The pre-Roe era, while not perfect, generally offered a more consistent legal framework for contraceptive access nationwide. Post-Roe, the landscape is dramatically different. A patchwork of state-level laws and regulations has emerged, creating significant disparities in access based on geographic location.
- Increased legal challenges to contraception access in some states: Several states have introduced or are considering legislation that restricts access to certain forms of contraception, including long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs) like IUDs and implants. These challenges threaten to roll back decades of progress in reproductive healthcare.
- Variations in state-level policies regarding insurance coverage for contraception: The Affordable Care Act (ACA) mandates contraception coverage, but legal challenges and state-level efforts to circumvent these mandates have created inconsistencies. Some states actively work to expand access, while others actively restrict it, creating a deeply unequal system.
- The rise of telehealth and its impact on contraceptive access: Telehealth has emerged as a crucial tool in expanding access, particularly for individuals in rural areas or those facing transportation barriers. However, its potential is hampered by regulatory hurdles and concerns about data security.
- Potential for increased reliance on less effective methods due to restricted access: When access to highly effective methods like IUDs or the pill is limited, individuals may be forced to rely on less effective methods, leading to higher unintended pregnancy rates. This disproportionately impacts marginalized communities.
The Role of Insurance Coverage in Ensuring Access
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) significantly improved access to contraception by requiring most employers to cover preventive services, including contraception, without cost-sharing. This provision has been a cornerstone of increased access to birth control for millions. However, the post-Roe era has brought renewed challenges.
- The impact of employer religious objections on contraceptive coverage: The Supreme Court has allowed some employers to claim religious exemptions from the ACA's contraception mandate, leaving some individuals without access to affordable birth control.
- State-level efforts to restrict or limit ACA coverage of contraception: Many states have actively sought to undermine the ACA's contraception coverage provisions, creating a confusing and fragmented system.
- The financial burden on individuals facing reduced or eliminated coverage: For those without insurance or whose insurance doesn't cover contraception, the cost can be prohibitive, especially for long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs).
- The disproportionate impact on low-income individuals and communities of color: Reduced access to birth control disproportionately affects low-income individuals and communities of color, exacerbating existing health disparities.
Telehealth and its Impact on Accessibility
Telehealth platforms offer a promising avenue for increased access to birth control. They provide convenient and discreet access to consultations and prescriptions, removing geographical and transportation barriers.
- Increased convenience and accessibility for individuals in rural areas or those facing transportation barriers: Telehealth eliminates the need for travel to a clinic, making birth control accessible to those in remote areas or those with limited mobility.
- Potential concerns about privacy and data security: Concerns remain about the security of patient data and the potential for breaches in telehealth platforms. Strong regulations and security protocols are crucial.
- Regulatory hurdles for telehealth providers offering contraceptive services: Varying state regulations and licensing requirements can create challenges for telehealth providers seeking to offer contraceptive services across state lines.
- The need for increased investment in telehealth infrastructure to ensure equitable access: Investment in broadband access and technology is vital to ensure that telehealth services are accessible to all, regardless of socioeconomic status or geographic location.
The Future of Birth Control Access and Advocacy
The fight for increased access to birth control continues, with ongoing legal battles and persistent advocacy efforts. Reproductive rights organizations are employing various strategies to protect and expand access.
- The importance of advocating for comprehensive sex education: Comprehensive sex education empowers individuals to make informed choices about their reproductive health, including contraception.
- The need for increased funding for reproductive healthcare services: Adequate funding is crucial to ensure access to a full range of reproductive healthcare services, including contraception.
- The role of community-based organizations in providing access to contraception: Community-based organizations play a vital role in providing education, counseling, and access to contraception in underserved communities.
- The potential for legal challenges to state-level restrictions on contraception: Legal challenges to state-level restrictions on contraception will be crucial in protecting access and ensuring reproductive freedom.
Conclusion
The overturning of Roe v. Wade has created significant uncertainty surrounding access to birth control, highlighting the urgent need for increased access to birth control. While telehealth offers promising solutions, significant challenges remain, including legal battles, insurance coverage limitations, and financial barriers. Protecting and expanding access to contraception requires a multifaceted approach involving legislative action, advocacy efforts, and expanded telehealth infrastructure. We must continue to fight for comprehensive reproductive healthcare, including guaranteed access to birth control for all, to ensure reproductive freedom and health equity. Let's work together to ensure increased access to birth control for everyone.

