The Implications Of US Solar Tariffs On Malaysia's Economy

Table of Contents
Disruption to Malaysia's Solar Energy Supply Chain
Malaysia's burgeoning solar energy sector relies heavily on a global supply chain. While the extent of Malaysian reliance on US-sourced solar components needs further investigation, any dependence would be significantly impacted by US solar tariffs. These tariffs lead to increased prices for solar panel imports, directly affecting the cost of solar energy projects within Malaysia. The implications are substantial:
- Increased costs for Malaysian solar projects: Higher import costs translate to higher project costs, making solar energy less competitive against traditional energy sources.
- Reduced competitiveness of Malaysian solar energy companies: Local companies face increased input costs, hindering their ability to compete effectively in both domestic and international markets.
- Potential delays in solar energy project completion: The uncertainty surrounding solar panel supply and pricing may cause delays in project timelines, impacting overall energy production goals.
- Impact on renewable energy targets set by the Malaysian government: The increased costs could jeopardize Malaysia's ambitious renewable energy targets, potentially slowing down the country's transition to a sustainable energy future. The Malaysian solar industry's growth trajectory is directly tied to the stability and affordability of its supply chain.
Impact on Malaysian Solar Manufacturers and Exporters
While Malaysia may not be a major exporter of solar products to the US, the US solar tariffs still indirectly affect Malaysian businesses. The tariffs create trade barriers, impacting market access and potentially reducing the competitiveness of Malaysian solar manufacturers in third-party markets. Companies that previously relied on the US market may experience:
- Reduced profitability for exporting companies: The loss of US market share directly impacts revenue and profitability.
- Potential job losses in the Malaysian solar industry: Reduced exports can lead to decreased production, potentially impacting employment within the sector.
- Need for diversification of export markets: Malaysian solar companies need to actively explore and develop new export markets to mitigate the impact of US tariffs. This requires strategic planning and investment in international market expansion. The Malaysian solar exports sector needs to adapt and diversify to secure its long-term viability.
Effects on Renewable Energy Adoption in Malaysia
The implications of US solar tariffs extend to the broader adoption of renewable energy in Malaysia. Higher solar energy costs, caused by the tariffs, could create a significant hurdle to achieving the country's sustainable energy goals. This may lead to:
- Increased costs hindering renewable energy transition: The increased cost of solar power could slow down the shift away from fossil fuels.
- Potential shift towards alternative renewable energy sources: Malaysia might explore alternative renewable energy sources, such as hydropower or wind power, which are less impacted by the US tariffs.
- Government policy responses to mitigate the impact: The Malaysian government might implement policies to support the solar industry and encourage renewable energy adoption, such as subsidies or tax incentives. Government intervention will be crucial in ensuring the continued growth of Malaysia's renewable energy sector.
Opportunities for Malaysian Businesses
While US solar tariffs pose significant challenges, they also present opportunities for Malaysian businesses. The increased costs of imported solar components could stimulate demand for domestically produced alternatives. This could lead to:
- Incentives for local solar component production: The government might introduce incentives to encourage local manufacturing, boosting the domestic solar industry.
- Investment opportunities in renewable energy technology: The need for a more resilient and locally sourced supply chain could attract investment in renewable energy technology within Malaysia.
- Growth of domestic solar installation companies: Local installation companies may benefit from increased demand as projects shift towards using domestically sourced components. This presents significant opportunities for growth and job creation within Malaysia.
Conclusion: Navigating the Challenges and Opportunities of US Solar Tariffs for Malaysia's Economy
The US solar tariffs present a complex challenge for Malaysia's economy. While the tariffs disrupt supply chains, increase costs, and potentially hinder renewable energy adoption, they also create opportunities for domestic manufacturing and technological advancement. The Malaysian solar industry needs to navigate these challenges strategically, diversifying export markets, seeking government support, and investing in local production. Further research into the specific impact of US solar tariffs on Malaysia is crucial, along with proactive engagement with government initiatives to ensure a sustainable future for the country's renewable energy sector. Understanding the complexities surrounding US solar tariffs is essential for both businesses and policymakers in Malaysia to make informed decisions and capitalize on emerging opportunities within the evolving renewable energy landscape.

