Understanding The Spread: The Impact Of The New COVID-19 Variant On Case Numbers

Table of Contents
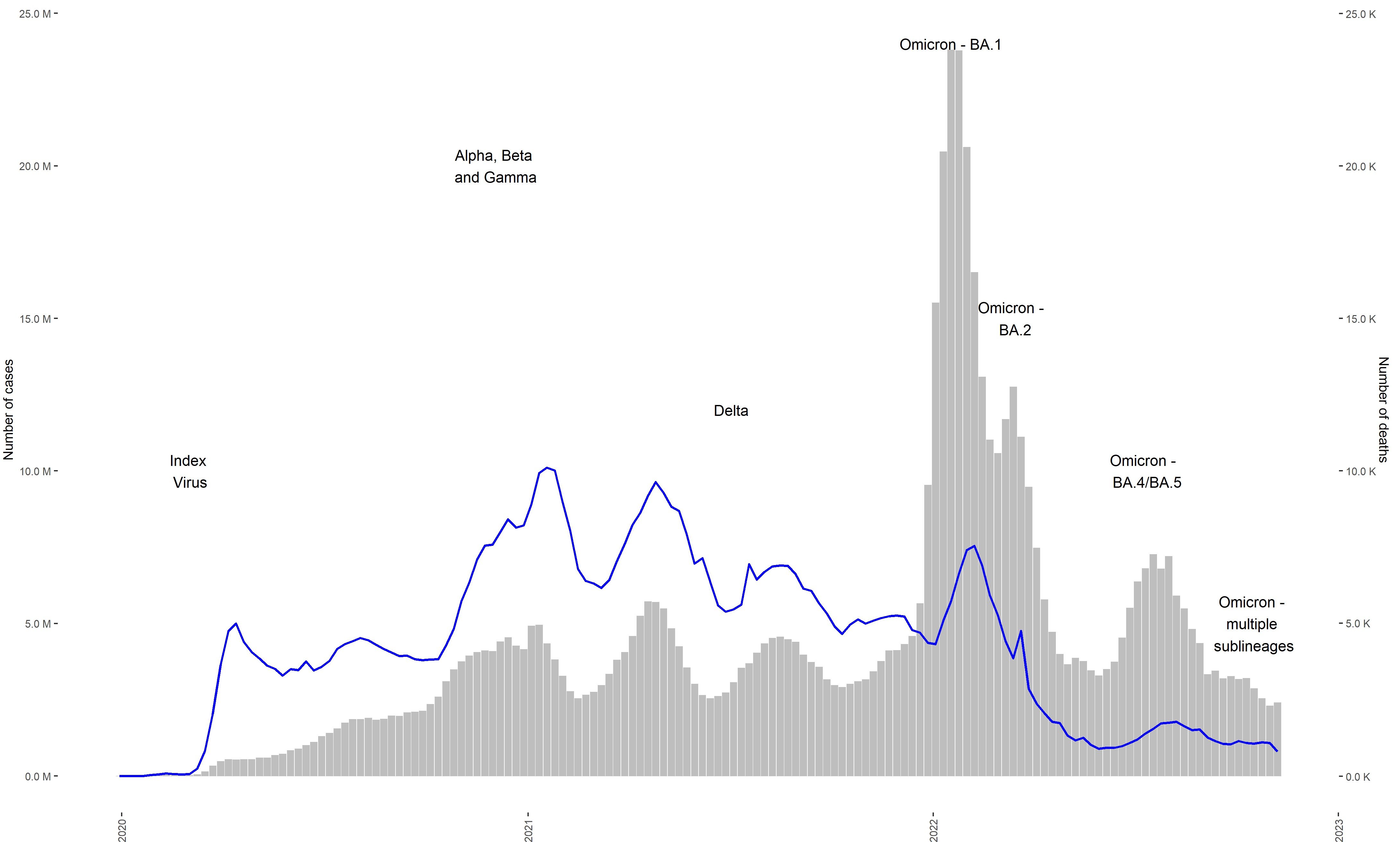
Transmission Rates and the New Variant
Increased/Decreased Transmissibility
The XBB.1.5 variant, like many preceding variants, has demonstrated notable changes in transmissibility compared to its predecessors. Understanding this change is key to predicting and mitigating future outbreaks. The basic reproduction number (R0), a crucial epidemiological metric, provides insight into the contagiousness of a virus. A higher R0 indicates greater transmissibility.
- Comparison of R0 values across different variants: Early data suggests XBB.1.5 exhibits a higher R0 than Omicron BA.5, meaning it spreads more easily. Precise figures vary depending on the study and location, but the trend towards increased transmissibility is consistent. Further research is needed to refine these estimates.
