Taiwan's Energy Transition: Increased Reliance On LNG Imports Following Nuclear Closure
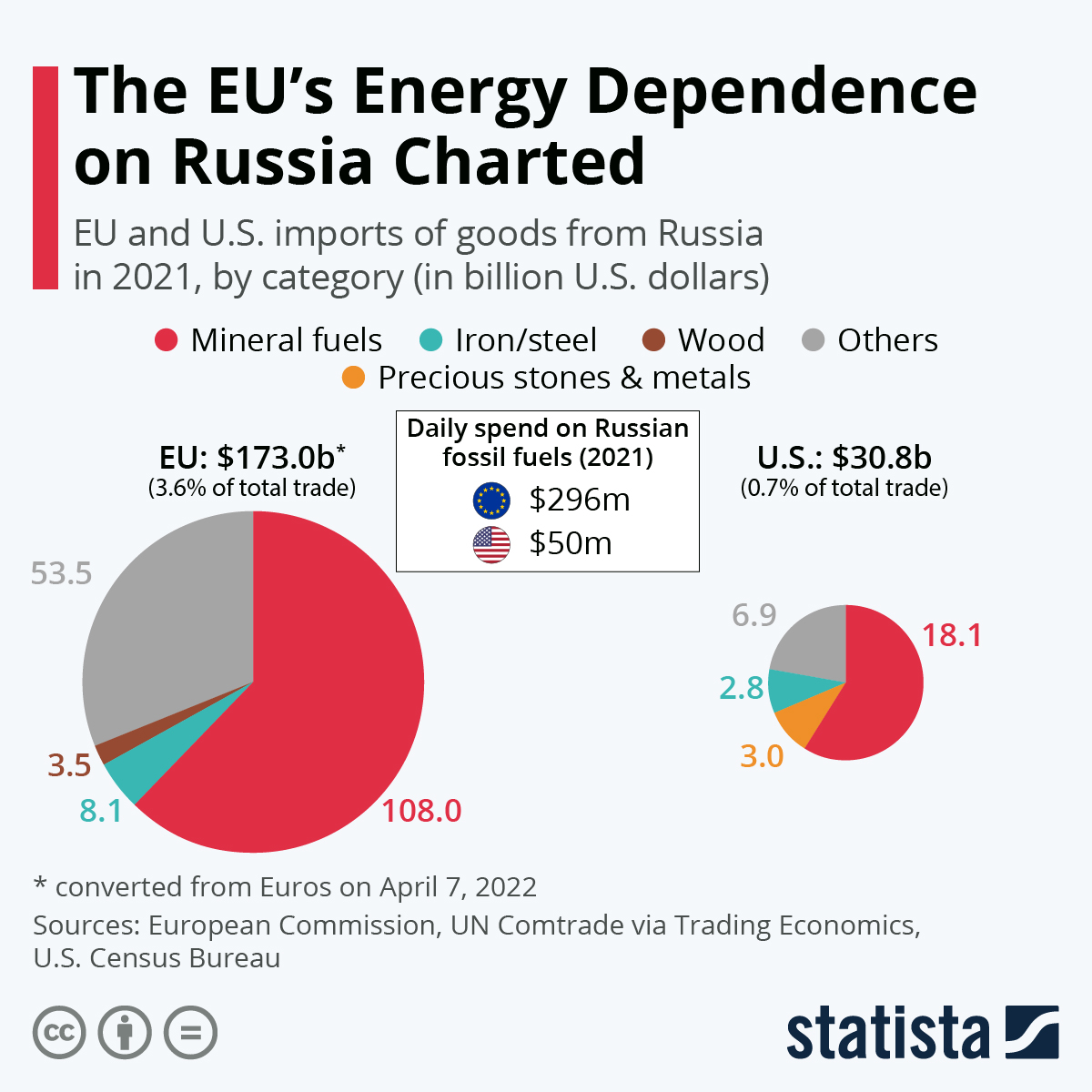
Table of Contents
The Phasedown of Nuclear Power in Taiwan
Taiwan's nuclear power history is complex. For decades, nuclear energy played a significant role in meeting the nation's electricity demands. However, a confluence of factors—including public safety concerns following the Fukushima disaster, growing anti-nuclear sentiment, and a commitment to renewable energy—led the government to announce a phased withdrawal from nuclear power. This policy decision has had profound implications for Taiwan's energy mix.
- Timeline of nuclear plant closures: The decommissioning process began with the oldest plants and continues to unfold, significantly altering Taiwan's energy production capacity.
- Public perception and protests: Public opposition to nuclear energy, fueled by safety anxieties and environmental concerns, played a major role in the government's decision to phase out nuclear power. Protests and public discourse significantly impacted policy decisions.
- Government policy and regulations: Specific government policies and regulations mandated the gradual shutdown of nuclear plants and the development of alternative energy sources. This involved significant investment and policy shifts.
The Rise of LNG as a Primary Energy Source
With the decline of nuclear power, LNG has emerged as a crucial component of Taiwan's energy mix, filling the gap left by nuclear power generation. This transition has necessitated substantial investments in infrastructure. The growth in LNG imports Taiwan is undeniable.
- Statistics on LNG import growth: Data reveals a sharp increase in LNG import volumes in recent years, highlighting the growing dependence on this fuel source. This growth trajectory is expected to continue in the short to medium term.
