Increased EU Scrutiny: Fueling A Brain Drain From Europe?
Table of Contents
H2: The Impact of Increased EU Regulations on Research and Development
The European Union has long been a powerhouse of scientific innovation, but increasingly stringent regulations are casting a shadow over its research and development landscape. This is contributing to a concerning brain drain from Europe, as researchers seek more conducive environments for their work.
H3: Funding Challenges
Securing research funding is a constant challenge, and the EU's complex regulatory framework is exacerbating the issue. Researchers face:
- Increased bureaucracy: Navigating intricate grant application processes consumes valuable time and resources, often delaying project commencement.
- Complex application processes: Multi-layered applications with demanding requirements often discourage researchers, particularly early-career scientists.
- Reduced funding opportunities: Competition for limited EU research funds is fierce, with many deserving projects left unfunded. This is further compounded by increased scrutiny and a heightened focus on specific, often narrowly defined, areas.
- Competition from other regions: Countries outside the EU often offer streamlined funding processes and more generous grants, making them attractive alternatives.
For instance, the Horizon Europe program, while substantial, is notorious for its complex application procedures and lengthy evaluation periods, potentially discouraging researchers from pursuing EU funding.
H3: Bureaucratic Hurdles
Beyond funding, the sheer weight of bureaucratic hurdles acts as a significant deterrent. Researchers grapple with:
- Lengthy approval processes: Research projects often face extensive delays due to prolonged approval timelines from various EU agencies.
- Excessive paperwork: Researchers spend considerable time on administrative tasks rather than focusing on their core research activities.
- Lack of clarity in regulations: Ambiguous and ever-changing regulations create uncertainty and complicate the research process.
- Difficulties navigating different EU agencies: The fragmented nature of EU agencies involved in research funding and approvals adds complexity and frustration.
One example is the time taken to secure ethical approvals for research involving human subjects, which can significantly delay project timelines and lead to researchers becoming frustrated with the process.
H2: The Effect on the Tech and Startup Sector
The EU's regulatory environment also significantly impacts its vibrant tech and startup sector, furthering the brain drain from Europe.
H3: Regulatory Uncertainty
Strict regulations and the frequent changes in EU policies create a climate of uncertainty that discourages investment in European startups. This includes:
- Fear of non-compliance: The complexity of EU regulations leads to a constant fear of unintentional breaches, potentially resulting in hefty fines.
- Unpredictable regulatory changes: Frequent shifts in EU policies create instability and make long-term planning difficult for startups.
- High compliance costs: Meeting EU regulatory requirements often places a significant burden on startups' resources.
- Difficulty attracting foreign investment: Uncertainty and high regulatory burdens make it difficult for European startups to compete for international investment.
For example, the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), while crucial for data privacy, has imposed significant compliance costs on many startups, hindering their growth and competitiveness.
H3: Talent Acquisition Difficulties
Attracting and retaining skilled workers is a major challenge for European tech companies, further exacerbated by regulations. This includes:
- Difficulty obtaining work permits for foreign talent: Complex immigration procedures make it challenging to hire skilled workers from outside the EU.
- Complex immigration processes: Lengthy and bureaucratic processes discourage highly skilled individuals from relocating to Europe.
- Less attractive compensation packages compared to other regions: Salaries and benefits in the European tech sector may not be competitive with those offered in other parts of the world, such as the US or Canada.
The result is a situation where European companies struggle to compete for top talent in a global market, pushing skilled workers to seek opportunities elsewhere, contributing to the brain drain from Europe.
H2: The Appeal of Alternative Destinations
The increasing difficulties within the EU drive researchers and entrepreneurs towards regions offering more favorable conditions.
H3: More Favorable Regulatory Environments
Countries like the United States, Canada, Australia, and Singapore offer significantly less stringent regulatory environments and more attractive incentives for businesses and researchers. These include:
- Streamlined regulatory processes: Simpler and more efficient processes for obtaining permits and approvals.
- Tax incentives for businesses and researchers: Attractive tax breaks and financial incentives to encourage innovation and investment.
- Pro-business policies: Government policies that support entrepreneurship and foster a culture of innovation.
This creates a stark contrast to the regulatory complexities within the EU, making alternative destinations far more appealing.
H3: Higher Salaries and Better Opportunities
Beyond regulatory hurdles, financial incentives and career prospects play a significant role in the brain drain from Europe. Other regions often offer:
- Higher salaries in the tech sector: Significantly higher compensation packages for skilled workers in the tech industry are commonly found elsewhere.
- More funding opportunities for research: More accessible and generous research funding opportunities are available in certain countries.
