INSACOG Reports New COVID-19 Variants BA.1 And LF.7 In India: Potential Risks Analyzed

Table of Contents
Understanding the BA.1 and LF.7 Variants
BA.1 and LF.7 are Omicron subvariants, meaning they are closely related to the Omicron variant (B.1.1.529). Understanding their "Omicron subvariants" lineage is key to assessing their behavior. BA.1, an earlier Omicron subvariant, shares some genetic similarities with later, more prevalent strains like BA.2 and BA.5. LF.7, a more recently identified variant, requires further study to fully understand its relationship to other Omicron sublineages and its "BA.1 characteristics".
Key genetic mutations within BA.1 and LF.7 influence their transmissibility, severity, and ability to evade vaccine-induced immunity. Analyzing these "viral mutations" is critical. While specific mutation details are still emerging, preliminary data suggests potential impacts on the "transmissibility rate" and "vaccine escape," although further research is needed to confirm the extent of these effects.
- Specific mutations found in BA.1 and LF.7: (Specific mutations would be listed here, pending availability from INSACOG reports. This section should be updated with the latest scientific findings).
- Comparison with other Omicron subvariants (e.g., BA.2, BA.5): (A comparative table outlining key differences in mutations and characteristics between BA.1, LF.7, BA.2, and BA.5 would be beneficial here).
- Evidence (or lack thereof) of increased severity: (Current evidence regarding severity should be presented here, citing relevant studies and INSACOG data. This may need an update as more information becomes available).
Prevalence and Spread of BA.1 and LF.7 in India
Determining the "variant prevalence India" and "geographical spread" of BA.1 and LF.7 is crucial for effective public health interventions. While precise data is still being collected and analyzed by INSACOG, initial reports suggest varying levels of prevalence across different Indian states. The "growth rate" and "transmission dynamics" of these variants are under close observation. Analyzing the "infection rate" in various regions allows for better resource allocation.
- Specific states or regions showing higher prevalence: (Specific regions with higher prevalence would be listed here based on available data from INSACOG reports and government publications).
- Data sources used (INSACOG reports, government publications): (Citations of relevant data sources should be included here to ensure transparency and credibility).
- Comparison to previous variant waves: (A comparison of the spread of BA.1 and LF.7 with previous COVID-19 variant waves in India would provide valuable context).
Potential Risks and Public Health Implications
The emergence of BA.1 and LF.7 raises concerns about their potential impact on India's healthcare system. The potential "healthcare burden," including "hospitalizations" and "ICU occupancy," needs careful monitoring. The risk of "reinfection risk" and "antibody escape" due to these variants is also a significant concern. The impact on the "immune response" and effectiveness of existing "vaccine efficacy" is being closely studied.
- Potential for increased hospitalizations and mortality: (Analysis of potential increases in hospitalizations and mortality rates based on current data and modeling).
- Impact on vulnerable populations (elderly, immunocompromised): (Specific analysis of the impact on high-risk groups is crucial).
- Recommendations for updated vaccination strategies: (Recommendations based on the characteristics of BA.1 and LF.7 and their potential to evade vaccine-induced immunity, including the need for "booster doses" and increased "vaccination coverage").
INSACOG's Ongoing Monitoring and Response
INSACOG's "genomic surveillance" program plays a vital role in "variant tracking" and informing the public health response. Their ongoing efforts in data collection and analysis are critical. The consortium's collaboration with national and international organizations ensures a coordinated approach to "pandemic preparedness." The measures being implemented by INSACOG, including "public health measures" and "infection control" strategies are paramount to minimizing the risk posed by these variants.
- INSACOG's data collection and analysis methods: (A brief description of the methods used by INSACOG for data collection and analysis).
- Collaboration with other organizations (national and international): (Highlighting the collaboration with relevant national and international organizations).
- Public health advisories and recommendations: (Mentioning any public health advisories and recommendations issued by INSACOG or the government).
Conclusion: Staying Informed About New COVID-19 Variants in India
The emergence of BA.1 and LF.7 highlights the ongoing need for vigilance and proactive measures to combat the evolving COVID-19 pandemic in India. Continued "genomic surveillance" and robust "public health measures" are crucial to mitigate potential risks. Staying informed about "COVID-19 variant updates" from sources like INSACOG reports and government health advisories is paramount. Following "INSACOG news" and adhering to "preventative measures" such as vaccination and masking remain vital steps in protecting individual and community health. Understanding the evolving nature of COVID-19 and following expert guidance is essential to mitigating the impact of new COVID-19 variants like BA.1 and LF.7. Stay informed and stay safe.

