Massive Wildfires Force Largest Evacuation In Canadian History, Sending Smoke South
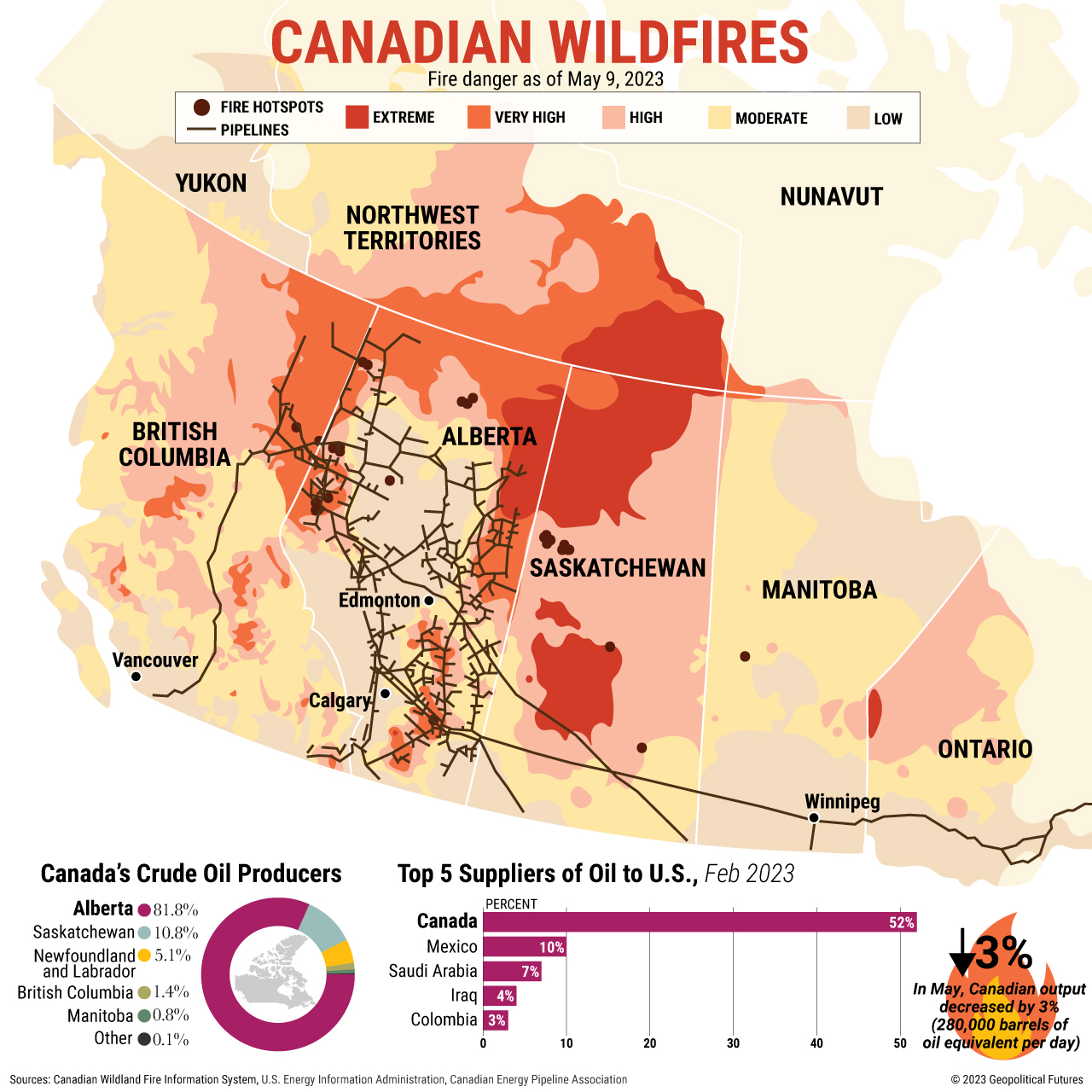
Table of Contents
Unprecedented Scale of Wildfires and Evacuations
The current wildfire season in Canada is unlike anything seen before. Hundreds of wildfires are burning across vast swathes of the country, creating a scene of unprecedented wildfire devastation. Provinces and territories including British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Ontario, and Quebec are particularly hard-hit, with the situation evolving rapidly. The sheer acreage consumed by flames and the number of people forced to evacuate their homes are staggering, representing the largest evacuation in Canadian history. This mass displacement highlights the urgent need for effective emergency response and support systems.
