The Fed And Interest Rates: Understanding The Delay In Cuts
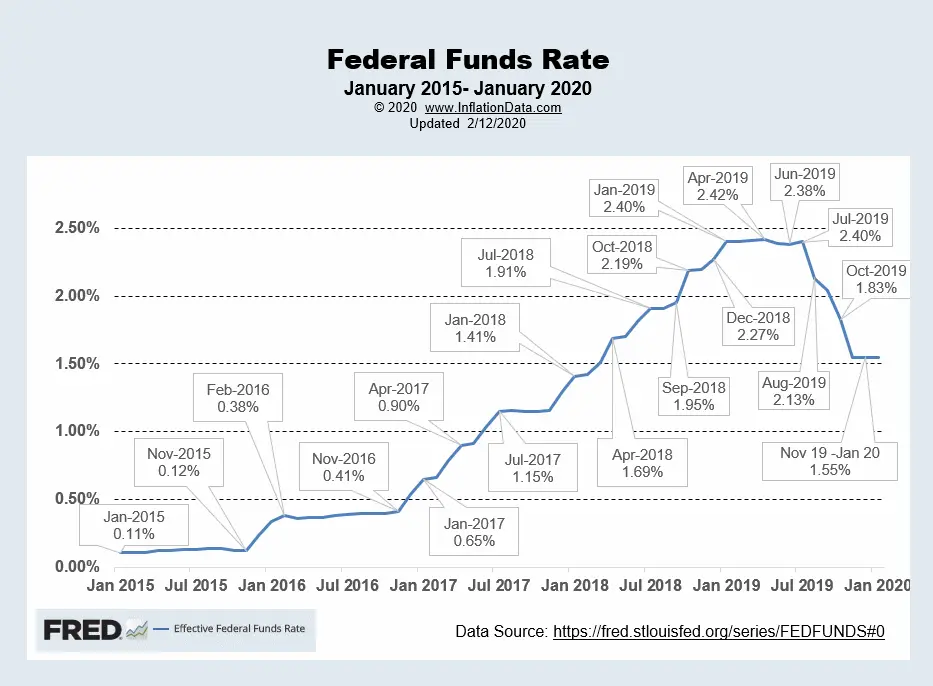
Table of Contents
Inflation Remains Stubbornly High
The current inflation rate significantly deviates from the Fed's target of 2%. While inflation has cooled somewhat from its peak, it remains stubbornly high. This persistent inflation is driven by several factors, making it a significant hurdle for anticipated Fed interest rate cuts. Keywords like "inflation rate," "CPI," "PCE," "inflation target," and "sticky inflation" are crucial to understanding this challenge.
- Recent CPI and PCE data: The Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) index, key measures of inflation, continue to show elevated levels, indicating that price increases are still widespread.
- Analysis of specific inflationary pressures: Specific sectors, such as housing and food, continue to experience significant price increases, contributing to the overall inflation rate. These "sticky" prices are resistant to decreases.
- Comparison with historical inflation data: Comparing current inflation rates with historical data reveals the current situation's severity and its deviation from typical economic patterns.
The Labor Market Remains Tight
The labor market is another critical factor delaying Fed interest rate cuts. Currently, unemployment is low, and wage growth is strong. This "tight" labor market creates upward pressure on wages, which, in turn, fuels inflation. Keywords like "unemployment rate," "job growth," "wage growth," and "labor market tightness" are crucial here.
- Statistics on unemployment rates and job openings: The low unemployment rate and the high number of job openings demonstrate the current labor market's strength.
- Discussion of wage growth trends across different sectors: Wage growth is happening across various sectors, indicating broad-based pressure on prices.
- Analysis of the impact of labor shortages on inflation: Businesses facing labor shortages often pass increased labor costs onto consumers, contributing to inflation.
Concerns about a Potential Recession
The Fed faces a delicate balancing act: reducing inflation without triggering a recession. Cutting interest rates too soon risks reigniting inflation. Keywords such as "recession risk," "economic slowdown," "soft landing," "monetary policy," and "interest rate hikes" are vital for this section.
- Economic indicators suggesting potential recessionary pressures: Certain economic indicators might show signs of slowing economic growth, raising concerns about a potential recession.
- Analysis of the Fed's balancing act between inflation and recession: The Fed must carefully consider the risks of both inflation and recession when making decisions about interest rates. This is a complex balancing act.
- Discussion of alternative economic scenarios: There are various potential economic scenarios, each with its own implications for interest rates and the likelihood of a recession.
The Fed's Data-Dependent Approach
The Fed employs a data-dependent approach to monetary policy, meaning its decisions are based on the latest economic data. Understanding this approach is essential to comprehending the delay in Fed interest rate cuts. Keywords like "data-dependent approach," "monetary policy," "Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)," and "economic indicators" are key here.
- Examples of key economic indicators the Fed is watching: The Fed monitors a range of indicators, including inflation, employment, consumer spending, and business investment.
- Explanation of the FOMC's role in setting interest rates: The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is responsible for setting the federal funds rate, the target rate for overnight lending between banks.
- Discussion of the uncertainty and unpredictability involved in economic forecasting: Economic forecasting is inherently uncertain, making the Fed's job particularly challenging.
Conclusion: Navigating the Uncertainty of Fed Interest Rate Cuts
The delay in Fed interest rate cuts stems from stubbornly high inflation, a tight labor market, and concerns about triggering a recession. The Fed's data-dependent approach necessitates patience and careful consideration of various economic indicators. The future path of interest rates remains uncertain, depending on incoming economic data.
Stay updated on the latest Fed announcements and economic data to make informed financial decisions. Visit the Federal Reserve website () for the most current information on monetary policy and economic data. Understanding the nuances of Fed interest rate cuts is crucial for navigating the current economic climate.

Featured Posts
-
 Retired Judge Deborah Taylor To Lead Nottingham Attacks Inquiry
May 09, 2025
Retired Judge Deborah Taylor To Lead Nottingham Attacks Inquiry
May 09, 2025 -
 Young Thug Drops Uy Scuti Album Release Date Clue
May 09, 2025
Young Thug Drops Uy Scuti Album Release Date Clue
May 09, 2025 -
 Golden Knights Defeat Blue Jackets 4 0 Hills Stellar Performance Leads The Way
May 09, 2025
Golden Knights Defeat Blue Jackets 4 0 Hills Stellar Performance Leads The Way
May 09, 2025 -
 St Albert Dinner Theatres New Production A Fast Flying Farce
May 09, 2025
St Albert Dinner Theatres New Production A Fast Flying Farce
May 09, 2025 -
 Bitcoin Madenciliginin Azalan Karliligi Iste Gercekler
May 09, 2025
Bitcoin Madenciliginin Azalan Karliligi Iste Gercekler
May 09, 2025
