LP.8.1 COVID-19 Variant: Current Status And Future Implications
Table of Contents
Current Status of XBB.1.16 Variant
Geographic Distribution and Prevalence
XBB.1.16's geographical spread has been remarkably swift. Initially detected in [Insert Location and Date of Initial Detection, citing source], it rapidly gained prevalence globally. Prevalence rates varied significantly across regions, with some experiencing substantial increases in case numbers attributed to this variant. Tracking its epidemiology requires robust surveillance systems, and ongoing data collection is crucial for understanding its spread.
- Notable Prevalence: High case numbers were initially reported in [List specific countries/regions with high prevalence, citing reliable sources like the WHO or CDC].
- Data Sources: The World Health Organization (WHO), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and national public health agencies are key sources for epidemiological data on XBB.1.16's spread.
Genetic Characteristics and Mutations
XBB.1.16 possesses a unique combination of mutations, primarily within the spike protein, which is responsible for viral entry into human cells. These mutations are of particular interest because they may influence the variant's transmissibility, immune evasion capabilities, and overall fitness. Genetic sequencing efforts are essential to track these mutations and understand their evolutionary trajectory.
- Key Mutations: The variant harbors mutations [List specific mutations and their locations on the spike protein, citing scientific publications]. These mutations are known/suspected to [Explain the potential impact of each mutation, e.g., increased binding to receptors, immune escape].
- Comparison to other variants: Compared to previous Omicron subvariants, XBB.1.16 demonstrates [Compare its characteristics, e.g., higher transmissibility, similar or different severity].
Severity and Clinical Outcomes
While XBB.1.16 exhibits higher transmissibility, data on its severity and clinical outcomes are still evolving. Initial reports suggest that the hospitalization and mortality rates associated with XBB.1.16 are [State the observed rates, comparing to previous variants, and citing sources]. However, more research is needed to fully understand the clinical presentation and long-term effects of this variant.
- Hospitalization and ICU Admissions: [Insert data on hospitalization and ICU admission rates if available, with appropriate caveats and limitations].
- Mortality Rates: [Insert data on mortality rates if available, emphasizing data limitations and ongoing research].
Potential Future Implications of XBB.1.16 Variant
Impact on Vaccine Efficacy
The mutations in XBB.1.16 raise concerns about its potential to partially evade immunity conferred by vaccines or previous infection. Studies are ongoing to evaluate the effectiveness of existing COVID-19 vaccines against this variant, particularly in terms of preventing severe disease and hospitalization. Booster shots targeting newer variants may enhance protection.
- Vaccine Effectiveness Studies: [Summarize results from studies assessing vaccine effectiveness against XBB.1.16, citing relevant publications].
- Booster Shot Recommendations: [Discuss the recommendations for booster shots, including the types of vaccines and timing].
Public Health Preparedness and Response
Robust public health measures remain crucial to managing the spread of XBB.1.16. This includes enhanced surveillance systems for variant tracking, maintaining adequate testing capacity, and continuing contact tracing efforts where feasible. International collaboration is essential for coordinating global responses and sharing data.
- Surveillance and Testing: Continued genomic surveillance and increased testing capacity are critical for early detection and monitoring of XBB.1.16's spread.
- Public Health Interventions: Strategies like improved ventilation, mask-wearing, and social distancing might be needed depending on local epidemiological situations.
Long-Term Impact and Research Needs
Understanding the long-term impact of XBB.1.16, including the potential for long COVID and other sequelae, remains a research priority. Further research is needed to predict the trajectory of viral evolution and the potential emergence of future variants. Increased funding and international collaboration are crucial for achieving these goals.
- Long COVID Research: Studies are needed to determine the frequency and severity of long COVID associated with XBB.1.16 infection.
- Variant Prediction: Investing in research on viral evolution and variant prediction is crucial for proactively addressing future threats.
Conclusion: Staying Informed about the XBB.1.16 COVID-19 Variant
The XBB.1.16 variant underscores the ongoing need for vigilance and preparedness in the face of evolving COVID-19. Its rapid spread highlights the importance of continuous monitoring, robust public health measures, and sustained research efforts. While current vaccines offer some protection, staying updated on the latest information is paramount. We must remain informed about new developments concerning the XBB.1.16 COVID-19 variant and other emerging variants through reputable sources such as the WHO and CDC. Staying informed about COVID-19 updates, including variant tracking and public health recommendations, is crucial for protecting your health and contributing to community safety.