- Number of hectares burned: As of [Insert most recent data - cite source], over [Insert number] hectares have burned. (Source: [Insert reputable source])
- Number of people evacuated: More than [Insert number] people have been forced to evacuate their homes. (Source: [Insert reputable source])
- Most affected provinces and territories: British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Ontario, and Quebec are among the areas experiencing the most significant impact.
- Key towns and cities impacted: [List impacted towns and cities]
- Types of wildfires: The fires range from typical forest fires to devastating peat fires, which burn underground and are notoriously difficult to extinguish.
The Southward Spread of Smoke and its Impact
The dense smoke from these Canadian wildfires isn't confined to Canada. Strong winds have carried the smoke plume southward, significantly degrading air quality across numerous states in the United States and impacting visibility. This transboundary pollution poses significant health hazards, primarily affecting respiratory and cardiovascular systems. The economic consequences are also substantial, impacting tourism, causing business closures, and leading to increased healthcare costs.
- States and regions affected by smoke: [List affected states and regions]. Air quality alerts have been issued across wide swathes of the US.
- Specific health concerns related to smoke inhalation: Wildfire smoke contains harmful pollutants that can trigger asthma attacks, bronchitis, and other respiratory illnesses. It can also exacerbate cardiovascular problems.
- Economic consequences of the smoke: Reduced visibility has led to flight cancellations and travel disruptions. Businesses have been forced to close due to poor air quality.
- Air quality index (AQI) data in affected areas: [Include AQI data for affected regions – cite sources].
Causes and Contributing Factors
The severity of these wildfires is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors. Climate change plays a significant role, with prolonged periods of drought and increasingly high temperatures creating tinderbox conditions. These extreme weather patterns, fueled by global warming, contribute to longer fire seasons and more intense wildfire activity. Human activity, such as unattended campfires and lightning strikes, also plays a part in wildfire ignitions.
- Statistics on average temperatures and rainfall: [Include data on temperature and rainfall anomalies – cite sources].
- Data on the number of fires caused by human activity vs. natural causes: [Provide statistics, if available, citing sources].
- Explanation of the impact of climate change on wildfire intensity and frequency: Climate change is leading to longer, hotter, and drier summers, increasing the risk and intensity of wildfires.
Government Response and International Aid
The Canadian government has mobilized significant resources to combat the fires and support evacuees. Emergency services are working tirelessly to contain the blazes, and efforts are underway to provide shelter, food, and other essential supplies to those displaced. International cooperation is crucial, with several countries offering assistance in the form of personnel, equipment, and financial aid.
- Resources deployed by the government: [Detail the resources – personnel, aircraft, equipment].
- Types of aid received from other countries: [List countries providing aid and the type of support offered].
- Details on evacuation efforts and support for evacuees: [Explain the process and support given to evacuees].
Conclusion
The massive Canadian wildfires represent a devastating environmental and humanitarian crisis. The sheer scale of the evacuations, coupled with the far-reaching impact of the smoke, underscores the urgency of addressing climate change and improving disaster preparedness. The role of climate change in exacerbating these events cannot be ignored. We must learn from this crisis and implement effective strategies to mitigate the effects of climate change and prevent future massive wildfires. Stay informed about wildfire updates, support relief efforts for those affected, and consider how you can contribute to mitigating the effects of climate change. Working together, we can strive to build a more resilient future and reduce the devastating consequences of extreme weather events.

