The Student Loan Crisis And Its Economic Ramifications
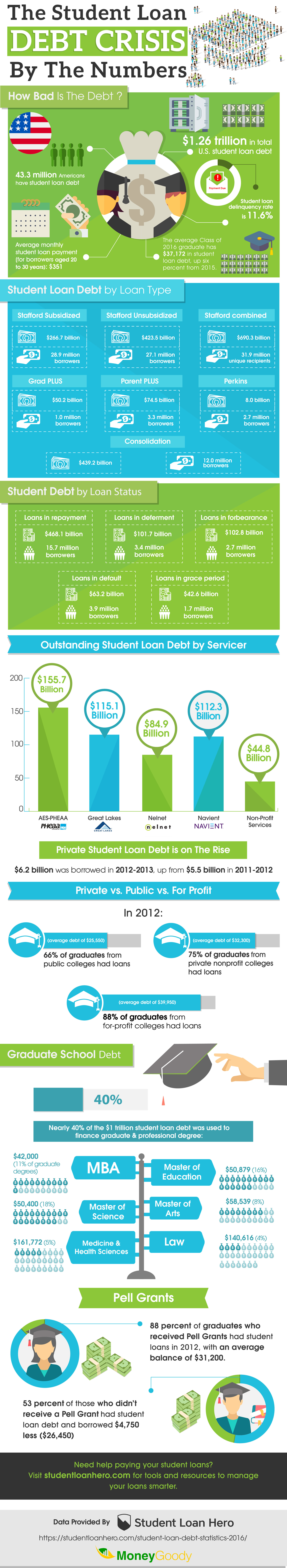
Table of Contents
The Growing Burden of Student Loan Debt
Rising Tuition Costs and Increased Borrowing
The escalating cost of higher education is a primary driver of the student debt crisis. Tuition fees at both public and private universities have increased significantly over the past decade, far outpacing inflation. This has forced students to borrow larger sums to finance their education.
- Tuition increases: Over the past 10 years, tuition at many public universities has increased by over 50%, and private universities have seen even steeper rises.
- Government funding cuts: Reduced government funding for higher education has shifted a larger burden of costs onto students and their families.
- Rising cost of living: The increased cost of housing, books, and other living expenses further exacerbates the financial strain on students.
Demographic Trends in Student Loan Debt
The student loan crisis disproportionately impacts certain demographics. Low-income students and minority groups often face greater challenges in accessing financial aid and are more likely to rely heavily on student loans.
- Debt disparities: Studies consistently show that Black and Hispanic borrowers have significantly higher debt burdens than white borrowers, even when controlling for factors such as education level and income.
- Access to resources: Limited access to financial literacy resources and family support contributes to higher levels of debt among certain groups.
The Psychological Impact of Student Loan Debt
The weight of significant student loan debt extends beyond financial hardship; it takes a substantial toll on mental health.
- Increased stress and anxiety: The constant pressure of loan repayments can lead to chronic stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Delayed life milestones: Many young adults postpone major life decisions like marriage, homeownership, and starting a family due to student loan burdens.
Economic Consequences of the Student Loan Crisis
Impact on Consumer Spending and Economic Growth
High student loan debt significantly impacts consumer spending and overall economic growth. The large monthly payments reduce disposable income, limiting spending on other goods and services.
- Reduced discretionary income: Student loan payments often consume a substantial portion of a borrower's income, leaving little room for discretionary spending.
- Delayed major purchases: Young adults are delaying major purchases like homes and cars due to the financial constraints imposed by student loan debt.
- Impact on GDP: Reduced consumer spending directly translates to lower economic growth and hampers the overall health of the economy.
Effects on the Housing Market
The student loan crisis is also impacting the housing market. The difficulty in securing mortgages with high student loan debt reduces homeownership rates among young adults.
- Difficulty qualifying for mortgages: Lenders often consider student loan debt when assessing mortgage applications, making it difficult for some borrowers to qualify.
- Lower home purchase rates: The rising student loan debt burden contributes to lower homeownership rates among young adults compared to previous generations.
- Impact on housing demand: This decreased demand influences housing prices and overall market stability.
Implications for Entrepreneurship and Innovation
The significant student loan burden discourages entrepreneurship and innovation. The fear of financial risk associated with starting a business can dissuade graduates from pursuing their entrepreneurial dreams.
- Reluctance to take risks: The financial pressure of student loan repayment makes it difficult for graduates to take the financial risks associated with starting a new business.
