The Great Decoupling And Its Effect On Technological Advancement

Table of Contents
Impact of the Great Decoupling on Innovation
The Great Decoupling presents a double-edged sword when it comes to innovation. While it hinders collaboration in some areas, it simultaneously accelerates domestic innovation efforts in both the U.S. and China.
Stifled Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
The decoupling significantly limits collaborative research and the free flow of scientific information, potentially hindering major breakthroughs. This restricted exchange impacts the speed of technological progress across various fields.
- Reduced joint ventures: Companies are hesitant to engage in joint ventures due to geopolitical uncertainties and increased regulatory scrutiny.
- Stricter visa policies for researchers: Restrictions on visas for scientists and engineers limit the movement of talent and knowledge between countries.
- Limitations on data sharing: Concerns about data security and intellectual property theft have led to restrictions on data sharing between the U.S. and China, hampering collaborative research projects.
For instance, the collaborative research projects in advanced materials science, once common between U.S. and Chinese universities, have significantly decreased due to these limitations, potentially delaying the development of next-generation technologies.
Accelerated Domestic Innovation
Paradoxically, the decoupling is also acting as a catalyst for domestic innovation. Both nations are investing heavily in their own research and development (R&D) ecosystems, focusing on self-reliance in critical technologies.
- Increased government funding for R&D: Both the U.S. and China have significantly increased government funding for R&D in strategic sectors, such as semiconductors and artificial intelligence.
- Focus on self-reliance in critical technologies: The decoupling has spurred a focus on developing domestic capabilities in crucial technologies, reducing reliance on foreign suppliers.
- Development of domestic supply chains: Countries are actively working to build resilient and independent supply chains for critical technologies, minimizing vulnerabilities to disruptions.
The CHIPS and Science Act in the U.S., for example, is a direct response to the decoupling, aiming to revitalize domestic semiconductor manufacturing and research. Similarly, China's Made in China 2025 initiative underscores its commitment to technological self-sufficiency.
The Great Decoupling's Effect on Global Supply Chains
The decoupling is profoundly reshaping global supply chains, creating both challenges and opportunities.
Fragmentation of Global Value Chains
The interconnected nature of global value chains is being disrupted, leading to increased costs and potential supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Reshoring and nearshoring initiatives: Companies are increasingly bringing manufacturing closer to home, or to nearby regions, to mitigate risks associated with long and complex supply chains.
- Difficulties in accessing crucial components: The decoupling creates difficulties in accessing certain crucial components, especially those reliant on specialized manufacturing capabilities in either the U.S. or China.
- Increased reliance on less efficient regional supply chains: The shift towards regionalization might result in less efficient and potentially more expensive supply chains.
The semiconductor industry provides a stark example. The reliance on Taiwan for advanced chip manufacturing highlights the vulnerabilities created by geographically concentrated supply chains.
Rise of Regional Tech Hubs
The decoupling is fostering the emergence of distinct regional technological hubs, with the U.S. and China becoming increasingly self-contained ecosystems.
- Increased investment in domestic infrastructure: Both countries are investing heavily in infrastructure to support their domestic tech sectors.
- Growth of start-up ecosystems: Domestic start-up ecosystems are flourishing as entrepreneurs and investors focus on creating innovative solutions within their own national contexts.
- Development of independent standards: There’s a growing divergence in technological standards, potentially creating fragmentation in global markets.
The rise of Silicon Valley in the U.S. and the emergence of tech hubs in cities like Shenzhen and Beijing in China exemplifies this trend.
Geopolitical Implications and Future Technological Leadership
The Great Decoupling has significant geopolitical implications, particularly regarding technological competition and future leadership.
Technological Competition and Arms Race
The decoupling fuels a technological competition, potentially escalating into an arms race, with implications for military capabilities and national security.
- Increased investment in defense-related technologies: Both nations are intensifying investments in defense-related technologies, including artificial intelligence, hypersonics, and cybersecurity.
- Development of cutting-edge weaponry: The competition is driving rapid advancements in weaponry and military technologies.
- Cybersecurity threats: The decoupling intensifies the risks of cyberattacks and espionage, adding to geopolitical tensions.
This technological competition could destabilize the global order if not carefully managed.
Shifting Global Technological Leadership
The long-term consequences of the Great Decoupling remain uncertain, leading to significant uncertainty about the future distribution of global technological leadership.
- Uncertainty about which nation will emerge as the dominant technological power: The outcome of this competition is far from clear, with both the U.S. and China vying for technological supremacy.
- Impact on global economic dynamics: The shift in technological leadership will have profound implications for global economic power and influence.
The future distribution of technological leadership will significantly shape the global economic and political landscape in the coming decades.
Conclusion
The Great Decoupling is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon with significant ramifications for technological advancement. While it presents challenges, such as fragmented supply chains and reduced collaboration, it also accelerates domestic innovation. The long-term consequences remain to be seen, but understanding the dynamics of the Great Decoupling is crucial for navigating the future of technological leadership and global economic stability. Further research into the intricacies of the Great Decoupling and its impact on various technological sectors is essential to effectively manage its consequences and shape a more predictable and stable future for global technological development. Analyzing the specific repercussions of this technological decoupling is vital for policymakers and businesses alike.

