The Devastating Rise In Global Forest Loss: A Wildfire Crisis
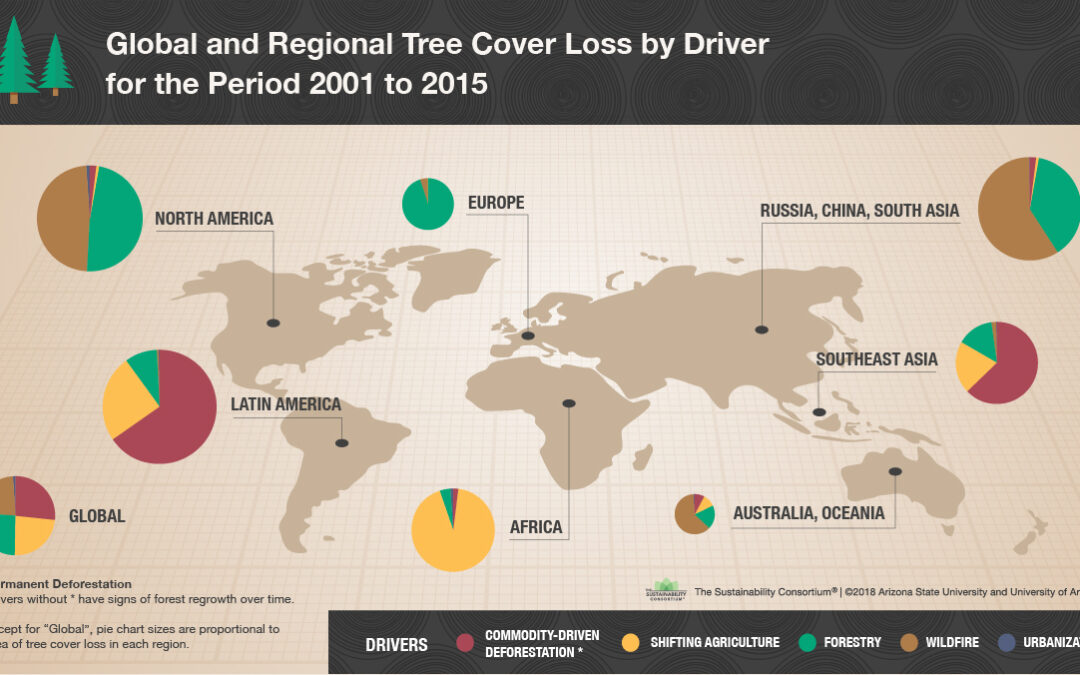
Table of Contents
The Escalating Threat of Wildfires
The dramatic increase in wildfires globally is not a random event; it's a symptom of a much larger, interconnected problem. Understanding the root causes is critical to finding effective solutions.
Climate Change as a Primary Driver:
Climate change is significantly exacerbating the wildfire crisis. Rising global temperatures, prolonged droughts, and increasingly erratic weather patterns create a perfect storm for devastating wildfires.
- Increased ignition potential: Higher temperatures and drier conditions increase the likelihood of wildfires starting, both naturally (lightning strikes) and through human activities.
- Longer fire seasons: Warmer springs and autumns extend the periods when forests are vulnerable to fire, leading to longer and more intense burning seasons.
- Faster fire spread: Drier vegetation and stronger winds fueled by climate change cause wildfires to spread rapidly, making them harder to contain.
Data from NASA and the IPCC clearly show a correlation between rising global temperatures and increased wildfire activity. Regions like the Amazon rainforest, California, and Australia have experienced unprecedented wildfire devastation in recent years, directly linked to climate change-induced extreme weather events.
Deforestation and its Contribution:
Deforestation plays a crucial role in creating conditions ripe for wildfires. The removal of trees weakens forest ecosystems, making them more susceptible to fire.
- Loss of natural firebreaks: Intact forests often have natural breaks in vegetation that can help slow or stop wildfire spread. Deforestation removes these natural barriers.
- Increased fuel loads: The accumulation of dry leaves, branches, and undergrowth creates significant fuel for wildfires, intensifying their severity.
- Altered microclimates: Deforestation can change local climates, creating drier, hotter conditions that increase wildfire risk.
Studies have repeatedly demonstrated a link between deforestation caused by logging, agriculture, and urbanization, and the increased frequency and intensity of wildfires.
Devastating Consequences of Global Forest Loss
The consequences of global forest loss extend far beyond the immediate destruction caused by wildfires. The impact on the planet and its inhabitants is profound and long-lasting.
Biodiversity Loss and Ecosystem Collapse:
Wildfires and the resulting forest loss cause catastrophic biodiversity loss. The destruction of habitats leads to population declines and extinction risks for countless plant and animal species.
- Loss of keystone species: The disappearance of keystone species – those crucial to maintaining ecosystem balance – can trigger a domino effect, disrupting entire food webs.
- Disruption of food webs: The loss of plant and animal life disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems, impacting the entire food chain.
- Reduced carbon sequestration: Forests play a vital role in absorbing atmospheric carbon dioxide. Their destruction diminishes this crucial carbon sink, exacerbating climate change.
Numerous endangered species, such as the orangutans of Borneo and the Sumatran tigers, are threatened by habitat loss due to deforestation and wildfires.
Climate Change Exacerbation:
Forest loss creates a dangerous positive feedback loop. Burning forests release massive amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to further climate change, which in turn increases the risk and intensity of future wildfires.
