Rare Earth Minerals: A Critical Resource In The New Cold War
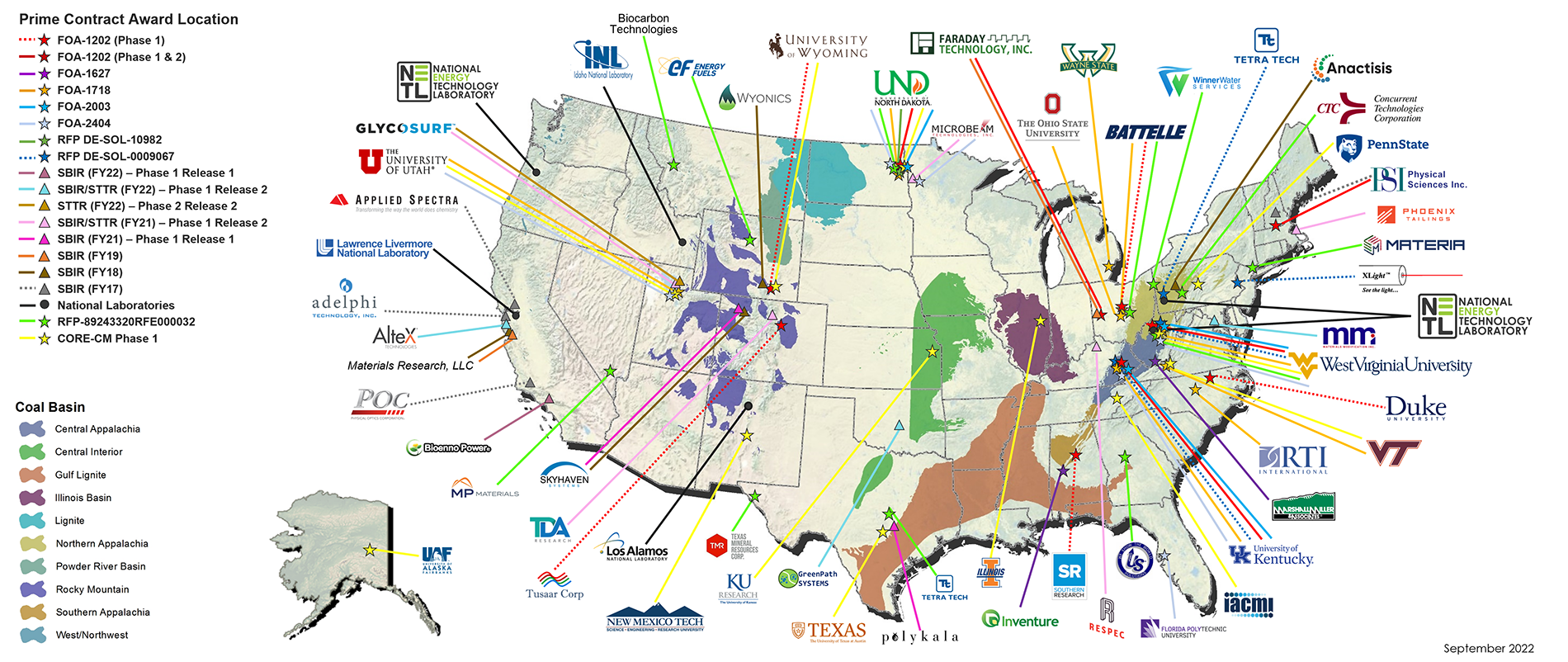
Table of Contents
The Strategic Importance of Rare Earth Minerals
Rare earth minerals, despite their name, are not particularly rare but are challenging to extract and process. Their unique magnetic, luminescent, and catalytic properties make them indispensable for a vast array of modern technologies.
Applications in Critical Technologies
Rare earth elements are critical components in countless high-tech applications:
- Permanent Magnets: Neodymium, dysprosium, and praseodymium are essential for powerful permanent magnets found in wind turbines, electric vehicles, and countless other devices. The global demand for these magnets is projected to increase exponentially in the coming decades, driven by the growth of renewable energy and electric vehicle sectors.
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, computers, and other consumer electronics rely heavily on rare earth elements for their functionality. For example, yttrium is a key component in many phosphors used in display screens.
- Military Equipment: Advanced weaponry, including guided missiles and radar systems, utilize rare earth minerals for their performance capabilities. This underscores the national security implications of their supply chains.
- Medical Devices: MRI machines and other medical imaging technologies rely on the unique properties of rare earth elements.
The market for rare earth minerals is booming. Industry reports project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 8% in the next decade, highlighting the increasing demand and the potential for market volatility.
Geopolitical Concentration of Rare Earth Production
The global production of rare earth minerals is heavily concentrated geographically, with China currently dominating the market, accounting for over 70% of global production. This dominance creates significant geopolitical implications:
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: Heavy reliance on a single source exposes global supply chains to potential disruptions from political instability, trade disputes, or environmental regulations in China.