Featured Posts
-
 Suncor Energy Record Production Despite Lower Sales Volumes
May 09, 2025
Suncor Energy Record Production Despite Lower Sales Volumes
May 09, 2025 -
 High Down Payments A Major Barrier To Homeownership In Canada
May 09, 2025
High Down Payments A Major Barrier To Homeownership In Canada
May 09, 2025 -
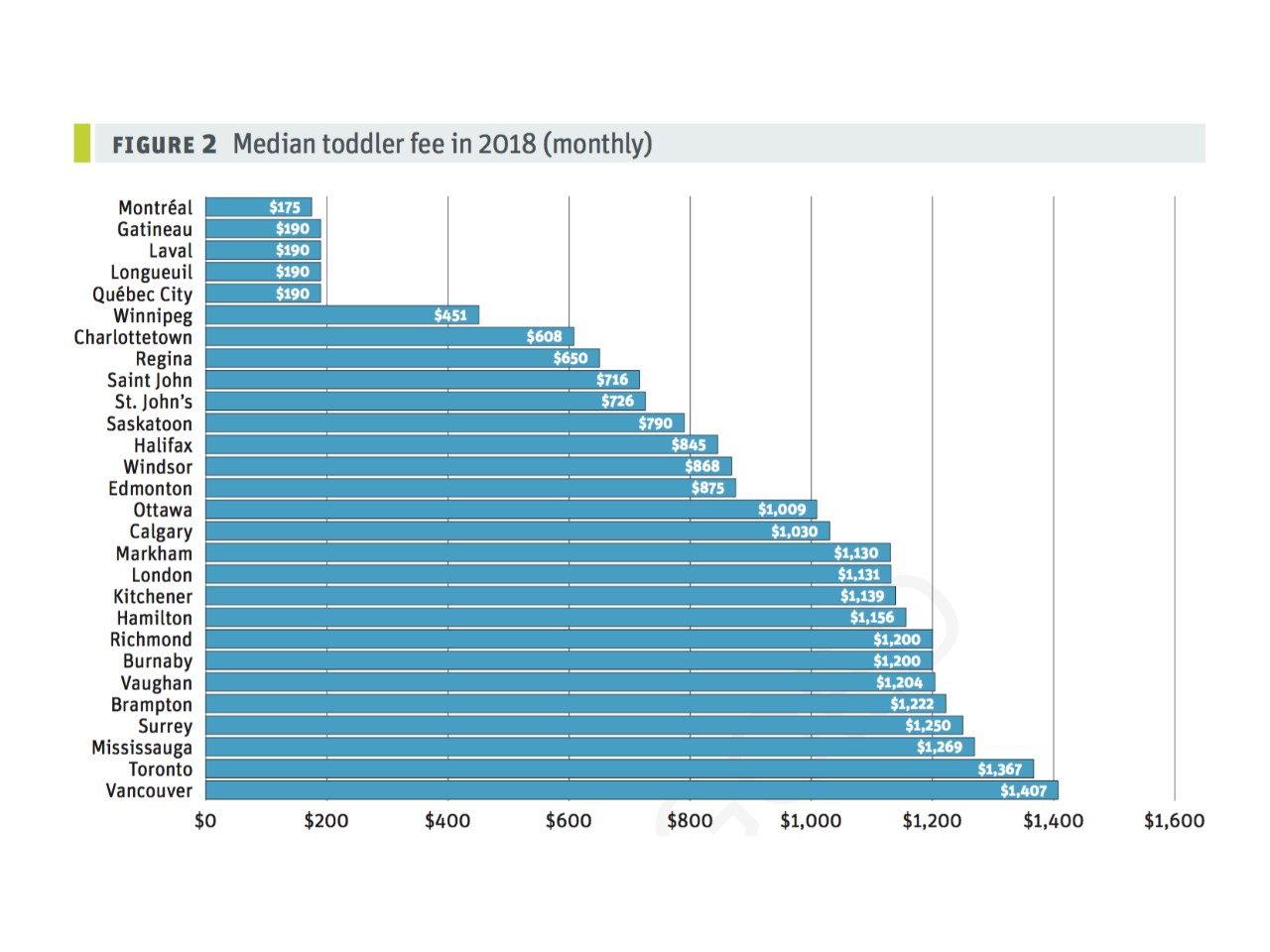 High Daycare Costs After Expensive Babysitting A Fathers Dilemma
May 09, 2025
High Daycare Costs After Expensive Babysitting A Fathers Dilemma
May 09, 2025 -
 Elizabeth Hurley Shows Off Her Figure In Maldives Bikini Photos
May 09, 2025
Elizabeth Hurley Shows Off Her Figure In Maldives Bikini Photos
May 09, 2025 -
 Nhs Staff Illegal Access Of Nottingham Stabbing Victim Records
May 09, 2025
Nhs Staff Illegal Access Of Nottingham Stabbing Victim Records
May 09, 2025