- Discussion of mutations impacting transmissibility: Specific mutations in the spike protein of XBB.1.5 are believed to contribute to its enhanced ability to bind to human cells and evade immune responses. These mutations, such as those in the receptor-binding domain (RBD), are under active investigation.
- Data sources and methodology for calculating R0: R0 estimations rely on complex epidemiological modeling, using data from confirmed cases, contact tracing, and genomic sequencing. Variations in data collection and modeling techniques can lead to slight discrepancies in reported R0 values.
Incubation Period and Symptoms
While the incubation period for XBB.1.5 remains largely similar to previous Omicron subvariants (typically 2-7 days), subtle differences in symptoms have been reported anecdotally. However, rigorous scientific data comparing symptom profiles across variants is still under development.
- Comparison of incubation periods: Currently, there's no significant evidence suggesting a drastic alteration in the incubation period for XBB.1.5.
- Analysis of reported symptom differences: Reports suggest that while symptoms remain largely consistent with previous variants (cough, fever, fatigue, etc.), some individuals have described a higher prevalence of certain symptoms, such as sore throat. More robust studies are necessary to confirm these observations.
- Prevalence of asymptomatic cases: As with earlier variants, a significant proportion of XBB.1.5 infections may be asymptomatic, making the accurate tracking and containment of the COVID-19 variant spread more challenging.
Impact on Hospitalizations and Deaths
Severity of Infection
Early evidence suggests that XBB.1.5 does not significantly increase the severity of illness compared to previous Omicron subvariants. However, the sheer increase in case numbers due to its higher transmissibility can still place considerable strain on healthcare systems.
- Data on hospitalization rates for the new variant: While hospitalization rates may appear higher overall due to increased transmission, the rate of hospitalization per infection hasn't shown a substantial increase compared to previous Omicron variants.
- Mortality rates compared to previous variants: Similarly, mortality rates associated with XBB.1.5 infection have not shown a marked increase compared to previous variants.
- Factors influencing disease severity: Individual factors, such as vaccination status, pre-existing health conditions (including age), and access to timely medical care, continue to significantly influence the severity of COVID-19 outcomes.
Strain on Healthcare Systems
The surge in infections caused by the higher transmissibility of XBB.1.5 can overwhelm healthcare systems, regardless of the severity of individual cases.
- Impact on hospital bed occupancy: Increased case numbers directly translate to increased demand for hospital beds, potentially leading to delays in care for other conditions.
- Shortages of medical staff and resources: Sustained high levels of COVID-19 cases can lead to burnout and shortages among healthcare professionals, compromising the quality of care.
- Regional variations in healthcare system capacity: The impact on healthcare systems varies significantly depending on factors such as existing healthcare infrastructure, access to resources, and vaccination rates within specific regions.
Effectiveness of Existing Countermeasures
Vaccine Efficacy
While existing COVID-19 vaccines are still effective in reducing the risk of severe illness and hospitalization from XBB.1.5, their effectiveness against infection might be somewhat reduced compared to earlier variants.
- Vaccine efficacy data against the new variant: Studies consistently demonstrate that vaccination remains a crucial tool in preventing severe disease, hospitalization, and death, even with emerging variants.
- Need for booster shots or updated vaccines: Booster shots, and updated vaccines tailored to the prevalent variants, are essential to maintain high levels of protection against infection and severe disease.
- Potential for vaccine escape mutations: The ongoing evolution of the virus necessitates continuous monitoring and potential adaptations in vaccine strategies to address emerging vaccine escape mutations.
Effectiveness of Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions
Non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) remain a critical tool in managing COVID-19 spread, even with the emergence of new variants.
- Effectiveness of mask mandates: Mask-wearing in high-risk settings continues to be an effective measure in reducing transmission.
- Impact of social distancing measures: Social distancing, while sometimes difficult to maintain consistently, helps to reduce contact and therefore transmission.
- Role of rapid testing and contact tracing: Rapid testing and effective contact tracing are essential for early identification and isolation of infected individuals, limiting further spread of the COVID-19 variant.
Conclusion
The emergence of new COVID-19 variants like XBB.1.5 significantly impacts case numbers and public health strategies. Understanding the unique characteristics of each variant – including transmissibility, severity, and response to vaccines and NPIs – is critical for effective pandemic management. Continued monitoring of the COVID-19 variant spread, along with proactive measures like vaccination, booster shots, and the implementation of appropriate public health interventions, are essential to mitigate the impact of future variants. Staying informed about the latest developments regarding the COVID-19 variant spread is crucial for personal safety and community well-being. Therefore, continue to consult reliable sources like the WHO and CDC for updated information on COVID-19 variant spread and implement recommended preventative measures. Understanding the complexities of COVID-19 variant spread is an ongoing process, requiring continuous vigilance and adaptation.