- Economic Leverage: China's control over rare earth mineral processing creates significant economic leverage, influencing global markets and potentially affecting the development of key technologies in other nations.
- Diversification Efforts: Countries like Australia, the United States, and others are investing heavily in expanding their domestic rare earth production, but catching up to China's established infrastructure and expertise poses a significant challenge. (See map illustrating global rare earth production below). [Insert map here]
The New Cold War and the Rare Earth Minerals Race
The competition for rare earth minerals is becoming an increasingly significant aspect of the emerging new Cold War.
Economic Leverage and Trade Wars
Control over rare earth minerals provides significant economic leverage, allowing nations to influence global markets through:
- Export Restrictions: The threat of or imposition of export controls on rare earth minerals can severely disrupt global supply chains and exert pressure on importing nations.
- Trade Disputes: Disputes over access to rare earth minerals can escalate into broader trade conflicts, with significant economic consequences for all involved parties.
- Price Manipulation: Control over supply can lead to price manipulation, impacting the cost of numerous technologies and potentially hindering innovation.
Technological Advancement and National Security
Access to rare earth minerals is directly tied to technological advancement and national security:
- Military Applications: The development of advanced weaponry and defense systems relies heavily on the unique properties of rare earth elements. Control over the supply of these materials can provide a significant military advantage.
- Technological Supremacy: Nations with secure access to rare earth minerals are better positioned to develop and deploy cutting-edge technologies, impacting their economic competitiveness and global influence.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Reducing reliance on foreign sources for rare earth minerals is a critical national security objective for many countries. Initiatives to diversify supply chains and develop domestic production capabilities are gaining momentum.
Strategies for Diversification and Sustainable Sourcing
Securing a stable and sustainable supply of rare earth minerals requires a multi-pronged approach.
Investing in Domestic Mining and Processing
Reducing reliance on foreign sources necessitates significant investment in domestic mining and processing capabilities:
- Government Support: Government policies, including subsidies, tax incentives, and streamlined permitting processes, are crucial for encouraging domestic rare earth development.
- Technological Advancements: Innovation in mining and processing technologies is essential to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Environmental Considerations: Sustainable mining practices are critical to minimize environmental impacts and secure public support for domestic rare earth development.
Recycling and Urban Mining
Recycling and urban mining offer significant opportunities to secure rare earth materials while minimizing environmental impact:
- Technological Advancements: Advances in recycling technologies are improving the economic viability of recovering rare earth elements from discarded electronics and other products.
- Environmental Benefits: Recycling significantly reduces the need for primary mining, lessening the environmental footprint associated with rare earth extraction.
- Waste Management: Urban mining offers a sustainable approach to resource recovery and waste management.
International Cooperation and Supply Chain Resilience
International cooperation is essential for ensuring a stable and secure supply of rare earth minerals:
- Transparency and Traceability: Establishing transparent and traceable supply chains helps to promote responsible sourcing and mitigate risks of conflict minerals.
- International Agreements: Collaboration through international organizations can facilitate the development of responsible mining practices and ensure equitable access to these critical resources.
- Sustainable Sourcing Initiatives: Supporting initiatives that promote sustainable mining and processing practices is essential for long-term supply chain resilience.
Conclusion
Rare earth minerals are undeniably critical resources in the new Cold War. Their strategic importance stems from their indispensable role in numerous high-tech applications, creating significant economic and national security implications. The current geopolitical landscape, with its concentration of production in China, highlights the risks associated with reliance on a single source. Diversifying supply chains through domestic production, recycling, and international cooperation is crucial for ensuring a secure and sustainable future. Understanding the complexities surrounding rare earth minerals is crucial in navigating the new Cold War. Learn more about the strategic importance of rare earth minerals and advocate for responsible sourcing today!

Featured Posts
-
 Nba Prediction Knicks Vs Pistons A Detailed Analysis
May 17, 2025
Nba Prediction Knicks Vs Pistons A Detailed Analysis
May 17, 2025 -
 I Episkepsi Tramp Stin Saoydiki Aravia Mia Meleti Protokolloy Kai Dynamis
May 17, 2025
I Episkepsi Tramp Stin Saoydiki Aravia Mia Meleti Protokolloy Kai Dynamis
May 17, 2025 -
 Elaekeyhtioeiden Osakesijoitusten Tappiot Alkuvuonna 2024
May 17, 2025
Elaekeyhtioeiden Osakesijoitusten Tappiot Alkuvuonna 2024
May 17, 2025 -
 Mlb Betting Tigers Vs Mariners Predictions And Best Odds Today
May 17, 2025
Mlb Betting Tigers Vs Mariners Predictions And Best Odds Today
May 17, 2025 -
 Djokovics Domination Tekrar Kortlarin Krali
May 17, 2025
Djokovics Domination Tekrar Kortlarin Krali
May 17, 2025