- Better career progression possibilities: Clearer career paths and greater opportunities for advancement often exist outside of Europe.
These factors combined make alternative destinations highly attractive to those seeking career advancement and financial security.
3. Conclusion
Increased EU scrutiny, while intended to improve various sectors, may unintentionally be contributing to a significant brain drain from Europe. The complex regulatory environment, coupled with challenges in securing funding and attracting talent, creates a less competitive landscape compared to other regions. Addressing the issue of brain drain from Europe requires a critical evaluation of current regulations and a proactive approach to creating a more attractive environment for researchers, entrepreneurs, and skilled workers. Let's work towards a regulatory framework that fosters innovation and growth while retaining Europe's brightest minds. A more streamlined and less burdensome approach to regulation is crucial to preventing further European talent migration and ensuring Europe remains a global leader in innovation.

Featured Posts
-
 Cold Plunge Fitness Orlando Blooms Friday Workout
May 19, 2025
Cold Plunge Fitness Orlando Blooms Friday Workout
May 19, 2025 -
 Reduced Apple Harvest Predicted Impact Of Rosy Apple Aphid Infestation
May 19, 2025
Reduced Apple Harvest Predicted Impact Of Rosy Apple Aphid Infestation
May 19, 2025 -
 Eurovision Belgium Leslie Cable Passes Torch To Michael De Lil In 2026
