Understanding The Wonder Of Animals: Their Habitats And Behaviors
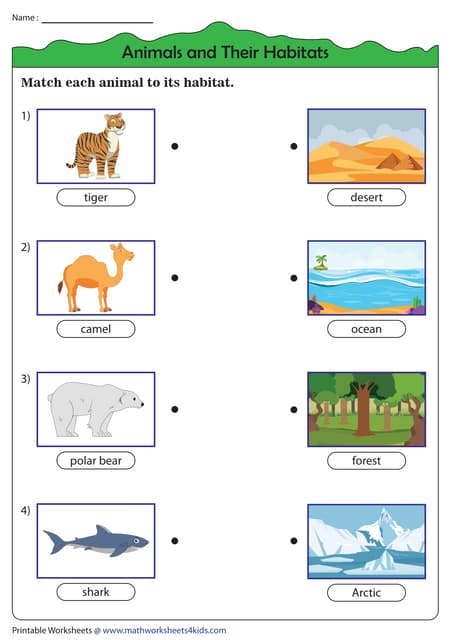
Table of Contents
Animal Habitats: A Diverse Landscape
Defining Animal Habitats
An animal's habitat is more than just its location; it's the complex interplay of factors necessary for its survival. This includes its food sources, access to shelter from predators and the elements, a reliable water supply, and a suitable climate. Without these essential components, an animal's ability to thrive is severely compromised.
-
Examples of Different Habitat Types:
- Forests: Characterized by dense tree cover, offering shelter and food for a wide range of animals, from insects to large mammals. Forest habitats vary greatly depending on climate, from tropical rainforests to boreal forests.
- Deserts: Extremely arid environments with sparse vegetation. Animals living in deserts have unique adaptations to conserve water and withstand extreme temperatures.
- Oceans: Vast aquatic habitats supporting an incredible diversity of marine life. Different zones within the ocean, from shallow coastal regions to deep-sea trenches, provide unique habitats for specialized organisms.
- Grasslands: Open areas dominated by grasses and herbs, supporting grazing animals and a variety of predators. Grasslands can range from prairies to savannas.
-
Habitat Loss and its Impact: Human activities are significantly impacting animal habitats worldwide. Deforestation, pollution (including water and air pollution), and climate change are leading to habitat loss and fragmentation, threatening countless species with extinction. These factors disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems and force animals to adapt or perish.
Adaptations to Specific Habitats
Animals exhibit remarkable adaptations that allow them to thrive in their specific environments. These adaptations can be physical, behavioral, or both.
-
Examples of Adaptations:
- Camouflage: The arctic fox's white fur provides excellent camouflage in snowy environments, helping it evade predators and ambush prey. Similarly, chameleons change their skin color to blend in with their surroundings.
- Specialized Diets: Giant pandas have evolved a specialized digestive system enabling them to subsist primarily on bamboo, a low-nutrient food source. Hummingbirds' long beaks allow them to reach nectar deep within flowers.
- Physical Adaptations: Camels possess humps for storing fat, providing energy and water during periods of scarcity in desert environments. Penguins have thick blubber layers for insulation in freezing Antarctic waters.
-
Niche and Habitat Occupancy: Each animal occupies a specific niche within its habitat, representing its role and interactions with other species and the environment. This niche reflects its food sources, its predators, its competitors, and its impact on the ecosystem.
Understanding Animal Behaviors: A Complex World
Types of Animal Behaviors
Animal behavior is incredibly diverse and complex, ranging from simple reflexes to sophisticated social interactions. Behaviors can be broadly categorized as innate (instinctive) or learned.
-
Innate vs. Learned Behaviors:
- Innate Behaviors: Migration is an example of innate behavior; birds instinctively know the routes and timing for their annual migrations. Hibernation, a period of dormancy during cold weather, is another example found in several mammals.
- Learned Behaviors: Hunting techniques, such as stalking prey or using tools, are often learned through observation and experience. Some primates display intricate tool use, demonstrating impressive cognitive abilities.
-
Communication in Animals: Animals communicate using various methods, including visual signals (body language, displays), auditory signals (vocalizations, calls), and chemical signals (pheromones). These communication systems are crucial for mating, territorial defense, and social interactions.