Featured Posts
-
 Bianca Censoris Life Under Kanye Wests Control An Insider Perspective
May 28, 2025
Bianca Censoris Life Under Kanye Wests Control An Insider Perspective
May 28, 2025 -
 Bts Featurette A Look At The World Design Of The Phoenician Scheme
May 28, 2025
Bts Featurette A Look At The World Design Of The Phoenician Scheme
May 28, 2025 -
 Manchester United To Offload Another Forward Not In Amorims Plans
May 28, 2025
Manchester United To Offload Another Forward Not In Amorims Plans
May 28, 2025 -
 Garnacho To Chelsea Transfer Rumours Intensify As Man Utd Considers Sale
May 28, 2025
Garnacho To Chelsea Transfer Rumours Intensify As Man Utd Considers Sale
May 28, 2025 -
 Post Victory Romes Champions Next Chapter
May 28, 2025
Post Victory Romes Champions Next Chapter
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Cts Eventims Q1 Financial Results Adjusted Ebitda And Revenue Up
May 30, 2025
Cts Eventims Q1 Financial Results Adjusted Ebitda And Revenue Up
May 30, 2025 -
 Strong Q1 Performance For Cts Eventim Adjusted Ebitda And Revenue Climb
May 30, 2025
Strong Q1 Performance For Cts Eventim Adjusted Ebitda And Revenue Climb
May 30, 2025 -
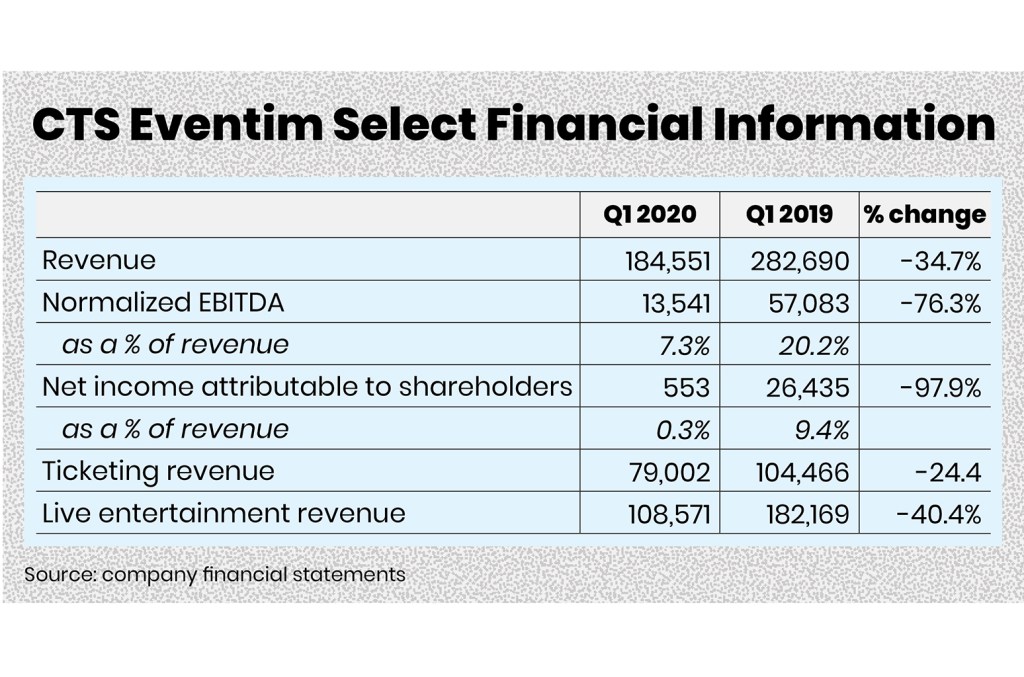 Cts Eventim Reports Q1 Revenue And Adjusted Ebitda Increase
May 30, 2025
Cts Eventim Reports Q1 Revenue And Adjusted Ebitda Increase
May 30, 2025 -
 Cts Eventim Q1 Adjusted Ebitda And Revenue Growth
May 30, 2025
Cts Eventim Q1 Adjusted Ebitda And Revenue Growth
May 30, 2025 -
 Metallica World Tour 2024 Glasgow Date Confirmed
May 30, 2025
Metallica World Tour 2024 Glasgow Date Confirmed
May 30, 2025