Featured Posts
-
 Discover Jacob Alons New Song August Moon
May 30, 2025
Discover Jacob Alons New Song August Moon
May 30, 2025 -
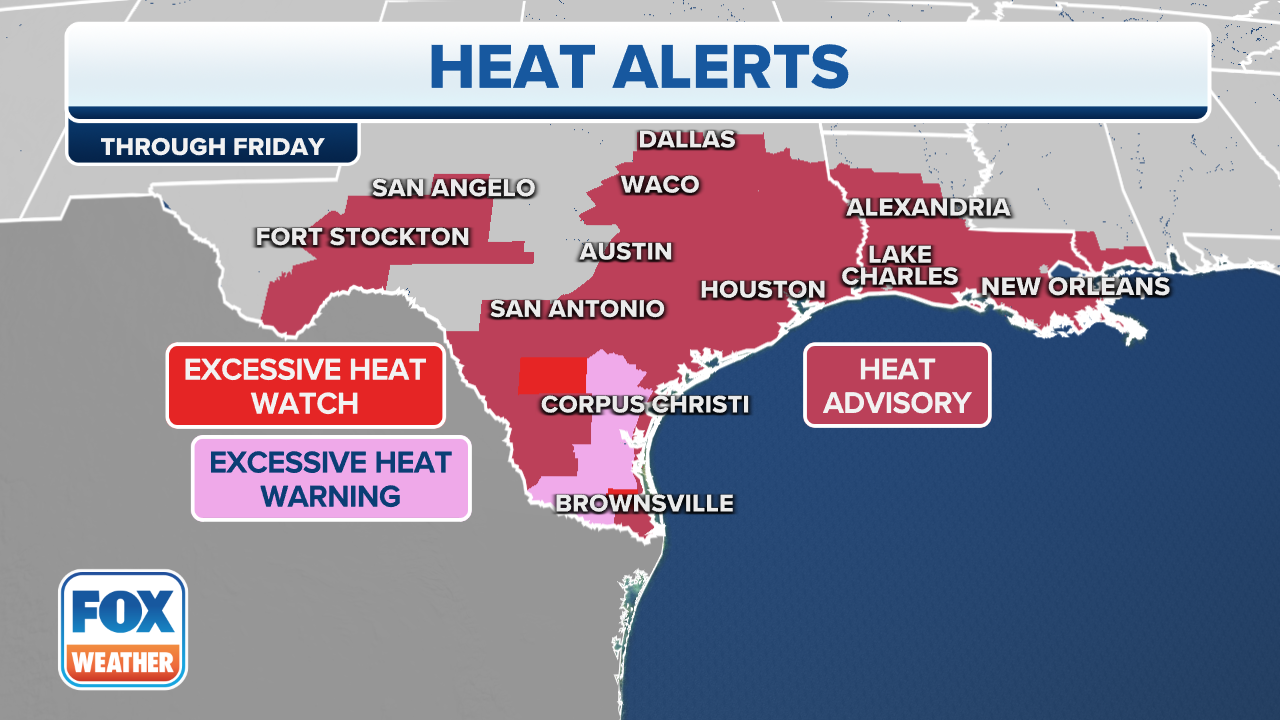 Texas Issues Heat Warning As Temperatures Expected To Soar To 111 F
May 30, 2025
Texas Issues Heat Warning As Temperatures Expected To Soar To 111 F
May 30, 2025 -
 Ai Driven Podcast Creation Transforming Repetitive Scatological Content
May 30, 2025
Ai Driven Podcast Creation Transforming Repetitive Scatological Content
May 30, 2025 -
 Pegula Vs Alexandrova Charleston Open Final Showdown
May 30, 2025
Pegula Vs Alexandrova Charleston Open Final Showdown
May 30, 2025 -
 Fwz Tarykhy Ldyl Twrw Fy Jyrw Iytalya Njah Bahr Llmksyk
May 30, 2025
Fwz Tarykhy Ldyl Twrw Fy Jyrw Iytalya Njah Bahr Llmksyk
May 30, 2025