Featured Posts
-
 Your Good Life A Personalized Approach To Wellbeing
May 31, 2025
Your Good Life A Personalized Approach To Wellbeing
May 31, 2025 -
 Flin Flon Wildfires Force Hudbay Minerals Staff Evacuation
May 31, 2025
Flin Flon Wildfires Force Hudbay Minerals Staff Evacuation
May 31, 2025 -
 High Value Banksy Prints 22 777 000 In Annual Sales
May 31, 2025
High Value Banksy Prints 22 777 000 In Annual Sales
May 31, 2025 -
 Analyzing The Visuals Miley Cyrus End Of The World Music Video
May 31, 2025
Analyzing The Visuals Miley Cyrus End Of The World Music Video
May 31, 2025 -
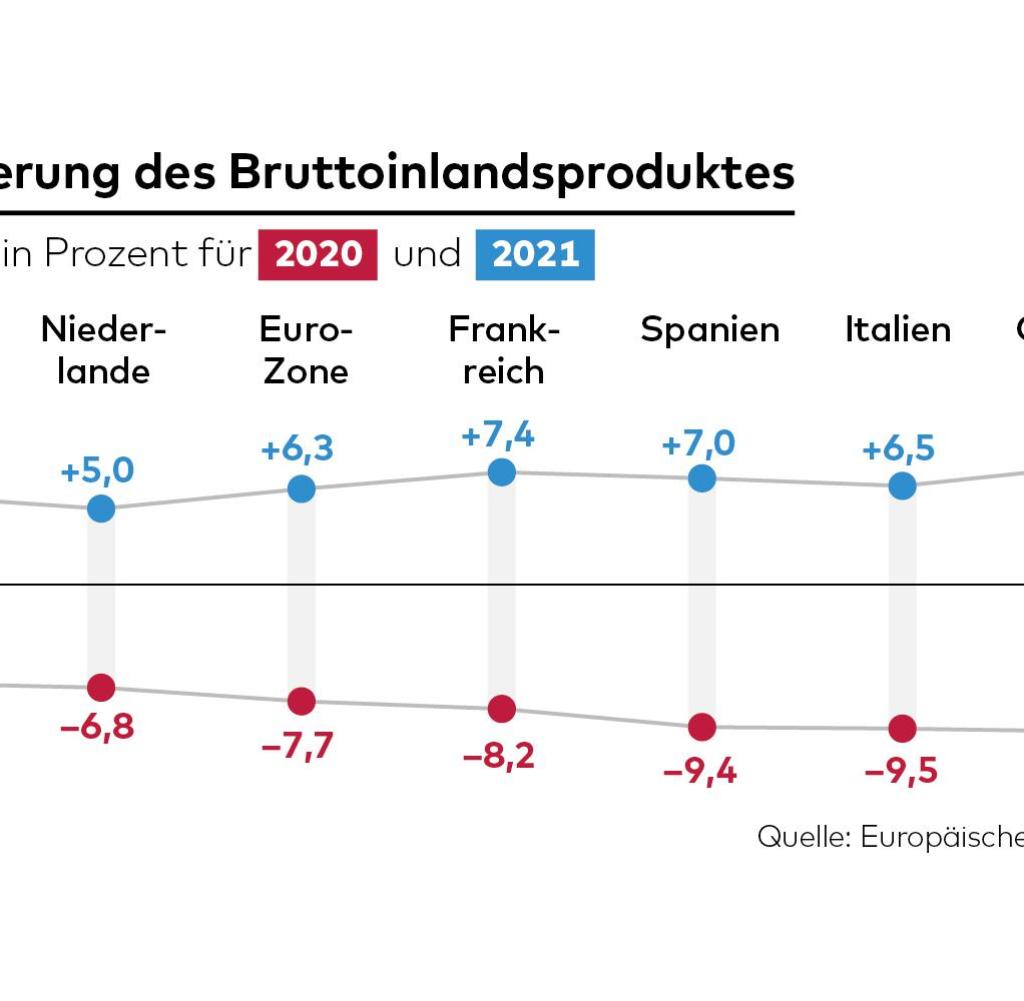 000 Jahre Bodensee Eine Prognose Und Die Dringlichkeit Des Klimaschutzes
May 31, 2025
000 Jahre Bodensee Eine Prognose Und Die Dringlichkeit Des Klimaschutzes
May 31, 2025
