Tracking The Spread: A New COVID-19 Variant And The Global Increase In Infections
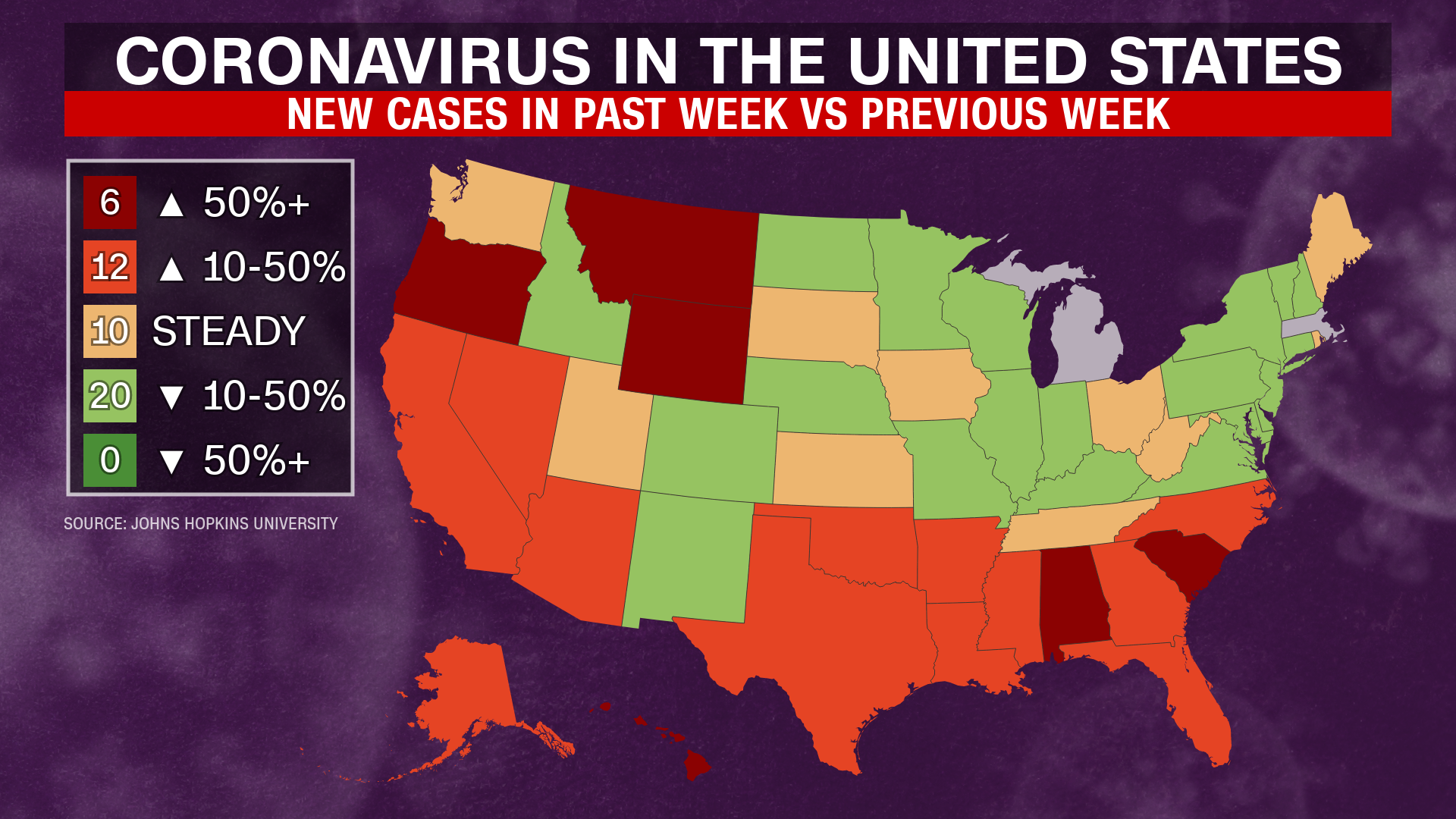
Table of Contents
Understanding the New COVID-19 Variant
Origin and Key Characteristics
The XBB.1.16 variant (replace with actual variant name) was first identified in [Location of origin] in [Date]. While the exact animal source remains under investigation, its genetic makeup suggests potential links to [mention potential links, if any]. Key mutations include:
- [Mutation 1]: This mutation is believed to enhance the variant's ability to bind to human cells, potentially increasing its transmissibility.
- [Mutation 2]: This mutation may affect the variant's ability to evade the immune response triggered by previous infections or vaccinations.
- [Mutation 3]: Studies suggest this mutation could influence the severity of illness caused by the variant.