May 19, 2025
Eurovision Belgium Leslie Cable Passes Torch To Michael De Lil In 2026
May 19, 2025 -
 Orlando Bloom Heats Things Up With A Cold Plunge Workout
May 19, 2025
Orlando Bloom Heats Things Up With A Cold Plunge Workout
May 19, 2025 -
 The Fight To Save Jersey Battle Of Flowers A Story Of Perseverance
May 19, 2025
The Fight To Save Jersey Battle Of Flowers A Story Of Perseverance
May 19, 2025
Latest Posts
-
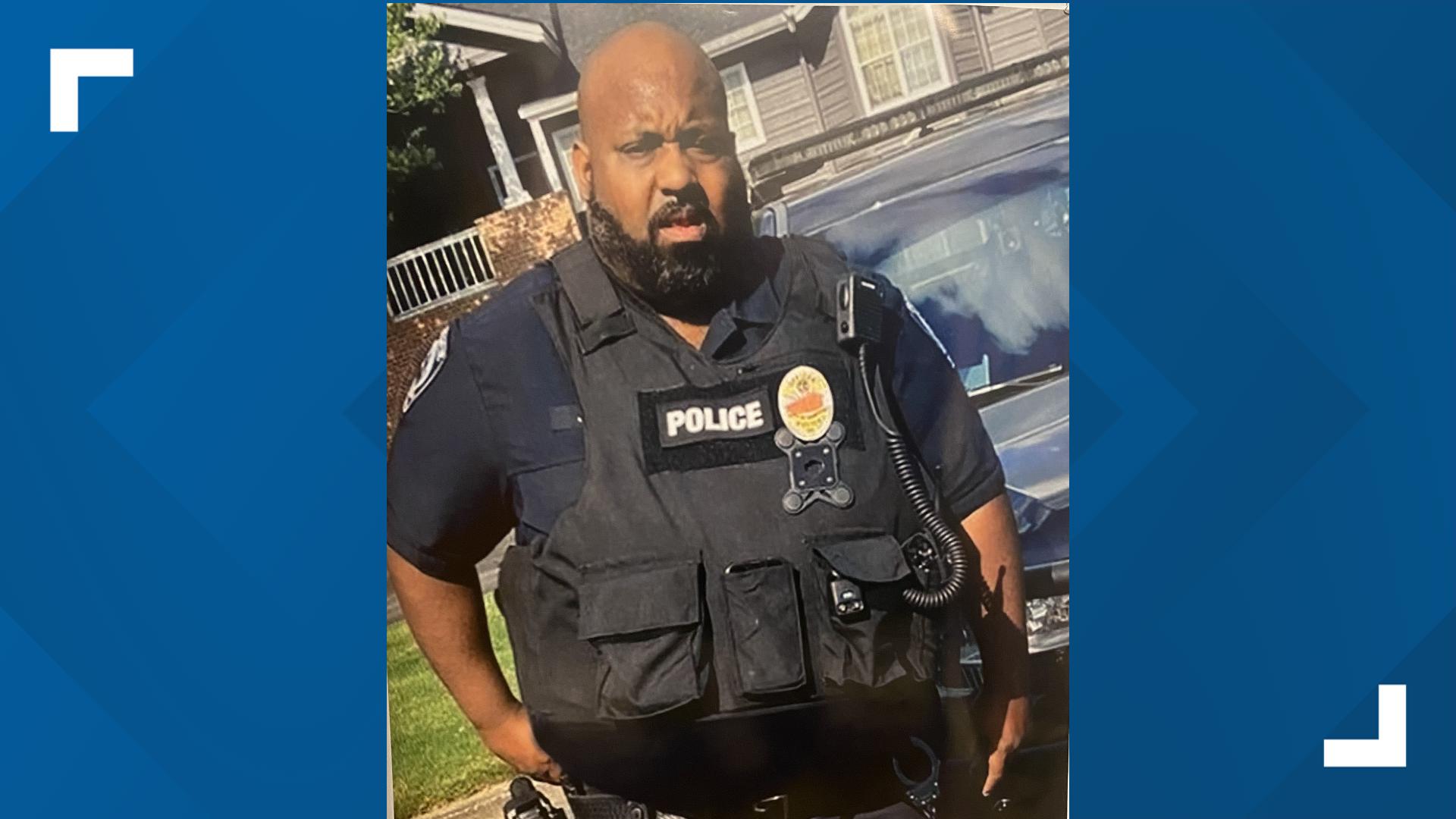 Southampton Police Charge East Hampton Officer Luis Morales With Driving While Intoxicated
May 19, 2025
Southampton Police Charge East Hampton Officer Luis Morales With Driving While Intoxicated
May 19, 2025 -
 Ufc Vegas 106 In Depth Look At Burns Vs Morales And Fight Card Odds
