U.S. Measles Outbreak: Latest Case Numbers And Locations
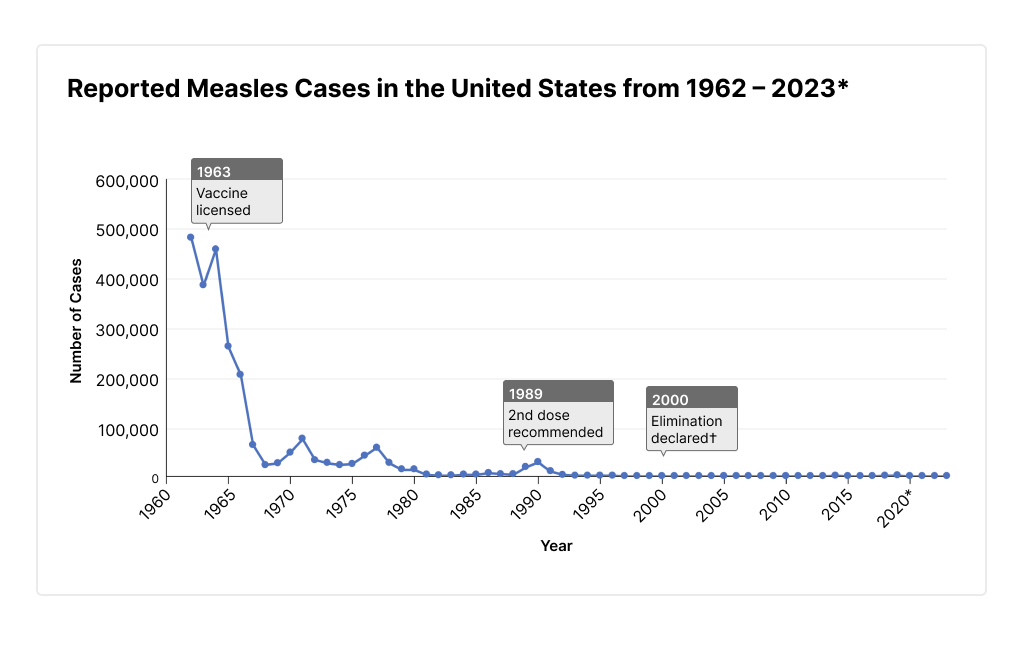
Table of Contents
Current Measles Case Numbers in the U.S.
The overall number of measles cases reported nationally is a serious indicator of the ongoing outbreak. While precise, up-to-the-minute numbers fluctuate, official sources like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provide regular updates. It's crucial to consult these sources for the most current data on the U.S. measles outbreak. Comparing these numbers to previous years reveals a significant increase, highlighting the severity of the current situation.
- Total confirmed cases (as of October 26, 2023): [Insert most recent data from the CDC – Note: This information needs to be updated regularly to maintain accuracy]
- Case numbers broken down by state (example): [Insert state-level data from the CDC – Note: This information needs to be updated regularly to maintain accuracy. Prioritize states with the highest numbers, e.g., "New York has reported X cases, while California has seen Y."]
- Age demographics of affected individuals: A concerning trend shows a higher-than-expected number of cases in older age groups, highlighting potential gaps in vaccine coverage amongst adults. [Insert data on age demographics if available from the CDC. Note: This information needs to be updated regularly to maintain accuracy ]
- Source of data: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), State Health Departments.
Geographic Distribution of Measles Cases
The spread of the measles outbreak is not uniform across the United States. Certain regions and states are experiencing significantly higher caseloads than others. Understanding this geographic distribution is vital for targeted public health interventions. Areas with high concentrations of cases often share common factors, such as lower vaccination rates or higher population density.
- States with the highest number of cases: [Insert list of states with the highest number of measles cases, citing the CDC as the source. Note: This information needs to be updated regularly to maintain accuracy]
- Counties/cities with notable outbreaks: [List specific locations experiencing significant outbreaks. Note: This information needs to be updated regularly to maintain accuracy]
- Reasons for geographic clustering: Lower vaccination rates in certain communities, higher population density leading to increased transmission, and outbreaks in specific schools or religious groups are potential contributing factors.
- CDC Map: [Insert a link to the CDC map showing the geographical distribution of measles cases, if available.]
Understanding the Risks of Measles
Measles is a highly contagious viral illness that poses serious health risks, especially to vulnerable populations like infants and those with compromised immune systems. Understanding its severity emphasizes the importance of prevention.
- Symptoms of Measles: High fever, cough, runny nose, conjunctivitis (pink eye), and a characteristic red, blotchy rash are common symptoms.
- Potential Complications: Pneumonia, encephalitis (brain swelling), and even death are potential, though rare, complications of measles.
- Contagiousness: Measles is incredibly contagious, spreading easily through the air through coughing and sneezing. An infected person can spread the virus to others several days before symptoms appear.
- Vaccine Effectiveness: The MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccine is highly effective in preventing measles, offering strong protection against infection.
Prevention and Vaccination
Vaccination remains the most effective strategy to prevent measles outbreaks and protect public health. The MMR vaccine is safe and highly effective, significantly reducing the risk of infection.
- Recommended Age for Vaccination: Two doses of the MMR vaccine are recommended, typically administered at 12-15 months and 4-6 years of age.
- MMR Vaccine: This combined vaccine protects against measles, mumps, and rubella, three highly contagious diseases.
- Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy: Concerns about vaccine safety are often raised, but extensive research demonstrates the safety and efficacy of the MMR vaccine. Addressing these concerns with factual information is crucial.
- Resources for Vaccination: [Include links to resources where people can find vaccination services, such as the CDC website or their local health department.]
Conclusion
The current U.S. measles outbreak underscores the critical importance of vaccination. The latest case numbers and geographic distribution highlight the need for increased vigilance and proactive preventative measures. The high contagiousness of measles and the potential for serious complications emphasize the urgency of ensuring high vaccination rates across the country. Understanding the risks and taking steps to protect yourself and your community is paramount.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the latest updates on the U.S. measles outbreak by regularly checking the CDC website and your local health department. Protect yourself and your community by ensuring you and your family are up-to-date on your measles vaccinations. Contact your doctor to schedule your MMR vaccine today and help stop the spread of the U.S. measles outbreak.

Featured Posts
-
 Ruuds Knee Injury Costs Him French Open Match Against Borges
May 30, 2025
Ruuds Knee Injury Costs Him French Open Match Against Borges
May 30, 2025 -
 Affaire Rn Verdict En Appel Prevu Pour 2026 Reaction De Jacobelli
May 30, 2025
Affaire Rn Verdict En Appel Prevu Pour 2026 Reaction De Jacobelli
May 30, 2025 -
 Plires Programma Tileorasis Gia Tin Kyriaki 16 3
May 30, 2025
Plires Programma Tileorasis Gia Tin Kyriaki 16 3
May 30, 2025 -
 Ticketmasters New Queue System Where Do You Stand For Taylor Swift Tickets
May 30, 2025
Ticketmasters New Queue System Where Do You Stand For Taylor Swift Tickets
May 30, 2025 -
 Understanding San Diego Airport Flight Delays Causes And Solutions
May 30, 2025
Understanding San Diego Airport Flight Delays Causes And Solutions
May 30, 2025