These mutations, supported by research from [cite scientific studies and sources], contribute to the variant's unique characteristics and its ability to spread rapidly.
Transmissibility and Severity
Early evidence suggests that XBB.1.16 (or the actual variant name) is significantly more transmissible than previous variants like Delta and Omicron subvariants. Studies indicate a [percentage]% increase in transmissibility compared to [previous variant]. This increased contagiousness leads to rapid spread within communities.
Data suggests that while the severity of illness caused by this variant appears [more/less/similar] severe compared to previous variants, further research is needed to fully understand its impact on hospitalization rates and mortality. Initial data shows a [percentage]% increase/decrease in hospitalization rates compared to [previous variant] in [specific location].
Global Impact of the New COVID-19 Variant
Regional Spread and Infection Rates
The XBB.1.16 variant (or actual variant name) is exhibiting a widespread global distribution. [Use a map or chart to visually represent the spread – this would require an image insertion into the article]. Regions showing the highest infection rates include [list regions/countries with highest infection rates, including specific data on infection rates]. Factors contributing to its rapid spread include increased international travel, high population density in urban areas, and varying levels of vaccination rates across different regions. For example, [Country A] experienced a [percentage]% surge in cases within [timeframe], while [Country B] saw a more moderate increase.
Strain on Healthcare Systems
The surge in infections caused by this new COVID-19 variant is putting significant strain on healthcare systems worldwide. Many hospitals in [list affected regions/countries] are experiencing increased patient loads, leading to:
- Overburdened hospital capacity: Hospitals are reaching maximum capacity, delaying treatment for both COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 patients.
- Staffing shortages: Healthcare workers are facing burnout and exhaustion, impacting the quality of care.
- Shortages of medical resources: There are potential shortages of essential medical supplies, including ventilators, beds, and personal protective equipment.
Global Response to the New COVID-19 Variant
Public Health Measures
Governments and public health organizations globally are responding to the emergence of this new COVID-19 variant by implementing various measures, including:
- Renewed emphasis on vaccination campaigns: Boosters and updated vaccines are being promoted to increase population immunity.
- Mask mandates (where applicable): Some regions are reintroducing mask mandates in indoor settings to curb transmission.
- Enhanced surveillance and testing: Increased testing and genomic sequencing are being implemented to track the variant’s spread and evolution.
- Travel advisories and restrictions (where applicable): Some countries may implement travel restrictions to limit the international spread.
The effectiveness of these measures varies depending on local contexts and adherence to guidelines.
Vaccine Effectiveness and Development
While existing COVID-19 vaccines still offer some protection against severe illness and hospitalization, their effectiveness against XBB.1.16 (or the actual variant name) may be reduced. Studies indicate a [percentage]% reduction in vaccine efficacy compared to [previous variant]. Research is underway to develop updated vaccines tailored to address this new variant, and the development of new antiviral treatments continues.
Conclusion
The emergence of this new COVID-19 variant highlights the ongoing challenges posed by the pandemic. Its increased transmissibility and potential to strain healthcare systems necessitate a robust global response. The key takeaways include the variant's rapid spread, the significant impact on healthcare systems, and the need for continued vigilance in following public health guidelines. Continue tracking the spread of this COVID-19 variant by consulting reliable sources such as the WHO ([link to WHO]) and the CDC ([link to CDC]). Stay informed about the latest developments regarding this new COVID-19 variant and its impact, and take proactive steps to protect yourself and your community. Remember that vaccination remains a crucial tool in mitigating the severity of infection.

Featured Posts
-
 La Receta Facil Y Sabrosa De Lasana De Calabacin De Pablo Ojeda Mas Vale Tarde
May 31, 2025
La Receta Facil Y Sabrosa De Lasana De Calabacin De Pablo Ojeda Mas Vale Tarde
May 31, 2025 -
 Partenariat Sanofi Dren Bio Un Anticorps Prometteur
May 31, 2025
Partenariat Sanofi Dren Bio Un Anticorps Prometteur
May 31, 2025 -
 Ex Nypd Commissioner Bernard Kerik Hospitalized Full Recovery Expected
May 31, 2025
Ex Nypd Commissioner Bernard Kerik Hospitalized Full Recovery Expected
May 31, 2025 -
 New Covid 19 Variant Driving Up Case Numbers In Several Regions According To Who
May 31, 2025
New Covid 19 Variant Driving Up Case Numbers In Several Regions According To Who
May 31, 2025 -
 My Dragons Den Experience Whats Real And Whats Not
May 31, 2025
My Dragons Den Experience Whats Real And Whats Not
May 31, 2025
