Russia's Economy Under Putin: A Focus On War
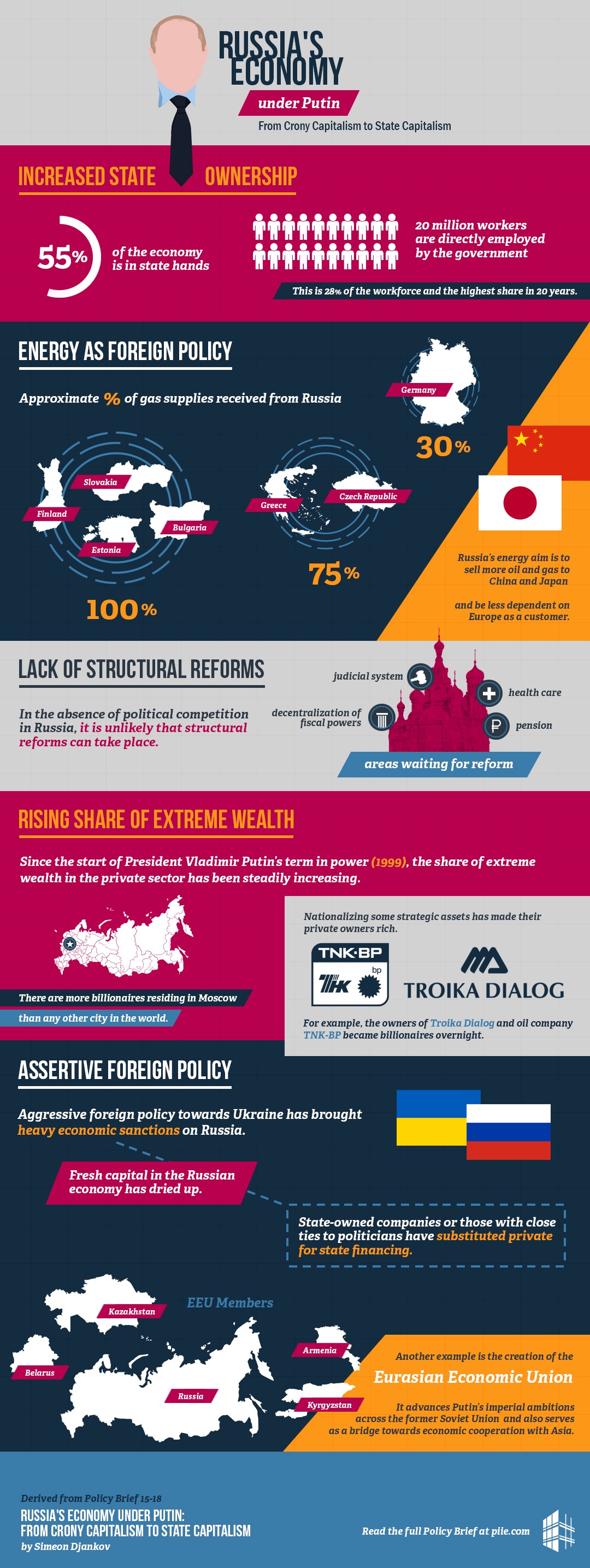
Table of Contents
Sanctions and Their Impact
The West's response to the invasion of Ukraine has been swift and comprehensive, encompassing a multi-layered sanctions regime designed to cripple the Russian economy. Understanding the impact of these sanctions on Russia's economy is crucial to grasping the current geopolitical landscape.
The West's Sanctions Regime
The sanctions imposed on Russia are unprecedented in their scope and severity. They target various sectors and individuals, aiming to disrupt the Russian economy and limit its ability to finance the war effort.
-
Financial Sanctions: These include freezing the assets of the Central Bank of Russia, restricting access to the SWIFT international payment system for certain banks, and imposing limitations on transactions with Russian entities. The total value of frozen assets is estimated in the hundreds of billions of dollars.
-
Technological Sanctions: Restrictions on the export of advanced technologies, including semiconductors and software, aim to hinder Russia's technological development and military capabilities. This includes restrictions on crucial components for various industries.
-
Trade Sanctions: Embargoes and tariffs on various goods, including energy, have been implemented to reduce Russia's export revenue and limit its access to essential imports.
-
Specific Examples: The exclusion of several major Russian banks from SWIFT significantly hampered their ability to conduct international transactions. Sanctions targeting specific oligarchs and their assets aimed to pressure the Kremlin and limit its access to funding. However, loopholes in sanctions regimes have been exploited in various ways, undermining their full impact.
Russia's Response to Sanctions
Faced with unprecedented sanctions, Russia has implemented various countermeasures. These strategies are aimed at mitigating the economic impact and maintaining economic stability.
- Import Substitution: Russia is attempting to reduce its dependence on foreign imports by boosting domestic production. This includes initiatives in agriculture, technology development, and the manufacturing sector. However, the success of these strategies is still largely uncertain, given the complexity and time required to replace established supply chains.
- Pivot to Asia: Russia is actively seeking to expand its economic ties with Asian countries, particularly China, to offset reduced trade with the West. This includes increased energy exports to China and investment deals in various sectors. The extent to which this pivot can truly compensate for lost Western trade remains to be seen.
- Circumventing Sanctions: Russia has employed various tactics to circumvent sanctions, including using shadow banking systems, relying on intermediaries, and exploiting vulnerabilities in international regulations. The effectiveness of these methods is continuously challenged by the ever-evolving sanctions landscape.
The Energy Sector's Shifting Landscape
Russia's economy is heavily reliant on its energy sector, and the war has dramatically altered its landscape.
Oil and Gas Revenue Fluctuations
The impact of sanctions and the war on Russia's oil and gas exports has been significant. Price volatility, coupled with sanctions limiting access to certain markets, has resulted in fluctuations in revenue.
