Is The Great Decoupling Inevitable? Exploring The Potential Scenarios
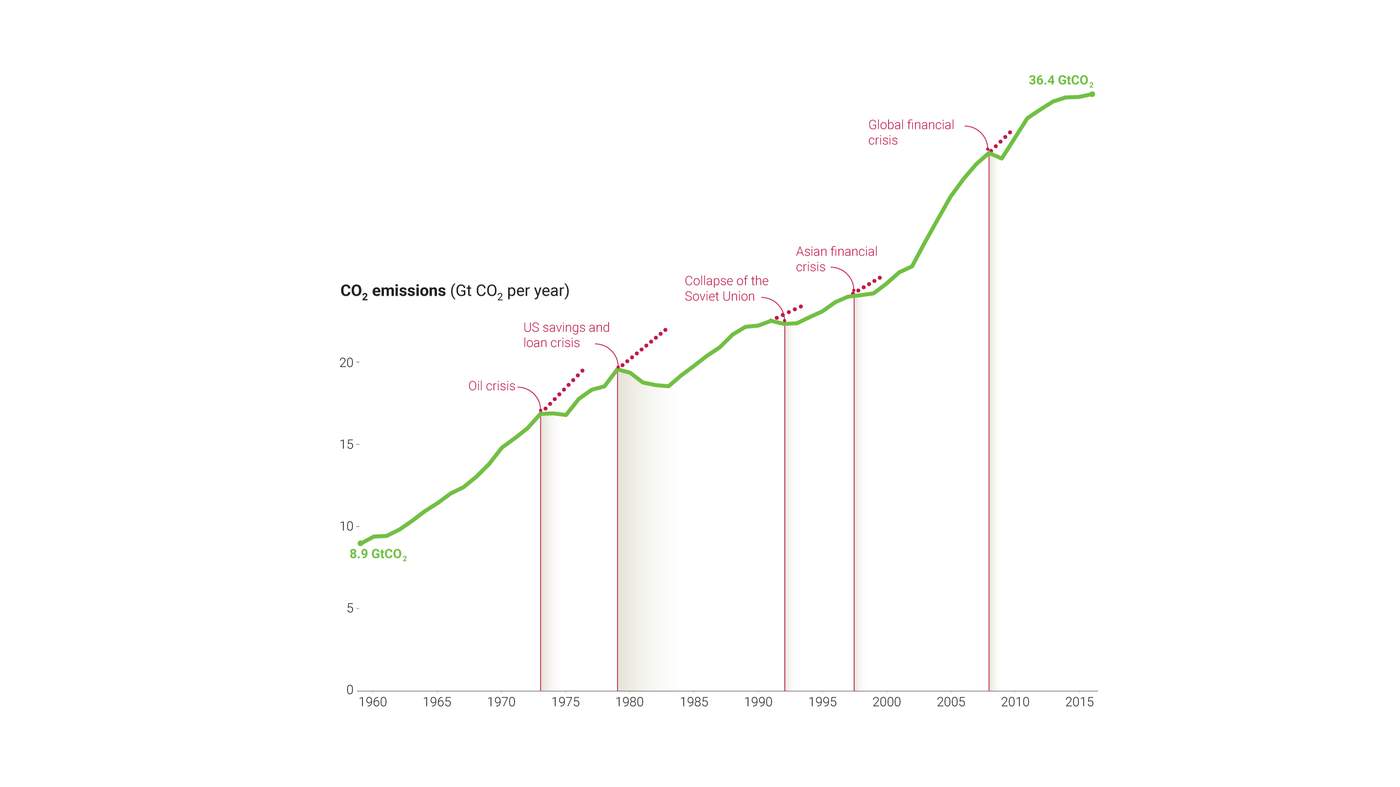
Table of Contents
Drivers of the Great Decoupling
Several interconnected factors are driving the potential for a Great Decoupling. Understanding these drivers is crucial to comprehending the evolving global landscape.
Geopolitical Tensions and Rivalries
Rising tensions between major global powers, particularly the complex relationship between the US and China, are a primary catalyst. These tensions manifest in various ways:
- Trade wars and sanctions: The use of tariffs, sanctions, and other trade restrictions as tools of geopolitical leverage is increasingly common, disrupting established trade flows and fostering economic fragmentation.
- Increased nationalism and protectionist policies: A surge in nationalist sentiment and protectionist policies in many countries prioritizes domestic industries over international competition, leading to trade barriers and reduced global integration.
- Examples of current decoupling initiatives: The ongoing efforts by some nations to reduce reliance on specific countries for critical technologies and resources exemplify this trend. This includes diversification of supply chains and the development of alternative trade partnerships.
Technological Competition and National Security Concerns
The intense competition for technological dominance in crucial areas like artificial intelligence (AI), semiconductors, and 5G is another significant driver.
- The race for technological dominance: Nations are investing heavily in research and development to secure a leading position in these strategically important technologies, often prioritizing national security concerns.
- Concerns over technology dependence and supply chain vulnerabilities: The reliance on specific countries for critical technologies exposes nations to vulnerabilities, prompting efforts to develop domestic capabilities and reduce dependence.
