Stricter Measures: Netherlands Introduces Low-Security Detention And Area Bans For Asylum Seekers
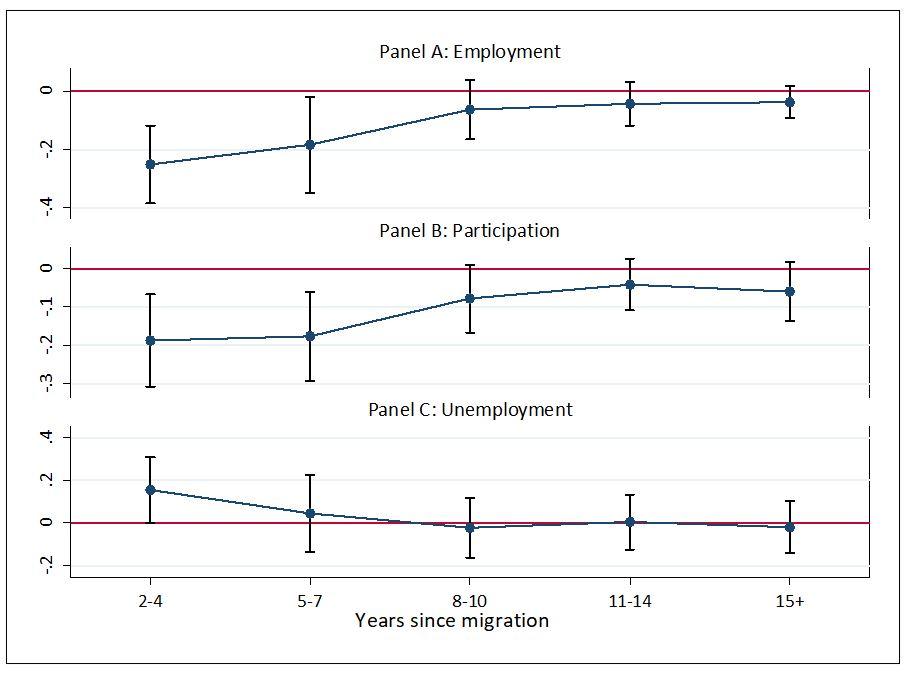
Table of Contents
Low-Security Detention Centers for Asylum Seekers in the Netherlands
What constitutes "low-security" detention?
The Netherlands' new low-security detention centers for asylum seekers represent a departure from the existing higher-security facilities. While the exact specifications vary depending on the location, the key difference lies in the level of freedom and restrictions imposed. Higher-security facilities typically involve stricter surveillance, limited movement, and greater restrictions on contact with the outside world. Low-security detention, in contrast, aims to provide a more open environment.
- Definition and description of the facilities: These facilities aim to provide a less restrictive environment than traditional detention centers, potentially including more communal spaces and greater freedom of movement within the facility.
- Comparison with existing higher-security detention: In comparison to higher-security facilities, low-security centers offer increased opportunities for activities such as education, work programs, and recreational activities. However, freedom of movement outside the designated area remains restricted.
- Focus on the level of freedom and restrictions imposed: Residents might have access to communal areas, workshops, and educational resources, but curfews and limitations on external contact are still likely to be in place.
- Specific examples of allowed activities and limitations:
- Allowed: Access to education programs, participation in work initiatives, use of communal facilities.
- Limitations: Restricted movement outside the facility, limited contact with the outside world, adherence to strict curfews.
Reasons behind the introduction of low-security detention.
The Dutch government justifies the introduction of low-security detention centers for asylum seekers based on several factors.
- Government's stated aims: The government aims to manage asylum applications more efficiently and cost-effectively. They argue that low-security detention is a less expensive alternative to higher-security facilities, allowing resources to be allocated more effectively.
- Addressing overcrowding in existing detention facilities: The new approach is partly driven by the need to alleviate pressure on overcrowded higher-security facilities. The government believes that low-security centers offer a more humane and scalable solution to manage the influx of asylum seekers.
- Potential impact on asylum seeker wellbeing: While the government maintains this approach improves wellbeing by offering a less restrictive environment, critics argue the opposite.
- Government's official justifications:
- Reduced costs associated with detention.
- Improved management of asylum applications.
- Alleviation of overcrowding in existing detention facilities.
Criticisms and concerns regarding low-security detention.
Despite the government's arguments, various concerns regarding low-security detention have been raised by human rights organizations and other critics.
- Human rights organizations' responses: Many human rights groups express concern about the potential for abuse and exploitation within these facilities, even if they are deemed "low-security."
- Potential for abuse or exploitation: Critics argue that the less restrictive environment could leave asylum seekers vulnerable to abuse or exploitation.
- Concerns about the impact on mental health: The impact on mental health, particularly for vulnerable individuals, is also a major concern.
- Specific concerns raised by critics:
- Insufficient monitoring and oversight.
- Increased risk of exploitation and abuse.