- Export Destinations: Russia has redirected some of its energy exports to Asia, particularly China and India, to compensate for reduced sales to Europe. This shift has strategic implications for global energy markets.
- Financing the War: Revenue from energy exports plays a crucial role in financing Russia's war effort and supporting its economy amidst sanctions. Fluctuations in this revenue directly affect the capacity of the state to wage war and address domestic issues.
- Price Volatility: Charts illustrating the fluctuating prices of oil and gas are essential to demonstrate the impact on Russia's revenues. The interaction of supply, demand, sanctions, and global market forces creates a complex and dynamic scenario.
Investment in Renewable Energy Sources
Despite its reliance on fossil fuels, Russia has also shown some interest in developing renewable energy sources. However, investment and progress in this area remain limited compared to other countries.
- Government Policies: Government policies have not been consistently supportive of renewable energy development, and bureaucratic obstacles often hinder progress. The focus remains primarily on fossil fuels, due to their pivotal role in the Russian economy.
- Statistics: The amount of investment in renewables is significantly lower than what would be needed for a substantial diversification of Russia’s energy sector. Data from international organizations like the IEA can provide insights into Russia's progress in this area in comparison to other nations.
The Impact on the Russian Ruble and Inflation
The war and subsequent sanctions have had a profound effect on the Russian ruble and inflation rates.
Ruble's Resilience and Volatility
Initially, the ruble experienced a sharp decline, but it has since stabilized, largely due to government intervention.
- Capital Controls: The Russian government implemented capital controls and other measures to support the ruble and prevent a collapse. The effectiveness and potential long-term economic consequences of these measures remain a matter of debate amongst economists.
- Currency Fluctuations: Charts illustrating the ruble's fluctuation against major currencies such as the US dollar and the euro show its volatility and the government's efforts to manage it.
Inflation and its Effects on the Russian Population
Sanctions and the war have contributed to increased inflation, impacting the living standards of the Russian population.
- Inflation Rates: Statistics on inflation rates and consumer prices reflect the rising cost of living in Russia. The impact on different segments of the population varies, with the poorest being the most vulnerable.
- Government Measures: The government has implemented various measures to control inflation, but their effectiveness has been limited, and many households have seen a decrease in their purchasing power.
Long-Term Economic Outlook for Russia
The long-term economic consequences of the war and sanctions for Russia are still unfolding and subject to considerable uncertainty.
The Path to Recovery
Several scenarios are possible for Russia's economic recovery, depending on factors such as the duration of the conflict, the effectiveness of sanctions, and the implementation of internal reforms. However, long-term stagnation remains a significant risk.
- Economic Forecast Models: Different forecast models offer varying predictions for Russia's economic growth, reflecting the wide range of possible outcomes. These forecasts often depend on specific assumptions regarding the conflict's duration and the evolution of the international environment.
Geopolitical Implications
The war has profoundly impacted Russia's international relations and its long-term economic prospects.
- Shifts in Global Power Dynamics: The war has accelerated shifts in global power dynamics, leading to a re-evaluation of global supply chains and a greater focus on energy security. Russia's standing on the world stage has significantly diminished, and its economic influence has waned.
Conclusion:
This analysis of Russia's economy under Putin, specifically focusing on the war in Ukraine, reveals a complex picture. While initial sanctions led to significant shocks, Russia has demonstrated resilience through import substitution and a shift in trade partnerships. However, the long-term economic outlook remains uncertain, heavily influenced by the duration of the conflict and the persistence of international sanctions. The future of Russia's economy will likely be defined by its ability to adapt to these challenges and diversify away from its dependence on energy exports. Understanding the intricacies of Russia's economy and its response to the war is crucial for navigating the evolving geopolitical landscape. Further research into Russia's economy is encouraged to gain a deeper comprehension of this dynamic situation.

Featured Posts
-
 Vatera Aukciok Rekordarakert Elkelo Ritka Kincsek
May 29, 2025
Vatera Aukciok Rekordarakert Elkelo Ritka Kincsek
May 29, 2025 -
 Why The Harry Potter Remake Alleviates My Fears
May 29, 2025
Why The Harry Potter Remake Alleviates My Fears
May 29, 2025 -
 El Presente De Victor Fernandez Logros Y Desafios
May 29, 2025
El Presente De Victor Fernandez Logros Y Desafios
May 29, 2025 -
 Ajax Nieuwe Trainer Arne Slot In De Spotlights
May 29, 2025
Ajax Nieuwe Trainer Arne Slot In De Spotlights
May 29, 2025 -
 Seattle Police Investigate Downtown Double Shooting
May 29, 2025
Seattle Police Investigate Downtown Double Shooting
May 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The History And Folklore Of Rosemary And Thyme
May 31, 2025
The History And Folklore Of Rosemary And Thyme
May 31, 2025 -
 Rosemary And Thyme Your Guide To Cultivating These Powerful Herbs
May 31, 2025
Rosemary And Thyme Your Guide To Cultivating These Powerful Herbs
May 31, 2025 -
 A Guide To Combining Rosemary And Thyme For Maximum Flavor
May 31, 2025
A Guide To Combining Rosemary And Thyme For Maximum Flavor
May 31, 2025 -
 Exploring The Differences Between Rosemary And Thyme Flavor Profiles And Uses
May 31, 2025
Exploring The Differences Between Rosemary And Thyme Flavor Profiles And Uses
May 31, 2025 -
 Rosemary And Thyme Recipes Simple Dishes With Big Flavor
May 31, 2025
Rosemary And Thyme Recipes Simple Dishes With Big Flavor
May 31, 2025