May 19, 2025
Ufc Vegas 106 In Depth Look At Burns Vs Morales And Fight Card Odds
May 19, 2025 -
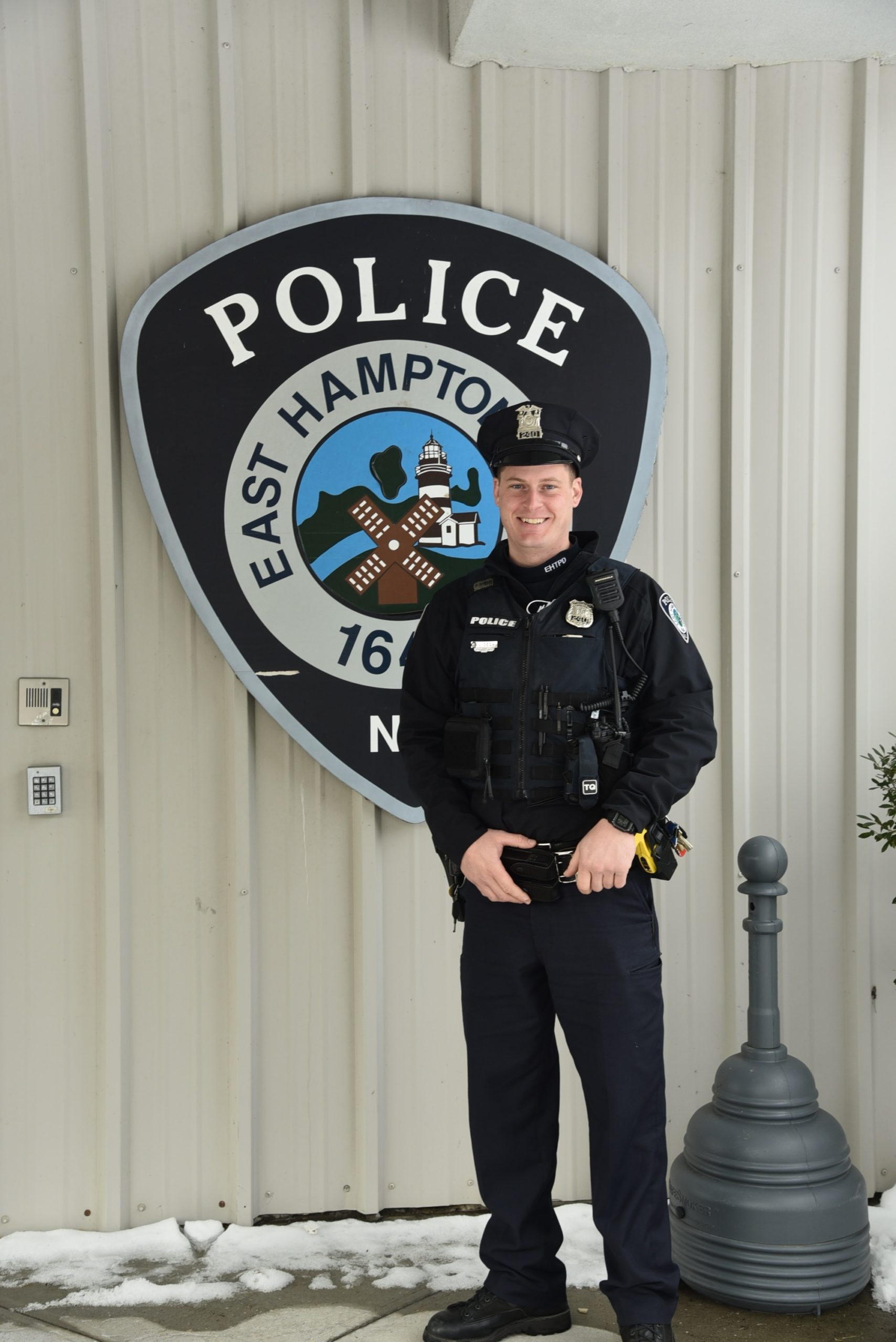 East Hampton Police Officer Luis Morales Charged With Dwi Southampton Police Report
May 19, 2025
East Hampton Police Officer Luis Morales Charged With Dwi Southampton Police Report
May 19, 2025 -
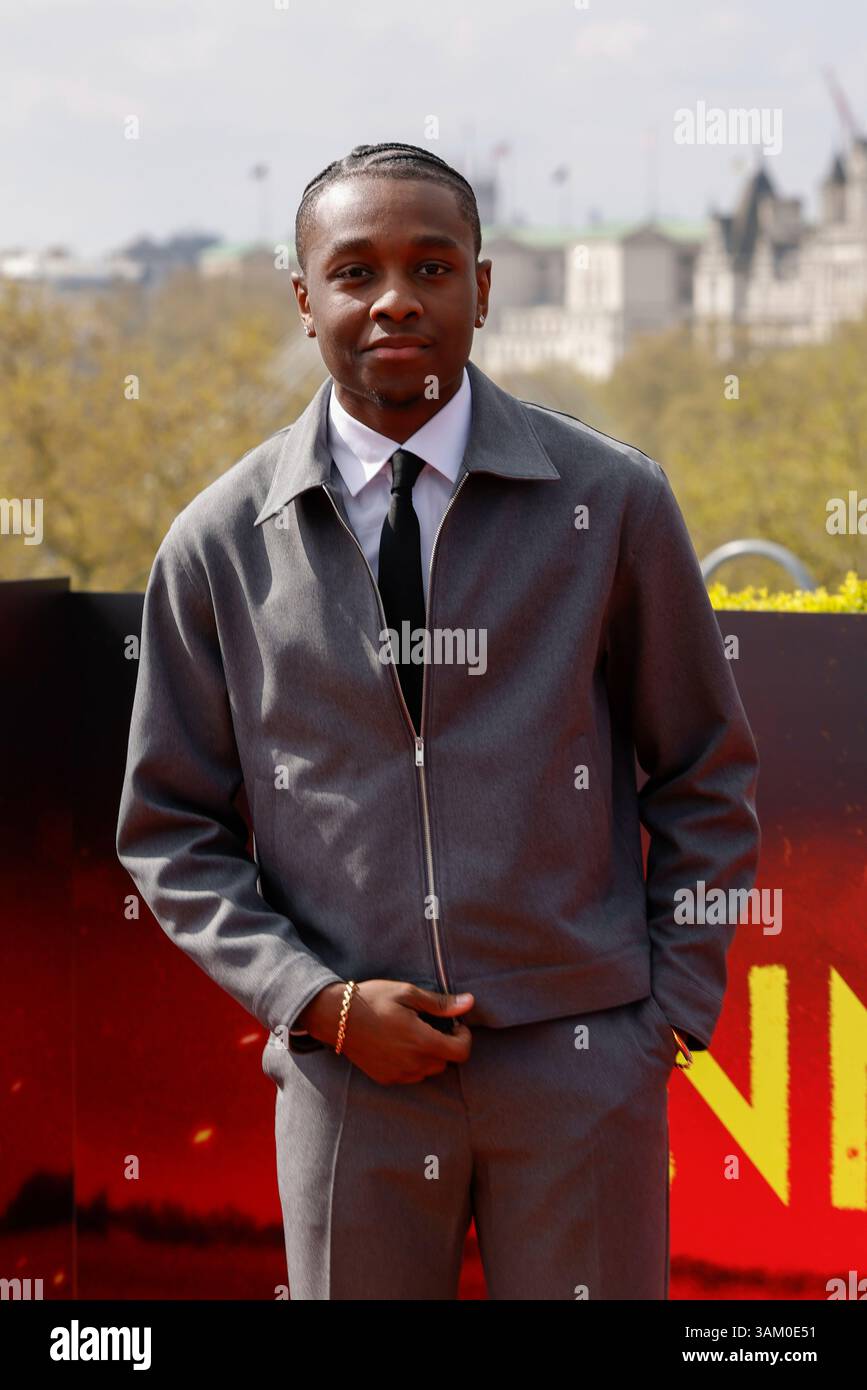 Sinner Star Miles Catons Spider Man Ambition An Mcu Aspiration
May 19, 2025
Sinner Star Miles Catons Spider Man Ambition An Mcu Aspiration
May 19, 2025 -
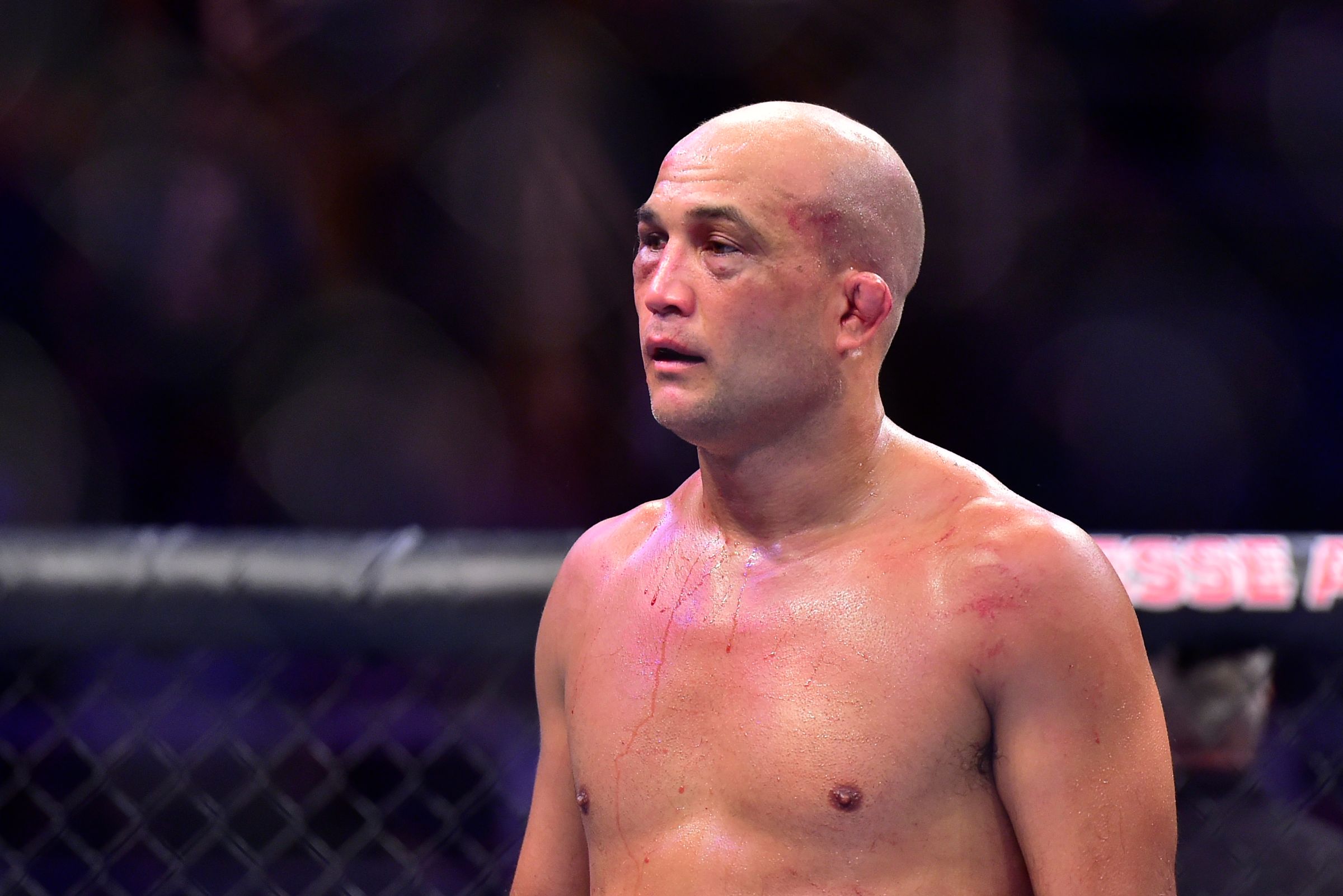 Michael Morales A Deep Dive Into The Ufc Welterweight Prospect
May 19, 2025
Michael Morales A Deep Dive Into The Ufc Welterweight Prospect
May 19, 2025
