Japan's Bond Market: Steep Yield Curve Poses Economic Challenges
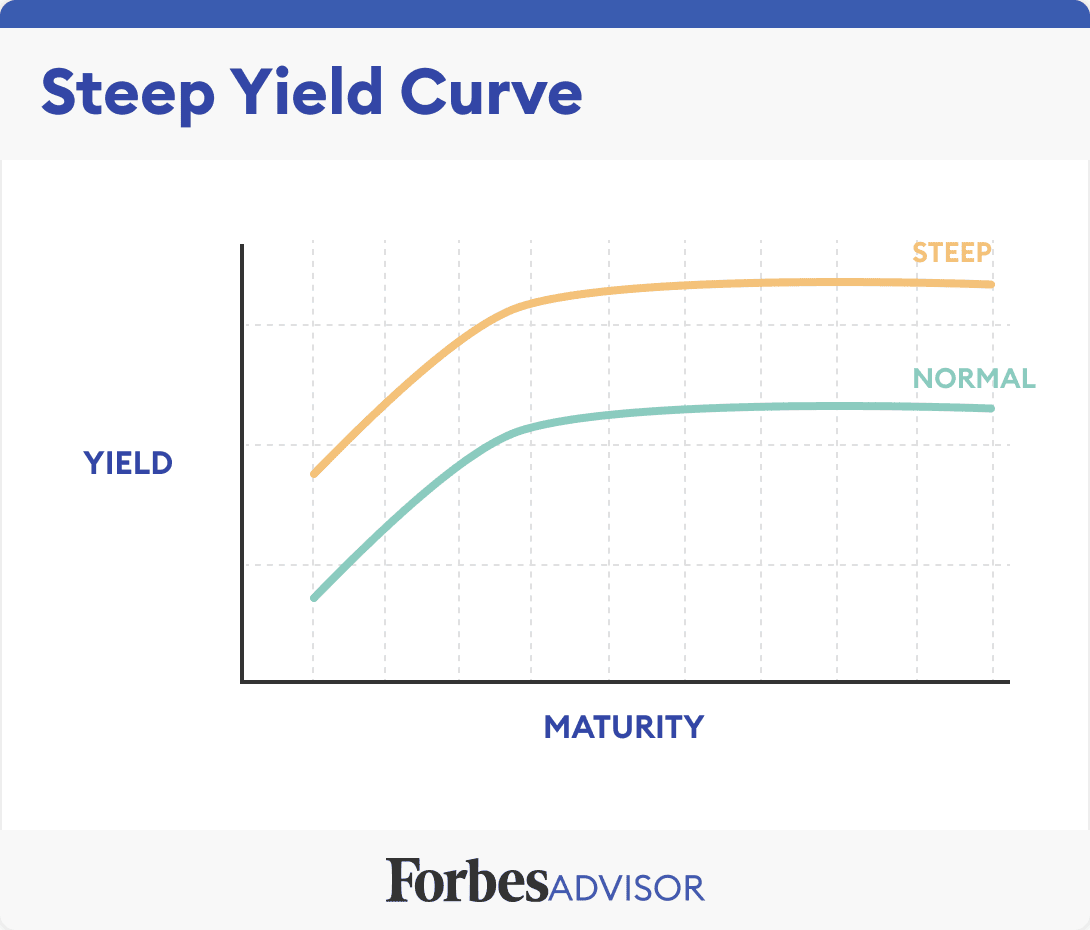
Table of Contents
Understanding the Steepening Yield Curve in Japan's Bond Market
The yield curve illustrates the relationship between the interest rates (yields) and the time to maturity of debt instruments, specifically, in this case, Japanese Government Bonds (JGBs). A normal yield curve slopes upward, indicating that longer-term bonds offer higher yields to compensate investors for the increased risk associated with longer maturities. However, a steep yield curve indicates a significant difference between short-term and long-term interest rates. Currently, Japan's JGB yield curve is exhibiting a steepening trend, a situation that warrants close examination.
-
Definition of yield curve and its typical shape: The yield curve plots the yields of bonds with different maturities. A normal yield curve slopes upward, while an inverted yield curve slopes downward. A flat yield curve shows little difference between short-term and long-term yields.
-
Explanation of the current steepening trend in Japan's JGB yield curve: Recent months have witnessed a notable widening of the spread between short-term and long-term JGB yields. This signifies that investors are demanding significantly higher returns for holding longer-term Japanese government debt.
-
Visual aid (chart or graph) showing the yield curve's evolution: [Insert a chart or graph here visually depicting the steepening yield curve for JGBs over a defined period, clearly labeling axes and providing a legend.]
-
Comparison to historical yield curve data for context: Comparing the current steepness to historical data reveals the magnitude of the current situation. This context helps assess whether the current steepness is unusual and potentially indicative of significant economic shifts.