- Increased greenhouse gas emissions: Wildfires are a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions, further accelerating global warming.
- Reduced carbon sinks: The destruction of forests reduces the planet's capacity to absorb carbon dioxide, trapping more greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Amplified global warming: This cycle intensifies global warming, creating a vicious cycle of increasing temperatures, more frequent wildfires, and further carbon emissions.
Large-scale forest fires release billions of tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere each year, significantly contributing to climate change.
Socioeconomic Impacts:
The human cost of wildfires and global forest loss is immense. Communities are displaced, economies suffer, and public health is threatened.
- Loss of livelihoods: Millions depend on forests for their livelihoods, including those involved in forestry, agriculture, and tourism. Wildfires destroy these livelihoods, leading to economic hardship.
- Infrastructure damage: Wildfires can cause significant damage to homes, businesses, and infrastructure, leading to massive economic losses and costly repairs.
- Increased healthcare costs: The smoke and air pollution from wildfires cause serious respiratory problems, increasing healthcare costs and impacting public health.
- Social unrest: The displacement and economic hardship caused by wildfires can lead to social unrest and conflict.
Communities affected by wildfires often face long-term economic hardship, struggling to rebuild their lives and livelihoods.
Combating Global Forest Loss: Strategies for Mitigation and Prevention
Addressing the global forest loss crisis requires a multi-pronged approach, focusing on both prevention and mitigation.
Strengthening Forest Management Practices:
Sustainable forestry practices are crucial in reducing the risk of wildfires and promoting forest resilience.
- Reforestation initiatives: Planting trees in deforested areas helps restore ecosystems and create natural firebreaks.
- Improved fire prevention techniques: Implementing better fire prevention measures, such as controlled burns and improved early detection systems, can reduce the impact of wildfires.
- Community-based forest management: Involving local communities in forest management ensures sustainable practices and protects forest resources.
Numerous successful forest conservation and restoration projects demonstrate the effectiveness of these strategies.
Addressing Climate Change:
Mitigating climate change is critical to reducing the frequency and intensity of wildfires. This requires a global commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Transition to renewable energy: Shifting from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources is essential in reducing carbon emissions.
- Sustainable transportation: Adopting sustainable transportation methods, such as electric vehicles and public transport, can significantly reduce carbon footprints.
- Carbon capture technologies: Investing in research and development of carbon capture technologies can help remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
International agreements like the Paris Agreement are crucial in coordinating global efforts to mitigate climate change.
Promoting International Cooperation:
Global collaboration is essential in tackling this transnational environmental challenge.
- Sharing best practices: Countries can learn from each other's successes and failures in forest management and wildfire prevention.
- Joint research efforts: Collaborative research efforts can help develop innovative solutions to combat global forest loss.
- International funding for conservation: International funding is crucial in supporting forest conservation and restoration projects in developing countries.
International organizations like the UN and WWF play a vital role in coordinating international efforts to protect forests and combat wildfires.
Conclusion:
The devastating rise in global forest loss, fueled by increasingly intense wildfires, presents a critical threat to our planet. The interconnectedness of climate change, deforestation, and wildfires creates a dangerous cycle with severe consequences for biodiversity, climate stability, and human societies. Combating this crisis demands immediate and concerted action. We must all work together – governments, organizations, and individuals – to implement sustainable forestry practices, mitigate climate change, and protect our precious forests from the devastating impact of wildfires. Support organizations dedicated to forest conservation and climate action, advocate for policies that prioritize environmental protection, and make conscious choices in your daily life to reduce your carbon footprint. Let's collectively fight the devastating rise in global forest loss and work towards a future where our forests thrive. Learn more and get involved by visiting [link to relevant organization 1] and [link to relevant organization 2].

Featured Posts
-
 The Trans Australia Run A Historic World Record In Jeopardy
May 22, 2025
The Trans Australia Run A Historic World Record In Jeopardy
May 22, 2025 -
 Statement From Switzerland Condemnation Of Prc Military Activities
May 22, 2025
Statement From Switzerland Condemnation Of Prc Military Activities
May 22, 2025 -
 Across Australia On Foot A Britons Challenging Run
May 22, 2025
Across Australia On Foot A Britons Challenging Run
May 22, 2025 -
 Kartels Trinidad Show Defence Minister Proposes Age And Song Restrictions
May 22, 2025
Kartels Trinidad Show Defence Minister Proposes Age And Song Restrictions
May 22, 2025 -
 Ea Fc 25 Fut Birthday Tier List Top Players To Target
May 22, 2025
Ea Fc 25 Fut Birthday Tier List Top Players To Target
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Blake Lively Alleged Controversies And Recent News
May 22, 2025
Blake Lively Alleged Controversies And Recent News
May 22, 2025 -
 Blake Lively And The Allegations A Timeline Of Events
May 22, 2025
Blake Lively And The Allegations A Timeline Of Events
May 22, 2025 -
 Recent News On Blake Lively Addressing The Allegations
May 22, 2025
Recent News On Blake Lively Addressing The Allegations
May 22, 2025 -
 Dissecting The Allegations A Deep Dive Into The Blake Lively Controversy
May 22, 2025
Dissecting The Allegations A Deep Dive Into The Blake Lively Controversy
May 22, 2025 -
 The Blake Lively Allegedly Situation Examining The Evidence And Implications
May 22, 2025
The Blake Lively Allegedly Situation Examining The Evidence And Implications
May 22, 2025