Featured Posts
-
 Former Mlb Player Brandon Inge Coaches In Kalamazoo
May 31, 2025
Former Mlb Player Brandon Inge Coaches In Kalamazoo
May 31, 2025 -
 Global Covid 19 Update Concerns Over A New Variant
May 31, 2025
Global Covid 19 Update Concerns Over A New Variant
May 31, 2025 -
 Pro Motocross News Chase Sexton Missing Hangtown National
May 31, 2025
Pro Motocross News Chase Sexton Missing Hangtown National
May 31, 2025 -
 Enhance Your Weather Knowledge Tom Atkins Spring Skywarn Class
May 31, 2025
Enhance Your Weather Knowledge Tom Atkins Spring Skywarn Class
May 31, 2025 -
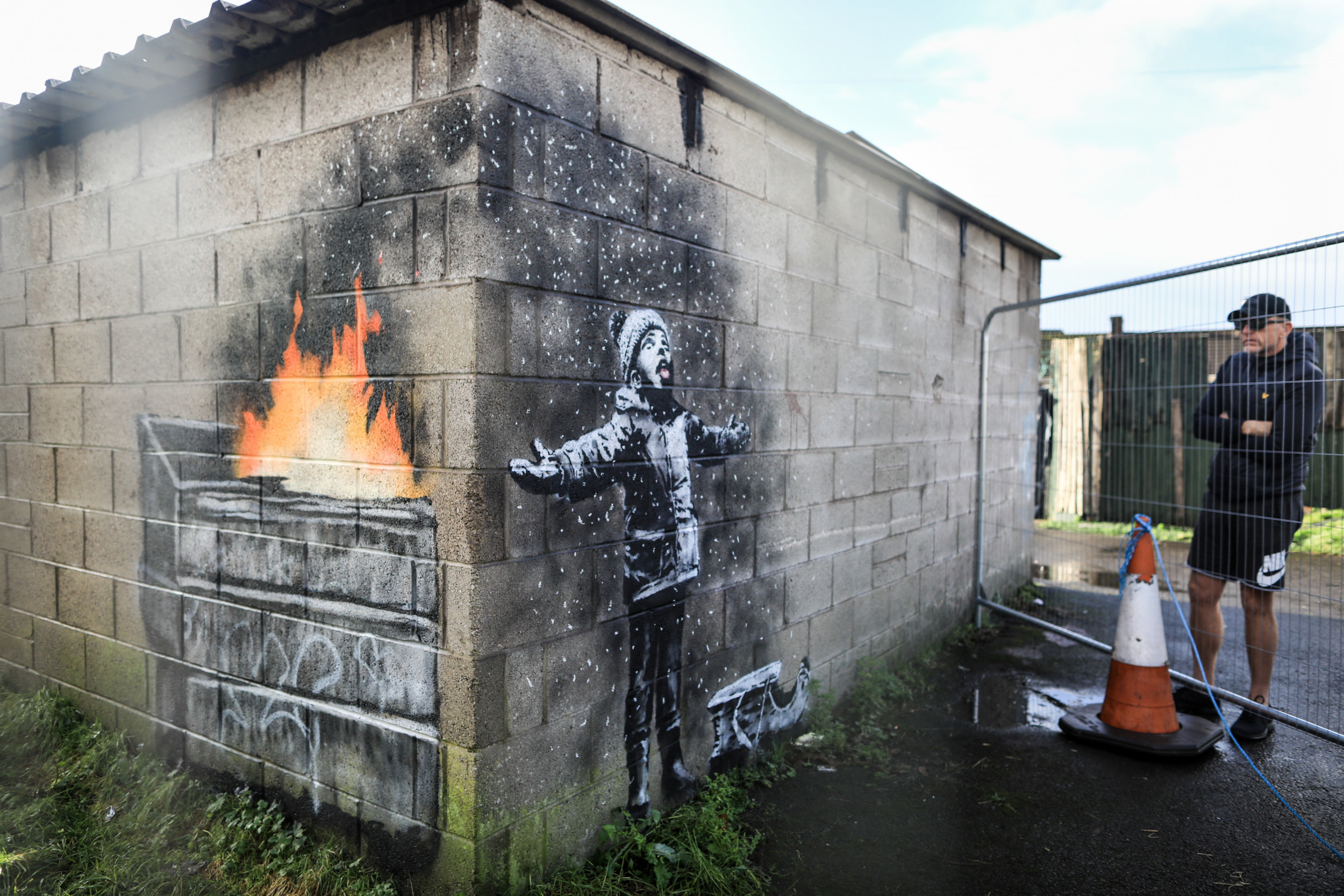 Unidentified Tag On Banksy Artwork Sale Details Revealed
May 31, 2025
Unidentified Tag On Banksy Artwork Sale Details Revealed
May 31, 2025