- Negative impact on mental health and well-being.
Area Bans for Asylum Seekers in the Netherlands
How area bans work and their implementation.
Area bans restrict asylum seekers from entering or remaining in certain geographical areas within the Netherlands.
- Geographic areas subject to bans: These bans typically target areas perceived as having high levels of social unrest or strain on public services.
- The legal basis for imposing these restrictions: The legal framework underpinning area bans is often based on public order concerns and the prevention of crime.
- Enforcement mechanisms and consequences of violations: Enforcement involves police monitoring and potential penalties for violations, which can include further detention or deportation.
- Practical implications for affected individuals: Area bans severely limit freedom of movement, access to services, and integration into Dutch society.
Justification for implementing area bans.
The government justifies area bans primarily on the grounds of public order and security.
- Government's reasoning behind area bans: The government often cites concerns about preventing crime, maintaining public order, and reducing the strain on specific regions.
- Focus on preventing crime or maintaining public order: Area bans are frequently framed as a necessary measure to prevent potential conflicts or maintain social stability in sensitive areas.
- Potential for reducing strain on specific regions: The government might argue that these bans reduce the strain on local resources and infrastructure in particular areas.
- Official reasons for the policy:
- Prevention of crime and maintaining public order.
- Reduction of strain on specific regions.
- Management of asylum seeker distribution.
Legal challenges and human rights implications of area bans.
Area bans raise serious legal and ethical questions concerning human rights.
- Potential conflicts with international human rights laws: These bans can conflict with international human rights laws guaranteeing freedom of movement and non-discrimination.
- Arguments against area bans based on principles of freedom of movement: Critics argue that area bans violate fundamental human rights, especially the right to freedom of movement.
- Ongoing legal battles and court cases: The legality of area bans is being challenged in various court cases, highlighting the ongoing legal debate.
- Legal and ethical concerns:
- Violations of freedom of movement.
- Discrimination and unequal treatment.
- Potential for arbitrary and unjust application.
Public Opinion and Political Debate Surrounding the New Measures
Public perception of the new policies.
Public opinion on the new measures is diverse and complex.
- Results of public opinion polls (if available): Polls (if available) would indicate the level of public support or opposition to these policies.
- Media coverage and public discourse: Media coverage and public discourse reflect a wide range of viewpoints, highlighting the divisive nature of the issue.
- Diverse viewpoints and perspectives from different segments of society: Public opinion is shaped by various factors, including political affiliation, geographic location, and personal experiences.
- Summary of public reactions and opinions: Public reaction ranges from support for stronger border controls to concerns about the human rights implications of stricter measures.
Political ramifications and party stances.
The introduction of stricter measures has significant political ramifications.
- Government's political strategy and motivations: The government's strategy often involves portraying these measures as necessary for maintaining public safety and controlling immigration.
- Reactions from opposition parties: Opposition parties often criticize the measures for their potential human rights violations and negative impact on asylum seekers.
- Potential impact on upcoming elections: The issue of asylum seeker detention is likely to play a significant role in upcoming elections.
- Political landscape surrounding the issue: The political landscape is characterized by strong divisions on immigration policy, with differing views on the appropriate balance between security concerns and human rights.
Conclusion
The introduction of low-security detention and area bans for asylum seekers in the Netherlands represents a significant shift in the country's immigration policy. While the government argues that these measures are necessary for efficient management and public order, concerns regarding their human rights implications and impact on the well-being of asylum seekers remain substantial. The legal and ethical implications are likely to continue fueling extensive debate. Further research is needed to understand the long-term effects of these stricter measures. Stay informed about developments concerning asylum seeker detention in the Netherlands and the ongoing discussion surrounding these important policy shifts. Understanding the complexities of asylum seeker policies in the Netherlands requires continued monitoring of the situation and engagement in the public discourse.

Featured Posts
-
 Adam Sandlers Wife Their Love Story Began On A Netflix Set
May 11, 2025
Adam Sandlers Wife Their Love Story Began On A Netflix Set
May 11, 2025 -
 Lily Collins Post Baby Body In Calvin Kleins New Campaign
May 11, 2025
Lily Collins Post Baby Body In Calvin Kleins New Campaign
May 11, 2025 -
 Naissance D Un Enfant Pour Eric Antoine Nouvelles Revelations Sur Sa Vie Privee
May 11, 2025
Naissance D Un Enfant Pour Eric Antoine Nouvelles Revelations Sur Sa Vie Privee
May 11, 2025 -
 Ultimul Meci Al Lui Thomas Mueller Un Omagiu Emotionant Pentru O Legenda
May 11, 2025
Ultimul Meci Al Lui Thomas Mueller Un Omagiu Emotionant Pentru O Legenda
May 11, 2025 -
 2024 Senior Calendar Of Trips Activities And Events
May 11, 2025
2024 Senior Calendar Of Trips Activities And Events
May 11, 2025