- Less funding available: Entrepreneurs burdened with student loan debt may struggle to secure additional funding to grow their businesses.
- Brain drain: Graduates may opt for higher-paying, less risky jobs instead of pursuing their passions or innovative ideas.
Potential Solutions and Policy Interventions
Government Policies to Address Student Loan Debt
Various policy interventions could help mitigate the student loan crisis. These include loan forgiveness programs, tuition reform, and increased funding for financial aid.
- Loan forgiveness programs: Targeted loan forgiveness programs for specific borrowers or professions could provide significant relief.
- Tuition reform: Policies that control tuition increases and make college more affordable are crucial.
- Increased financial aid: Expanding access to grants and scholarships can reduce reliance on loans.
Role of Educational Institutions in Reducing Costs
Educational institutions also play a critical role in addressing affordability. They can invest in online learning to reduce operational costs and explore alternative funding models.
- Increased transparency in tuition costs: Universities should increase transparency around tuition costs and the overall value of their education.
- Investment in online learning: Expanding access to affordable online courses can help reduce the overall cost of education.
- Exploring alternative funding models: Universities can explore innovative funding models to reduce reliance on tuition fees.
Financial Literacy and Responsible Borrowing
Educating students about responsible borrowing and financial planning is essential to prevent future problems.
- Understanding loan terms: Students need to understand the terms and conditions of their student loans before signing.
- Budgeting and financial planning: Financial literacy programs can help students develop effective budgeting and financial planning skills.
- Exploring alternative funding options: Students should be made aware of alternative funding options such as scholarships and grants.
Conclusion: Navigating the Student Loan Crisis – A Call to Action
The student loan crisis poses a serious threat to individual well-being and the overall economy. The rising cost of tuition, combined with limited financial aid and a lack of financial literacy, has created a significant burden on millions of Americans. Addressing this crisis requires a multi-pronged approach, including government policy changes, institutional reforms, and a focus on responsible borrowing. We must actively seek solutions for student loan debt relief and student loan forgiveness, promoting financial literacy programs to help individuals manage student loan debt effectively. Learn more about the student loan crisis solutions available and advocate for changes that will create a more equitable and affordable higher education system for future generations. Take action today to help navigate this ongoing student loan crisis.

Featured Posts
-
 Cuaca Semarang Besok 22 4 Peringatan Hujan Siang Hari Di Jawa Tengah
May 28, 2025
Cuaca Semarang Besok 22 4 Peringatan Hujan Siang Hari Di Jawa Tengah
May 28, 2025 -
 Nato Allies Closer To 5 Defense Spending Goal Stoltenberg
May 28, 2025
Nato Allies Closer To 5 Defense Spending Goal Stoltenberg
May 28, 2025 -
 Saudia Buka Rute Baru Bali Jeddah
May 28, 2025
Saudia Buka Rute Baru Bali Jeddah
May 28, 2025 -
 Giannis And Pacers Player Heated Exchange After Bucks Loss
May 28, 2025
Giannis And Pacers Player Heated Exchange After Bucks Loss
May 28, 2025 -
 Mathurin Injury Impacts Pacers Matchup Against The Kings
May 28, 2025
Mathurin Injury Impacts Pacers Matchup Against The Kings
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Preventa Bad Bunny Consigue Tus Entradas En Ticketmaster Y Live Nation
May 30, 2025
Preventa Bad Bunny Consigue Tus Entradas En Ticketmaster Y Live Nation
May 30, 2025 -
 Entradas Bad Bunny Conciertos Madrid Y Barcelona Preventa Live Nation
May 30, 2025
Entradas Bad Bunny Conciertos Madrid Y Barcelona Preventa Live Nation
May 30, 2025 -
 Setlist Fm Y Ticketmaster Nueva Integracion Para Una Mejor Gestion De Conciertos
May 30, 2025
Setlist Fm Y Ticketmaster Nueva Integracion Para Una Mejor Gestion De Conciertos
May 30, 2025 -
 Integracion De Setlist Fm Y Ticketmaster Beneficios Para Los Amantes De La Musica
May 30, 2025
Integracion De Setlist Fm Y Ticketmaster Beneficios Para Los Amantes De La Musica
May 30, 2025 -
 Experiencia Mejorada Para Fans Setlist Fm Se Integra Con Ticketmaster
May 30, 2025
Experiencia Mejorada Para Fans Setlist Fm Se Integra Con Ticketmaster
May 30, 2025