Featured Posts
-
 Posthaste Deciphering The New Tariff Ruling And Its Consequences For Canada
May 31, 2025
Posthaste Deciphering The New Tariff Ruling And Its Consequences For Canada
May 31, 2025 -
 Neue Buerger Gesucht Deutsche Stadt Bietet Kostenlose Unterbringung
May 31, 2025
Neue Buerger Gesucht Deutsche Stadt Bietet Kostenlose Unterbringung
May 31, 2025 -
 The History And Folklore Of Rosemary And Thyme
May 31, 2025
The History And Folklore Of Rosemary And Thyme
May 31, 2025 -
 Dragons Den Success Story 40 Profit Increase
May 31, 2025
Dragons Den Success Story 40 Profit Increase
May 31, 2025 -
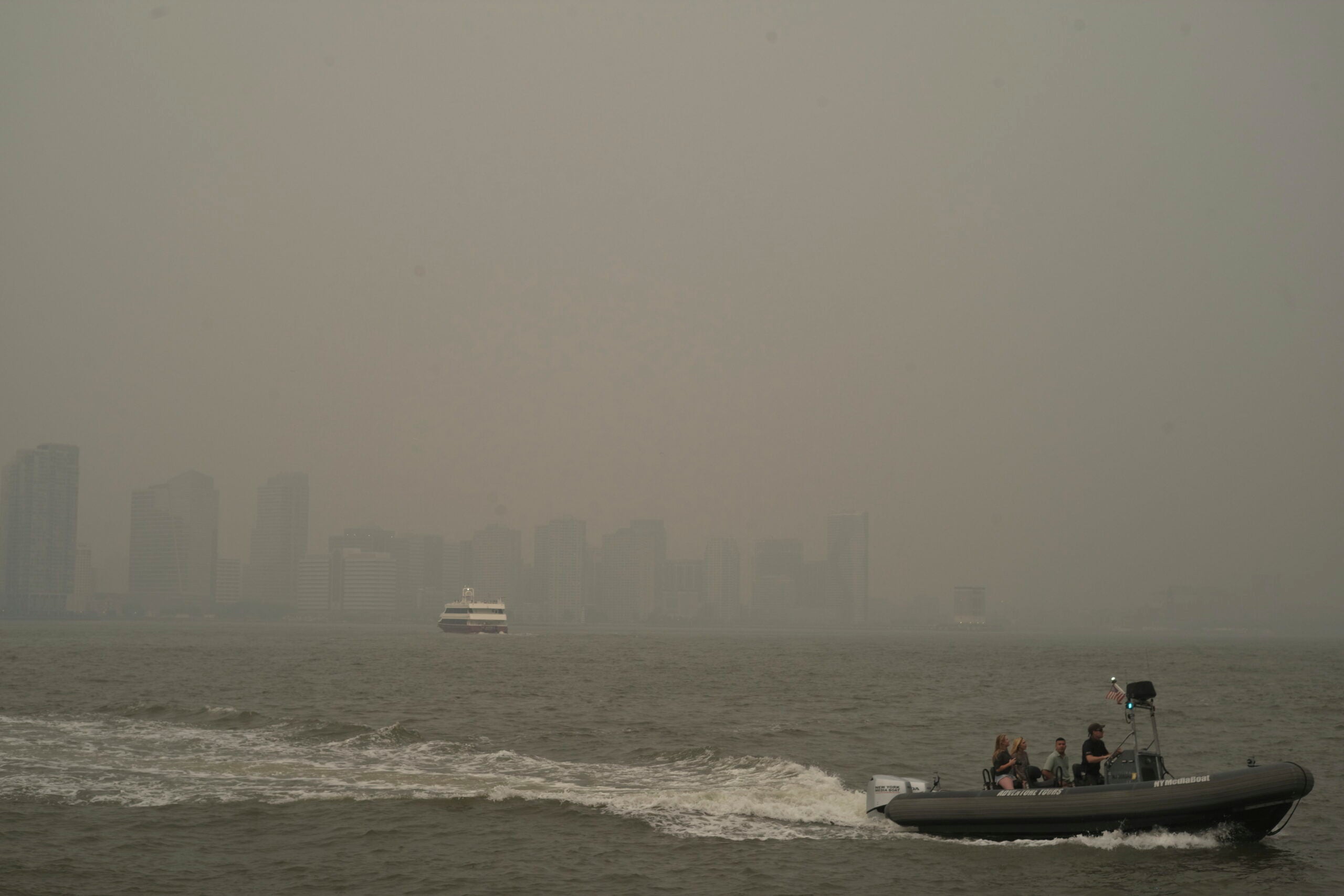 Canadian Wildfires New York Citys 3 C Temperature Drop And Elevated Air Toxicants
May 31, 2025
Canadian Wildfires New York Citys 3 C Temperature Drop And Elevated Air Toxicants
May 31, 2025
