Long COVID Risk Reduction: The Role Of COVID-19 Vaccines
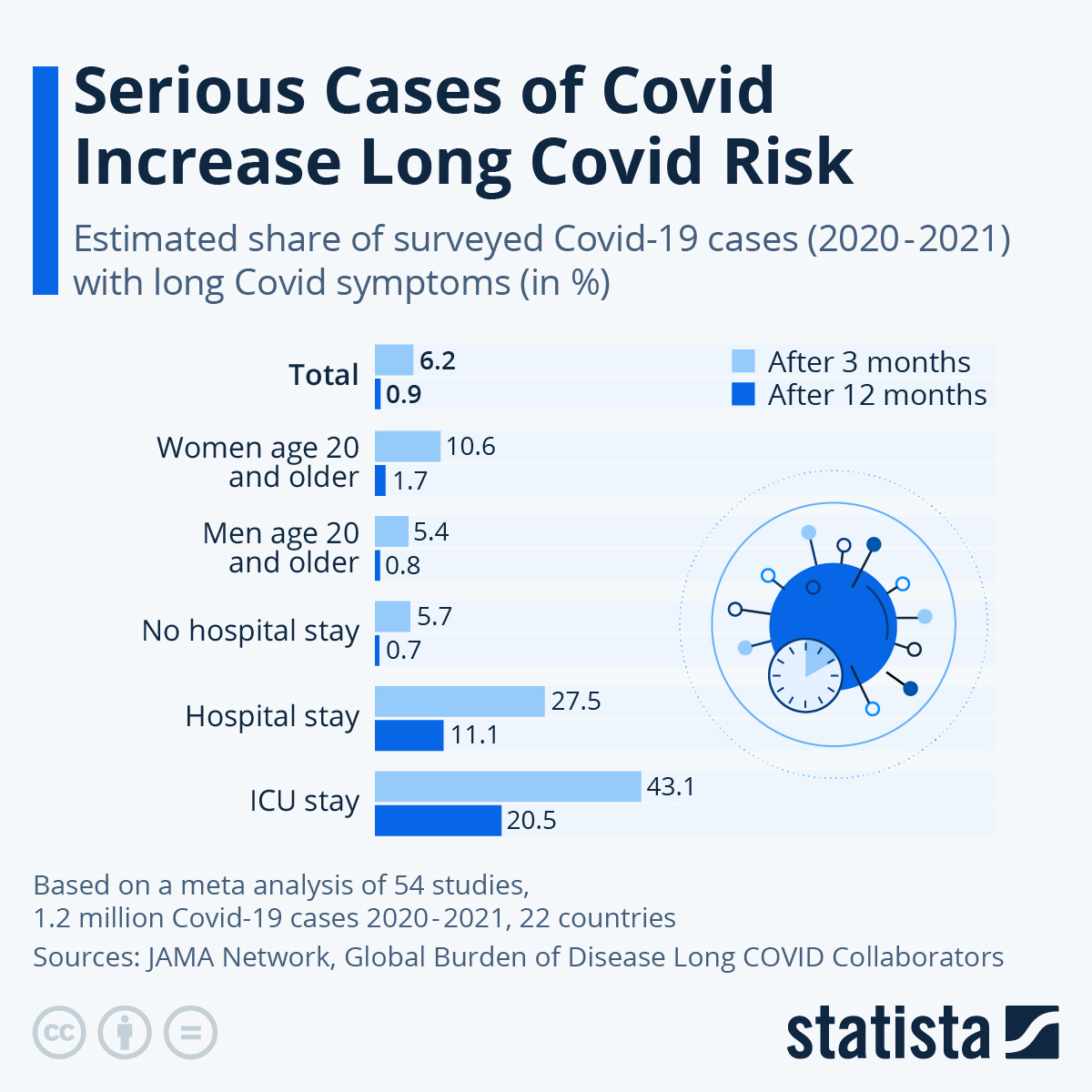
Table of Contents
COVID-19 Vaccines and Reduced Risk of Initial Infection
H3: Lowering Viral Load: COVID-19 vaccines significantly reduce the severity and duration of COVID-19 infection. By weakening the virus's ability to replicate, vaccines lower the viral load—the amount of virus present in the body. A lower viral load translates to less inflammation and a faster recovery time, minimizing the chances of long-term complications associated with Long COVID.
- Reduced viral shedding: Vaccinated individuals shed less virus, reducing transmission and overall viral exposure.
- Less inflammation: Vaccines help to mitigate the inflammatory response triggered by the virus, a key factor in the development of Long COVID.
- Faster recovery times: Studies show vaccinated individuals recover from acute COVID-19 infection more quickly than unvaccinated individuals.
H3: Preventing Severe Illness: The link between severe COVID-19 and Long COVID is undeniable. Preventing severe illness is paramount in reducing the risk of developing Long COVID. Vaccines dramatically reduce the likelihood of hospitalization, ICU admission, and death, all of which are strongly associated with an increased risk of persistent symptoms.
- Reduced hospitalization rates: Data consistently shows a substantial decrease in hospitalization rates among vaccinated individuals compared to unvaccinated individuals.