- Expansion of LNG import terminals and storage facilities: Significant investment has been directed toward expanding existing LNG import terminals and constructing new ones. This expansion is essential to handle the growing import volumes.
- Investment in LNG infrastructure projects: Private and public sectors are heavily invested in infrastructure projects related to LNG import, storage, and distribution to ensure a reliable supply. This includes building new pipelines and storage tanks.
- Role of specific companies: Several key players in the energy sector have been instrumental in driving the expansion of LNG infrastructure in Taiwan.
Geopolitical Implications of Increased LNG Imports
Taiwan's heightened reliance on LNG imports presents significant geopolitical risks. The country's energy security is now heavily dependent on the stability of its LNG supplier countries and the global LNG market.
- Major LNG supplying countries for Taiwan: Identifying the key suppliers of LNG to Taiwan is crucial to understand the geopolitical vulnerabilities. Diversification of suppliers is key to mitigating risk.
- Vulnerability to geopolitical instability: Geopolitical instability in major LNG-producing regions poses a direct threat to Taiwan's energy supply. Any disruptions in these regions could have severe consequences.
- Potential risks of supply chain disruptions and price volatility: Global events and market fluctuations can cause significant price volatility and supply disruptions, impacting Taiwan's economy.
- Strategies to mitigate geopolitical risks: Diversifying LNG import sources and developing alternative energy sources are critical strategies to mitigate these risks.
Environmental Concerns and the Transition to Renewable Energy
The increased reliance on LNG raises significant environmental concerns due to its greenhouse gas emissions. While a less carbon-intensive alternative to coal, LNG still contributes to climate change. Taiwan is actively pursuing a transition to renewable energy sources to mitigate these environmental impacts.
- Taiwan's renewable energy targets: The government has set ambitious targets for renewable energy adoption to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lessen the environmental impact.
- Investments in solar, wind, and other renewable energy technologies: Significant investments are being made in solar, wind, and other renewable energy technologies to achieve these goals.
- Challenges in scaling up renewable energy generation: Despite the investments, scaling up renewable energy generation faces challenges, including land availability and grid integration issues.
- Role of energy efficiency improvements: Improving energy efficiency across all sectors is a crucial strategy to reduce overall energy consumption and lower reliance on LNG imports.
Economic Impacts of the Energy Transition
The shift towards LNG imports and renewable energy has substantial economic implications for Taiwan. While LNG imports represent a significant cost, the development of renewable energy presents both costs and economic opportunities.
- Fluctuations in global LNG prices: Global LNG price fluctuations directly impact Taiwan's energy costs and the overall economy.
- Costs of building new LNG infrastructure and renewable energy projects: The large-scale investments required for both LNG infrastructure and renewable energy projects represent a considerable economic outlay.
- Economic opportunities created by the renewable energy sector: The renewable energy sector is creating new job opportunities and economic growth potential in Taiwan.
- Potential for job creation in the green energy sector: Investing in renewable energy creates a pathway to economic development and jobs in a rapidly growing sector.
Conclusion: Navigating Taiwan's Energy Future with LNG Imports and Beyond
Taiwan's energy transition, driven by the phase-out of nuclear power, has resulted in a significant increase in LNG imports Taiwan. This reliance on LNG imports presents both economic opportunities and significant geopolitical and environmental challenges. Diversifying energy sources and accelerating the development of renewable energy are crucial for ensuring energy security, economic stability, and environmental sustainability. Further research into Taiwan's energy policy, the role of LNG imports Taiwan, and the potential for a sustainable energy future is crucial. Stay informed about developments in Taiwan's energy transition and the long-term implications of its increased reliance on LNG imports Taiwan.

Featured Posts
-
 The Fight For Clean Energy Navigating Opposition In A Growing Market
May 20, 2025
The Fight For Clean Energy Navigating Opposition In A Growing Market
May 20, 2025 -
 Hmrc Website Down Widespread Access Issues Reported In The Uk
May 20, 2025
Hmrc Website Down Widespread Access Issues Reported In The Uk
May 20, 2025 -
 A Nigerian Context Analyzing The Themes Of Redemption In The Kite Runner
May 20, 2025
A Nigerian Context Analyzing The Themes Of Redemption In The Kite Runner
May 20, 2025 -
 Michael Strahan Soaked By Susan Lucci Video Goes Viral
May 20, 2025
Michael Strahan Soaked By Susan Lucci Video Goes Viral
May 20, 2025 -
 Us Typhon Missile System In Philippines A Counter To Chinese Aggression
May 20, 2025
Us Typhon Missile System In Philippines A Counter To Chinese Aggression
May 20, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Nyt Mini Crossword Hints And Solutions April 26 2025
May 20, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Hints And Solutions April 26 2025
May 20, 2025 -
 Ginger Zee Slams Critic Over Aging Comments
May 20, 2025
Ginger Zee Slams Critic Over Aging Comments
May 20, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword March 26 2025 Complete Answers And Solutions
May 20, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword March 26 2025 Complete Answers And Solutions
May 20, 2025 -
 Get The Answers Nyt Mini Crossword Hints April 26 2025
May 20, 2025
Get The Answers Nyt Mini Crossword Hints April 26 2025
May 20, 2025 -
 Ginger Zee Responds To Aging Criticism
May 20, 2025
Ginger Zee Responds To Aging Criticism
May 20, 2025
