Months-Long Presence Of Toxic Chemicals In Buildings After Ohio Derailment
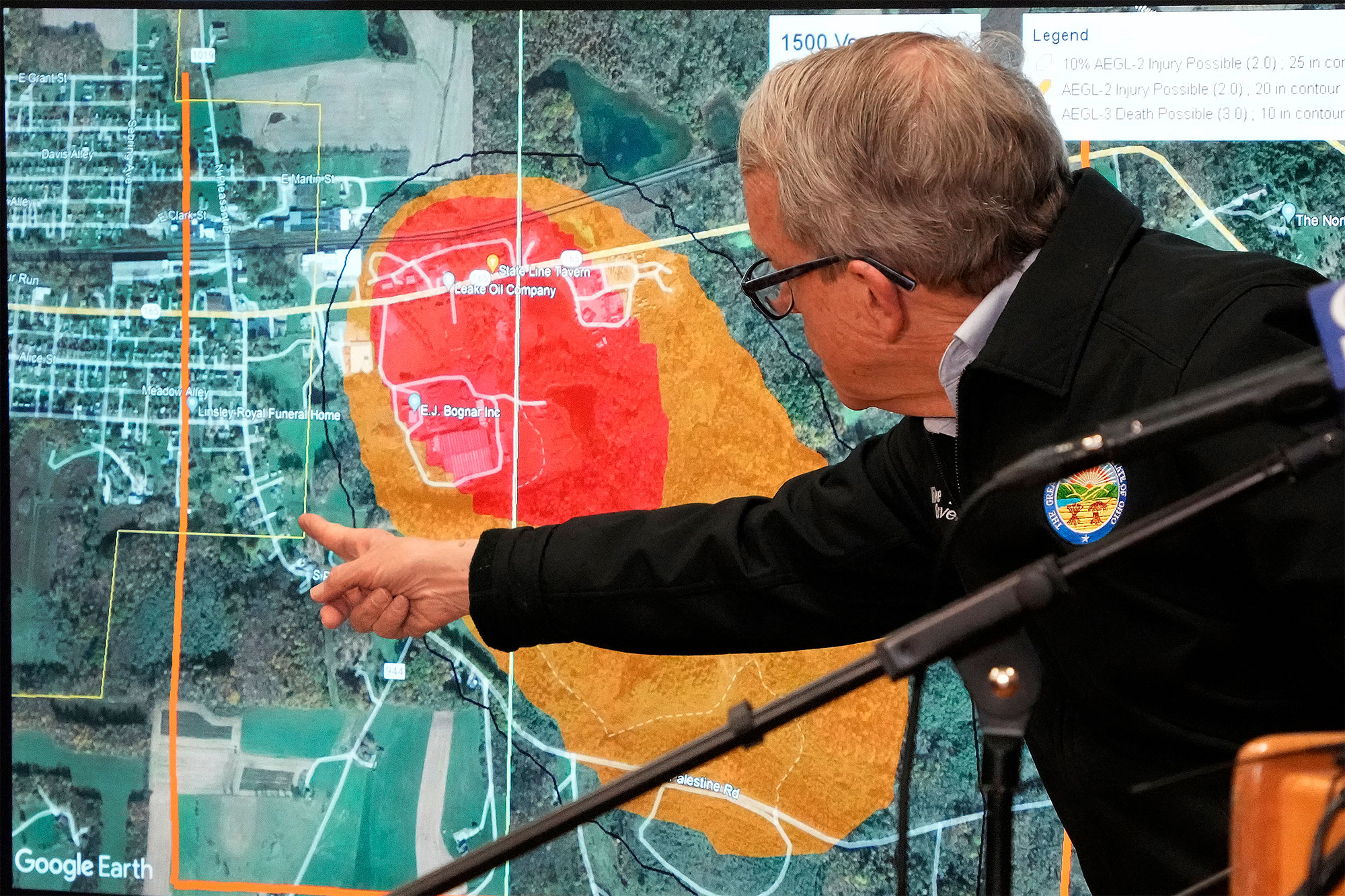
Table of Contents
Types of Toxic Chemicals and Their Persistence
The derailment released a cocktail of hazardous chemicals, many of which are known for their persistence in the environment and potential for long-term health effects. Understanding the properties of these chemicals is crucial for assessing the risk and developing effective remediation strategies.
Vinyl Chloride and its Long-Term Effects
Vinyl chloride, a known carcinogen, is a significant concern following the derailment. Its volatility allows it to spread easily, but its ability to adhere to porous materials, like fabrics and drywall, means it can persist in buildings for extended periods. Long-term exposure to vinyl chloride is linked to a range of serious health problems, including:
- Increased risk of liver cancer: Vinyl chloride is a class 1 carcinogen, meaning it is directly linked to causing cancer.
- Liver damage: Exposure can lead to various forms of liver disease, including cirrhosis.
- Angiosarcoma: A rare and aggressive form of cancer that affects the blood vessels.
Vinyl chloride's persistence is further complicated by:
- Slow degradation rates: It doesn't break down quickly in the environment, potentially remaining in buildings for months or even years.
- Accumulation in specific areas: Its volatility can lead to high concentrations in poorly ventilated spaces, increasing exposure risks.
- Difficulty of complete removal: Complete elimination from porous materials often requires extensive remediation efforts, including potentially demolition and replacement.
Other Persistent Chemicals
Beyond vinyl chloride, other chemicals released during the derailment pose long-term contamination risks. These include:
- Butyl acrylate: An irritant that can cause respiratory problems and skin irritation, and may have long-term health consequences with chronic exposure.