- Decreased ICU admissions: Vaccines significantly reduce the need for intensive care, a critical factor in minimizing long-term health consequences.
- Lower mortality rate: Vaccines save lives and, by doing so, prevent the development of Long COVID in those who would have otherwise succumbed to severe disease. (Cite relevant studies here, e.g., CDC data on vaccine effectiveness).
The Impact of Vaccines on Long COVID Symptoms
H3: Reduced Prevalence of Specific Symptoms: While vaccines don't provide 100% protection against Long COVID, studies suggest that vaccinated individuals who do develop the condition tend to experience milder symptoms and a shorter duration of illness.
- Less fatigue: Vaccinated individuals with Long COVID often report less debilitating fatigue compared to their unvaccinated counterparts.
- Reduced brain fog: Cognitive impairments, commonly known as "brain fog," are less severe in vaccinated individuals experiencing Long COVID.
- Fewer respiratory issues: Persistent respiratory problems, such as shortness of breath, are less prevalent and less severe among vaccinated individuals with Long COVID. (Cite relevant research studies here).
H3: Faster Recovery Rates: Vaccination contributes to a faster and more complete recovery from acute COVID-19 infection. This shortened illness duration minimizes the window of opportunity for long-term complications to take root.
- Improved immune response: Vaccines stimulate a robust and targeted immune response, enabling the body to clear the virus more efficiently.
- Quicker clearance of the virus: A faster viral clearance reduces the duration of inflammation and tissue damage, thus lowering the risk of Long COVID.
- Reduced inflammation: The moderated inflammatory response in vaccinated individuals contributes to faster healing and a lower likelihood of persistent symptoms. (Cite relevant studies supporting these claims).
Types of COVID-19 Vaccines and Their Effectiveness
H3: mRNA Vaccines: mRNA vaccines (Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna) have demonstrated high efficacy in preventing COVID-19 infection and severe disease, thus indirectly reducing the risk of Long COVID. Their high effectiveness in triggering a strong immune response makes them a powerful tool in Long COVID prevention. (Include specific data on their effectiveness from reputable sources, such as clinical trial results).
- High efficacy in preventing infection and severe disease: Data shows a significantly lower incidence of severe COVID-19 among those vaccinated with mRNA vaccines.
H3: Other Vaccine Types: Other vaccine types, such as viral vector vaccines (e.g., Johnson & Johnson/Janssen), also contribute to reducing the risk of Long COVID, primarily by preventing severe disease. While their efficacy might differ slightly from mRNA vaccines, they still offer substantial protection. (Include data on their effectiveness and any relevant comparisons to mRNA vaccines).
- Effectiveness in reducing severe disease: Although the effectiveness might vary slightly between different vaccine types, all authorized vaccines significantly reduce the risk of severe illness, hospitalization, and death.
Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy and Misinformation
H3: Debunking Myths: Addressing vaccine hesitancy is crucial. Many misconceptions exist regarding COVID-19 vaccines and their relationship to Long COVID. It's important to debunk these myths with factual information from reliable sources.
- Vaccines do not cause Long COVID: This is a critical point to emphasize. Long COVID is a consequence of the viral infection itself, not the vaccine.
- Vaccines significantly reduce the risk of Long COVID: The evidence overwhelmingly supports the protective role of vaccines against Long COVID. (Provide links to credible sources like the CDC and WHO).
H3: Promoting Vaccine Uptake: Encouraging vaccination is paramount in minimizing the devastating impact of Long COVID on individuals and communities. Providing access to reliable information and addressing concerns are key steps in promoting vaccine uptake.
- Access to reliable information: Ensure individuals have access to clear, concise, and accurate information about COVID-19 vaccines and their benefits.
- Addressing concerns and questions: Openly address concerns and answer questions from individuals who are hesitant to get vaccinated.
Conclusion
COVID-19 vaccines significantly reduce the risk of developing Long COVID by minimizing the severity of initial infection, reducing viral load, and lessening the likelihood of severe illness. Vaccination is a crucial preventative measure, offering substantial protection against this debilitating condition. Protect yourself from Long COVID – get vaccinated today! For more information on COVID-19 vaccines and how to get vaccinated, visit [link to relevant resource, e.g., CDC website].

Featured Posts
-
 Who Are Taylor Deardens Mom And Dad
May 29, 2025
Who Are Taylor Deardens Mom And Dad
May 29, 2025 -
 Nasjonaldagen 17 Mai I Moss Opplev En Spesiell Feiring
May 29, 2025
Nasjonaldagen 17 Mai I Moss Opplev En Spesiell Feiring
May 29, 2025 -
 The Pressure Intensifies Will Live Nation Fracture
May 29, 2025
The Pressure Intensifies Will Live Nation Fracture
May 29, 2025 -
 Bayerns Concrete Talks With Barcelona Target Jonathan Tah
May 29, 2025
Bayerns Concrete Talks With Barcelona Target Jonathan Tah
May 29, 2025 -
 The Art Of Disconnection Lessons From Wellness Entrepreneur Ella Mills
May 29, 2025
The Art Of Disconnection Lessons From Wellness Entrepreneur Ella Mills
May 29, 2025