Featured Posts
-
 L Usine Sanofi De Mourenx Depakine Et Les Consequences Des Rejets Toxiques
May 31, 2025
L Usine Sanofi De Mourenx Depakine Et Les Consequences Des Rejets Toxiques
May 31, 2025 -
 April 29th Twins Guardians Game Progressive Field Weather And Potential Delays
May 31, 2025
April 29th Twins Guardians Game Progressive Field Weather And Potential Delays
May 31, 2025 -
 Podrobnosti Za Kontuziyata Na Grigor Dimitrov
May 31, 2025
Podrobnosti Za Kontuziyata Na Grigor Dimitrov
May 31, 2025 -
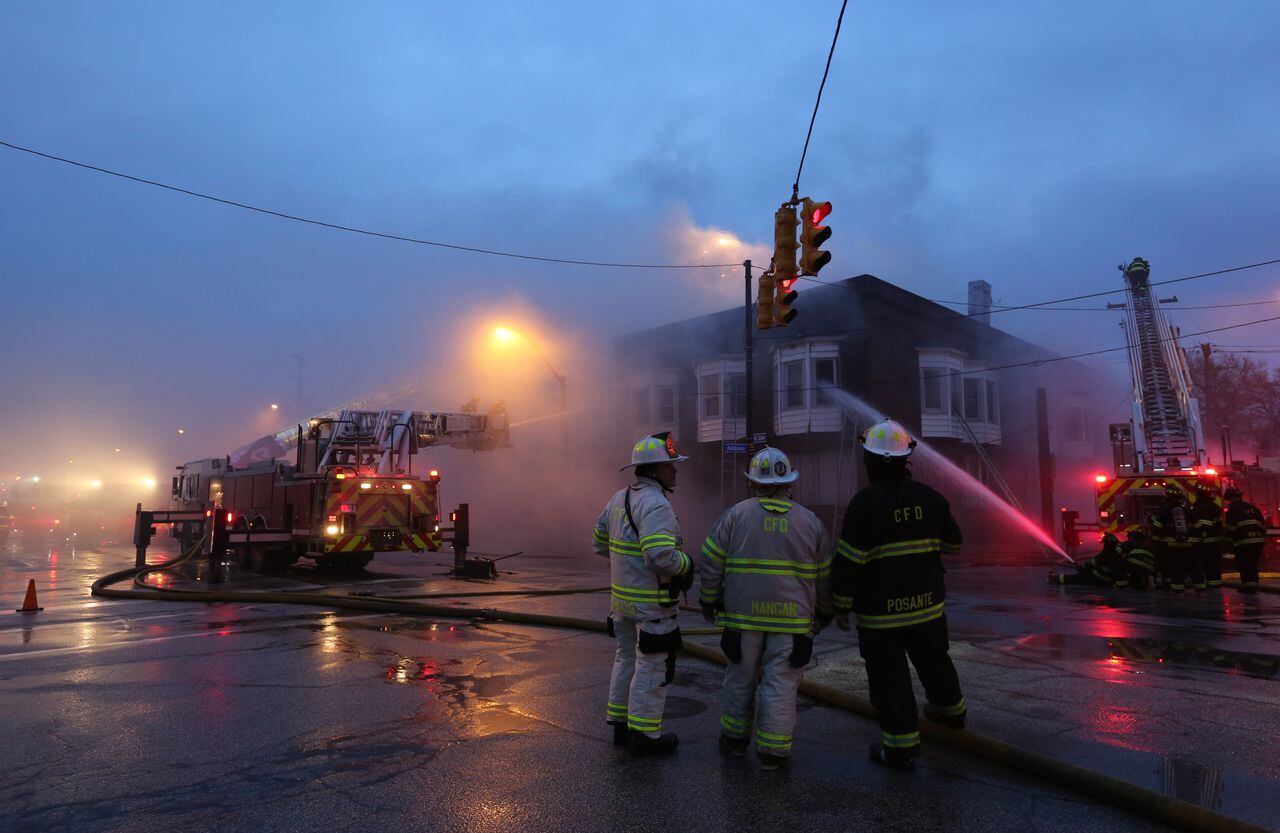 East London Shop Blaze 125 Firefighters Battle Large Fire
May 31, 2025
East London Shop Blaze 125 Firefighters Battle Large Fire
May 31, 2025 -
 Orange County High School Sports Friday May 23rd Game Results And Player Statistics
May 31, 2025
Orange County High School Sports Friday May 23rd Game Results And Player Statistics
May 31, 2025