- Ethylene glycol monobutyl ether: A solvent with potential reproductive and developmental toxicity.
- Ethylhexyl acrylate: Another irritant with potential respiratory and skin effects.
Studies are ongoing to fully understand the long-term environmental impact of these chemicals and their synergistic effects when combined. The potential for these chemicals to leach into groundwater and soil also presents a significant concern for long-term environmental health.
Testing and Monitoring of Building Contamination
Accurate assessment of toxic chemical contamination in buildings is crucial for effective remediation and public health protection. However, challenges exist regarding testing methods and data transparency.
Methods Used for Detection and Quantification
Several methods are employed to detect and quantify the levels of toxic chemicals in affected buildings:
- Air sampling: Measures airborne concentrations of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including vinyl chloride.
- Surface wipe sampling: Detects the presence of chemicals on surfaces, providing information on contamination levels.
- Material analysis: Involves laboratory testing of building materials to determine the extent of chemical penetration.
These methods have limitations:
- Sensitivity variations: Different methods have varying sensitivities, leading to potential underestimation of contamination levels.
- Cost and time constraints: Comprehensive testing can be expensive and time-consuming, limiting the scope of investigations.
- Challenges in accessing all areas: Testing might not reach every area of a building, leading to incomplete assessments.
Inconsistencies in Testing and Data Transparency
Concerns have been raised regarding inconsistencies in testing protocols and a lack of transparency in data release:
- Discrepancies in reported data: Variations in reported contamination levels raise questions about the reliability of testing and data reporting.
- Calls for independent testing: Advocacy groups and residents are calling for independent verification of test results to ensure accuracy.
- Need for greater government accountability: Transparency in data release and testing methodologies is critical for public trust and effective remediation.
The lack of consistent and transparent data hinders accurate risk assessment and complicates remediation efforts.
Health Impacts and Remediation Efforts
The long-term health implications of the Ohio derailment and the effectiveness of remediation strategies are critical aspects of the ongoing crisis.
Reported Health Problems in Affected Communities
Residents near the derailment site have reported various health issues potentially linked to exposure to toxic chemicals:
- Respiratory problems: Coughing, shortness of breath, and wheezing.
- Headaches and nausea: Symptoms commonly associated with chemical exposure.
- Skin irritation: Rashes, itching, and other dermatological problems.
Epidemiological studies are needed to establish a definitive link between these health complaints and the chemical exposure. Ongoing medical monitoring is essential to track the long-term health consequences.
Remediation Strategies and Challenges
Remediation efforts involve various strategies:
- Air filtration: Installing and maintaining high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters to remove airborne contaminants.
- Surface decontamination: Cleaning and sanitizing contaminated surfaces to remove chemical residues.
- Material removal/replacement: Removing and replacing severely contaminated building materials.
Challenges include:
- Cost effectiveness of different methods: Different remediation methods have varying costs and levels of effectiveness.
- Extent of contamination: Determining the precise extent of contamination is difficult, impacting the effectiveness of remediation strategies.
- Long-term monitoring plans: Long-term monitoring is crucial to ensure the safety of buildings and the health of residents.
Conclusion:
The lingering presence of toxic chemicals in buildings months after the Ohio train derailment highlights the severe and long-lasting consequences of such disasters. The inconsistent testing, lack of transparency, and reported health issues emphasize the urgency of thorough investigation, effective remediation, and long-term monitoring. Further research is crucial to fully understand the long-term health and environmental impacts of this contamination. Addressing the issue of toxic chemical contamination requires immediate action to protect affected communities and prevent similar tragedies in the future. Understanding the persistence of these chemicals, like vinyl chloride, is vital for developing effective remediation strategies and ensuring the safety of residents. We must continue to demand transparency and accountability from responsible parties to ensure comprehensive cleanup and support for those impacted by this devastating event. Continued vigilance and further investigation into the effects of Ohio Derailment toxic chemical contamination are crucial for long-term public health and environmental protection.

Featured Posts
-
 How To Write Effective Briefs A Step By Step Guide
May 23, 2025
How To Write Effective Briefs A Step By Step Guide
May 23, 2025 -
 Resultados Sorteo 23 Entradas Dobles Cb Gran Canaria Vs Unicaja
May 23, 2025
Resultados Sorteo 23 Entradas Dobles Cb Gran Canaria Vs Unicaja
May 23, 2025 -
 Rybakina Itogi Matcha Tretego Kruga V Rime
May 23, 2025
Rybakina Itogi Matcha Tretego Kruga V Rime
May 23, 2025 -
 Billie Jean King Cup Rybakina Propels Kazakhstan To Finals
May 23, 2025
Billie Jean King Cup Rybakina Propels Kazakhstan To Finals
May 23, 2025 -
 Dan Lawrences England Ambitions A Look At His Test Opening Prospects
May 23, 2025
Dan Lawrences England Ambitions A Look At His Test Opening Prospects
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Solve The Nyt Mini Crossword March 3 2025 Answers And Hints
May 23, 2025
Solve The Nyt Mini Crossword March 3 2025 Answers And Hints
May 23, 2025 -
 Complete Nyt Mini Crossword Answers March 13 Daily Puzzle Solved
May 23, 2025
Complete Nyt Mini Crossword Answers March 13 Daily Puzzle Solved
May 23, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword March 3 2025 Solutions And Clues
May 23, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword March 3 2025 Solutions And Clues
May 23, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword Puzzle Solution March 6 2025
May 23, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Puzzle Solution March 6 2025
May 23, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword March 6 2025 Complete Solution
May 23, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword March 6 2025 Complete Solution
May 23, 2025
