The Impact Of Rising Federal Debt On Mortgage Lending And Interest Rates
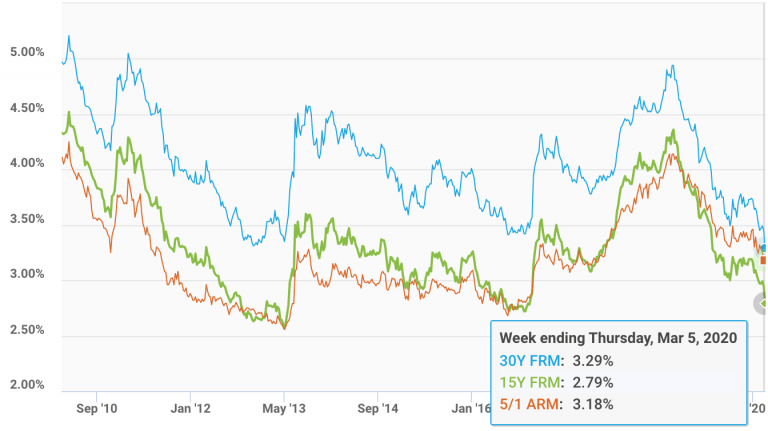
Table of Contents
How Federal Debt Influences Interest Rates
The relationship between federal debt and interest rates is fundamentally tied to the supply and demand of loanable funds. When the government borrows heavily to finance its spending, it increases the demand for these funds. This increased demand competes directly with private sector borrowing—businesses seeking loans for expansion, individuals seeking mortgages, and so on. This heightened competition pushes interest rates upward.
The Federal Reserve (the Fed), the central bank of the US, plays a crucial role in managing interest rates. To combat inflation often spurred by increased government spending (a consequence of high debt), the Fed may raise interest rates. This makes borrowing more expensive, aiming to cool down the economy. However, this also impacts mortgage rates.
- Increased government borrowing competes with private sector borrowing. This creates a scarcity of loanable funds, driving up prices (interest rates).
- Higher demand for loanable funds pushes interest rates up. This makes it more expensive for individuals and businesses to borrow money.
- Inflationary pressures from increased government spending can also lead to higher interest rates. The Fed responds to inflation by raising rates to curb excessive spending.
- Impact of the national debt on investor confidence and its effect on interest rates. High national debt can erode investor confidence, leading to higher interest rates as lenders demand higher returns to compensate for perceived increased risk.
The Impact of Rising Interest Rates on Mortgage Lending
Higher interest rates directly translate to higher mortgage payments. This reduced affordability significantly impacts the demand for mortgages. As borrowing becomes more expensive, fewer people can afford to buy homes, potentially leading to a slowdown or even a decline in the housing market. This ripple effect extends to related industries like construction and real estate.
- Higher rates increase monthly mortgage payments, making homes less affordable. This reduces the pool of potential homebuyers.
- Reduced demand can lead to a slowdown in the housing market. Prices may stagnate or even decline in a softening market.
- Potential impact on housing construction and related industries. Reduced demand for new homes can lead to decreased construction activity and job losses.
- Increased risk of mortgage defaults. Higher interest rates make it more challenging for borrowers to meet their monthly payments, increasing the likelihood of defaults.
Types of Mortgages Affected by Rising Rates
Different mortgage types react differently to interest rate changes. Fixed-rate mortgages offer stability, locking in an interest rate for the loan's duration. Adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs), on the other hand, have rates that fluctuate with market interest rates, making them more vulnerable to rising rates. Rising rates also affect refinancing options. When rates rise, refinancing to secure a lower rate becomes less attractive.
Government Policies and Their Influence
Government policies play a significant role in mitigating the effects of rising federal debt on mortgage lending and interest rates. Fiscal policies, such as government spending and taxation, directly influence the level of federal debt. Monetary policies, implemented by the Federal Reserve, primarily affect interest rates.
- Government intervention in the housing market (e.g., tax incentives, subsidies). These can stimulate demand and help make homes more affordable.
- Federal Reserve's monetary policy tools and their impact on interest rates. The Fed's actions influence the overall cost of borrowing.
- Government debt management strategies. Effective debt management can help to control the rate of debt accumulation and its impact on interest rates.
Predicting Future Trends and Their Implications
Predicting future trends requires considering various scenarios based on different levels of federal debt growth and the Federal Reserve's response. Sustained high interest rates could have significant long-term consequences for the economy.
- Potential long-term consequences of sustained high interest rates. These include slower economic growth, reduced investment, and potential recessions.
- Impact on economic growth and employment. High interest rates can stifle economic growth and lead to job losses.
- Forecasting models and their limitations. While forecasting models can provide insights, they are not perfect and are subject to various uncertainties.
Conclusion: Understanding the Impact of Rising Federal Debt on Your Mortgage
Rising federal debt significantly impacts mortgage lending and interest rates. Understanding this connection is vital for both homebuyers and lenders. Higher federal debt often leads to increased interest rates, making mortgages more expensive and potentially slowing the housing market. Homebuyers should carefully assess their affordability, plan for potential rate hikes, and explore various mortgage options. Lenders need to adapt to the changing market dynamics and manage their risk effectively. Stay informed about the impact of rising federal debt on mortgage interest rates, manage your mortgage effectively in a rising interest rate environment, and learn how rising federal debt affects your mortgage options. Proactive planning and financial literacy are key to navigating this complex landscape.

Featured Posts
-
 Eurovision 2025 Breitbarts Analysis Of Winners And Losers
May 19, 2025
Eurovision 2025 Breitbarts Analysis Of Winners And Losers
May 19, 2025 -
 Ufc 313 A Rookie Report Prospect Spotlight
May 19, 2025
Ufc 313 A Rookie Report Prospect Spotlight
May 19, 2025 -
 London Culture Faces Devastating Blow Court Case Threatens Major Festivals
May 19, 2025
London Culture Faces Devastating Blow Court Case Threatens Major Festivals
May 19, 2025 -
 College Baseball History Made Parker Byrds Inspiring Achievement
May 19, 2025
College Baseball History Made Parker Byrds Inspiring Achievement
May 19, 2025 -
 Azzi Fudd And Paige Bueckers Different Looks U Conn Vs Wnba Draft Night
May 19, 2025
Azzi Fudd And Paige Bueckers Different Looks U Conn Vs Wnba Draft Night
May 19, 2025