Causes of the Steepening Yield Curve
Several factors contribute to the steepening yield curve in Japan's bond market. The Bank of Japan's (BOJ) monetary policy adjustments play a central role. Specifically, the gradual unwinding of its yield curve control (YCC) policy has allowed long-term interest rates to rise more freely.
-
BOJ's shift away from ultra-loose monetary policy: The BOJ's previous policy of keeping short-term interest rates near zero and controlling the yield on 10-year JGBs is being modified. This shift reflects a response to rising inflationary pressures.
-
Impact of rising inflation expectations on long-term bond yields: Increased inflation expectations lead investors to demand higher yields on long-term bonds to compensate for the erosion of purchasing power. This pushes up long-term JGB yields.
-
Influence of global interest rate hikes on Japanese bond yields: Global central banks, including the Federal Reserve, have been raising interest rates to combat inflation. This upward movement in global interest rates puts upward pressure on Japanese bond yields as well.
-
Role of market speculation and investor sentiment: Investor sentiment and speculation also play a role in influencing bond yields. Concerns about Japan's future economic outlook and potential risks can impact investor demand for JGBs.
Economic Challenges Posed by the Steep Yield Curve
The steepening yield curve presents several economic challenges for Japan. Higher borrowing costs for the government and businesses will impact investment and economic growth.
-
Higher borrowing costs for the Japanese government: A steep yield curve increases the cost of borrowing for the Japanese government, which has a substantial level of public debt. This necessitates higher government spending on interest payments, potentially crowding out other essential expenditures.
-
Increased financing costs for Japanese corporations: Higher interest rates increase borrowing costs for Japanese businesses, potentially dampening investment and economic expansion. This could lead to reduced corporate spending and job creation.
-
Potential slowdown in business investment and expansion: Increased borrowing costs can discourage businesses from investing in new projects and expansion plans, leading to slower economic growth.
-
Impact on consumer spending due to higher interest rates on loans: Higher interest rates on mortgages and other consumer loans can reduce consumer spending, further dampening economic activity.
-
Risks of financial instability due to rising bond yields: Rapid increases in bond yields can create volatility in the financial markets and potentially lead to financial instability.
Potential Solutions and Outlook for Japan's Bond Market
Addressing the challenges posed by the steepening yield curve requires a multifaceted approach involving both monetary and fiscal policies.
-
Potential for further adjustments to the BOJ's monetary policy: The BOJ may need to further adjust its monetary policy to manage the steepening yield curve, potentially through gradual adjustments to its bond-buying program.
-
Government fiscal policies to support economic growth: Fiscal policies aimed at stimulating economic growth can help offset the negative impacts of higher borrowing costs. This could include targeted infrastructure spending or tax cuts to boost consumption.
-
The role of market intervention to stabilize bond yields: The BOJ might intervene in the bond market to stabilize yields, although such interventions carry their own risks and limitations.
-
Long-term strategies for sustainable economic growth in Japan: Addressing Japan's long-term demographic challenges and fostering structural economic reforms are essential for sustainable growth and reducing reliance on debt financing.
Conclusion
The steepening yield curve in Japan's bond market presents a significant challenge, driven by the BOJ's policy adjustments, rising inflation expectations, and global interest rate movements. This leads to higher borrowing costs for the government and businesses, potentially slowing economic growth and impacting consumer spending. Potential solutions include further adjustments to the BOJ's monetary policy, supportive fiscal measures, and strategic market interventions. However, long-term sustainable economic growth necessitates addressing structural economic challenges and fostering reforms. Understanding the dynamics of Japan's bond market and the implications of the steep yield curve is crucial for investors and policymakers alike. Stay informed about developments in Japan's bond market to make informed decisions and navigate the evolving economic landscape. Further research into Japan's bond market and the impact of the steep yield curve is encouraged.

Featured Posts
-
 This Weeks Setbacks A Retrospective Analysis
May 17, 2025
This Weeks Setbacks A Retrospective Analysis
May 17, 2025 -
 Kevin Durants Pre Game Remark Reignites Speculation About Angel Reese Relationship
May 17, 2025
Kevin Durants Pre Game Remark Reignites Speculation About Angel Reese Relationship
May 17, 2025 -
 Nba Rungtynes Retas Teisejo Klaidos Pripazinimas Ir Jo Pasekmes
May 17, 2025
Nba Rungtynes Retas Teisejo Klaidos Pripazinimas Ir Jo Pasekmes
May 17, 2025 -
 Pistons Knicks Teisejo Klaida Pakeite Rungtyniu Baigtis
May 17, 2025
Pistons Knicks Teisejo Klaida Pakeite Rungtyniu Baigtis
May 17, 2025 -
 Pregnant Cassie Ventura And Husband Alex Fine Make Public Appearance At Mob Land Premiere
May 17, 2025
Pregnant Cassie Ventura And Husband Alex Fine Make Public Appearance At Mob Land Premiere
May 17, 2025