- Emphasis on domestic production and technological self-sufficiency: Governments are actively promoting domestic production of key technologies and aiming for greater self-sufficiency to reduce reliance on foreign suppliers.
- Investment in domestic technology sectors and R&D: Significant public and private investment is flowing into domestic technology sectors and research and development to bolster technological independence.
Economic Diversification and Regionalization
A growing trend towards economic diversification and regionalization is further fueling the potential for decoupling.
- Shift towards regional trade agreements and blocs: Nations are increasingly forming regional trade agreements and economic blocs, reducing their dependence on broader global trade networks.
- Reshoring and nearshoring of manufacturing and supply chains: Companies are relocating manufacturing and supply chains closer to their home markets to mitigate risks associated with global disruptions. This reduces reliance on distant suppliers and strengthens domestic economies.
- Focus on building resilient and diversified economies: Countries are prioritizing the development of more resilient and diversified economies less vulnerable to global shocks.
- Examples of countries actively pursuing economic diversification strategies: Many nations are actively pursuing diversification strategies, reducing reliance on specific export commodities or trading partners.
Potential Scenarios and Consequences
The potential outcomes of the Great Decoupling range from a relatively mild shift to a complete restructuring of the global economy.
Partial Decoupling
This scenario involves a selective decoupling, where certain sectors or industries become less interconnected while others remain integrated. This could lead to the emergence of regional trade blocs and increased regionalization.
- Impact on specific industries: Some industries will be more affected than others, with those reliant on complex global supply chains facing the greatest challenges.
- Benefits and drawbacks: Partial decoupling may offer increased resilience to shocks but could also reduce efficiency and limit economic growth.
Complete Decoupling
A complete separation of major economies is a more extreme scenario with potentially catastrophic consequences. This would result in significant disruptions to global trade and supply chains.
- Economic costs and benefits: The economic costs would be substantial, but some argue that increased self-sufficiency could offer long-term benefits for certain nations.
- Impact on global stability and security: Such a scenario could destabilize the global political and security environment, increasing the risk of conflict.
A Hybrid Model
This model represents a blend of partial and complete decoupling, with some aspects of the global economy remaining integrated while others become more fragmented.
- Factors influencing the trajectory: The interplay of geopolitical factors, technological advancements, and economic policies will shape the trajectory.
- Cooperation and competition: This scenario would likely involve a complex mix of both cooperation and competition between nations.
Mitigating the Risks of the Great Decoupling
Mitigating the risks associated with the Great Decoupling requires a multi-faceted approach.
International Cooperation and Diplomacy
International organizations play a crucial role in fostering collaboration, reducing tensions, and promoting a more stable and integrated global economy.
Strengthening Supply Chain Resilience
Diversifying supply chains and reducing reliance on single sources is critical to mitigating vulnerabilities. This includes geographically diversifying suppliers, developing domestic production capabilities, and fostering greater supply chain transparency.
Investing in Technological Innovation
Sustained investment in research and development is crucial for maintaining technological competitiveness and reducing reliance on foreign technologies. This includes supporting both public and private sector R&D efforts.
Promoting Fair Trade and Open Markets
Reducing trade barriers and promoting free and fair competition can help to mitigate the negative consequences of decoupling. This requires a commitment to multilateral trade agreements and a reduction in protectionist measures.
Conclusion
The "Great Decoupling" presents a complex and uncertain future. While various factors are pushing towards greater economic and technological separation, the ultimate extent and consequences remain uncertain. The scenarios outlined above highlight the potential ramifications, ranging from modest shifts in global trade patterns to a complete restructuring of the global economic order. Mitigating the risks requires a proactive approach involving robust international cooperation, strategic supply chain management, and sustained investment in technology and innovation.
Call to Action: Understanding the implications of the Great Decoupling is crucial for businesses and policymakers alike. Further research and informed discussions are essential to navigate this evolving landscape effectively and prepare for the potential challenges and opportunities presented by this significant global transformation. Continue exploring the multifaceted implications of the Great Decoupling to ensure your organization is well-prepared for the future.

Featured Posts
-
 Elon Musks Business Strategies How He Accumulated His Massive Wealth
May 09, 2025
Elon Musks Business Strategies How He Accumulated His Massive Wealth
May 09, 2025 -
 Dijon 2026 Le Projet Ecologiste Pour Les Municipales
May 09, 2025
Dijon 2026 Le Projet Ecologiste Pour Les Municipales
May 09, 2025 -
 Wall Streets Palantir Prediction Buy Before May 5th
May 09, 2025
Wall Streets Palantir Prediction Buy Before May 5th
May 09, 2025 -
 Dakota Johnson And Melanie Griffith Shine At Materialists Screening
May 09, 2025
Dakota Johnson And Melanie Griffith Shine At Materialists Screening
May 09, 2025 -
 Travaillez A Dijon Restaurants Et Rooftop Dauphine
May 09, 2025
Travaillez A Dijon Restaurants Et Rooftop Dauphine
May 09, 2025