Social Structures and Interactions
Animals exhibit diverse social structures, ranging from solitary lifestyles to complex societies.
-
Social Structures and Interactions:
- Packs (Wolves): Wolves live in packs with a hierarchical structure, characterized by cooperation in hunting and defense.
- Herds (Zebras): Zebras live in herds for protection against predators, with individuals benefiting from increased vigilance and collective defense.
- Colonies (Ants): Ants form highly organized colonies with specialized castes, exhibiting remarkable cooperation and division of labor.
-
The Role of Social Behavior: Social behaviors are critical for survival and reproduction. Cooperation enhances hunting success, resource acquisition, and offspring care, improving the chances of survival for individuals within the group.
The Interconnectedness of Habitats and Behaviors
An animal's behavior is inextricably linked to its habitat, and changes in one directly impact the other.
-
Examples of Interconnectedness:
- Food Scarcity and Migration: If food resources become scarce in a habitat, animals may migrate to find alternative food sources. This is evident in wildebeest migrations across the African savanna.
- Climate Change and Breeding Behaviors: Climate change is altering breeding patterns in many species, affecting reproductive success and population dynamics. Changes in temperature and rainfall can affect nesting sites and food availability for young.
- Habitat Fragmentation and Social Structures: Habitat fragmentation, the breaking up of continuous habitats, can disrupt social structures and limit animal movement, impacting breeding, foraging, and predator avoidance.
-
Conservation Efforts: Conservation efforts focus on protecting animal habitats and mitigating the effects of human activities. These efforts include habitat restoration, protected area establishment, and anti-poaching initiatives, all aimed at preserving biodiversity and ensuring the survival of animal populations.
Conclusion
Understanding animal habitats and behaviors offers a profound insight into the intricate workings of the natural world. By studying these aspects, we gain a deeper appreciation for the incredible diversity of life on our planet and the importance of conservation. From the smallest insect to the largest mammal, each species plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of its ecosystem. Continue exploring the wonders of the animal kingdom and learn more about animal habitats and behaviors to become a better steward of our planet. Learn more about specific animal habitats and behaviors by researching your favorite species!

Featured Posts
-
 Learning Life Cycles Through Campus Farm Animals A Students Guide
May 13, 2025
Learning Life Cycles Through Campus Farm Animals A Students Guide
May 13, 2025 -
 Didcot Dog Walk Supports Mental Health Awareness Week
May 13, 2025
Didcot Dog Walk Supports Mental Health Awareness Week
May 13, 2025 -
 Von Braunschweig Nach Hannover Die Geschichte Von Jannes Horn
May 13, 2025
Von Braunschweig Nach Hannover Die Geschichte Von Jannes Horn
May 13, 2025 -
 Es I Britaniya Obsuzhdenie Novogo Soglasheniya Po Bezopasnosti
May 13, 2025
Es I Britaniya Obsuzhdenie Novogo Soglasheniya Po Bezopasnosti
May 13, 2025 -
 Britansko Evropeyskoe Soglashenie O Bezopasnosti Peregovory Nachalis
May 13, 2025
Britansko Evropeyskoe Soglashenie O Bezopasnosti Peregovory Nachalis
May 13, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Preobrazba Leonarda Di Caprija Je Li Ovo Isti Glumac Slobodna Dalmacija
May 13, 2025
Preobrazba Leonarda Di Caprija Je Li Ovo Isti Glumac Slobodna Dalmacija
May 13, 2025 -
 Leonardo Di Caprio Nevjerojatna Transformacija Slobodna Dalmacija
May 13, 2025
Leonardo Di Caprio Nevjerojatna Transformacija Slobodna Dalmacija
May 13, 2025 -
 Leonardo Di Caprio And Romeo Juliet A Rollerblading Story You Wont Believe
May 13, 2025
Leonardo Di Caprio And Romeo Juliet A Rollerblading Story You Wont Believe
May 13, 2025 -
 Leonardo Di Caprios Near Miss The Romeo Juliet Rollerblading Incident
May 13, 2025
Leonardo Di Caprios Near Miss The Romeo Juliet Rollerblading Incident
May 13, 2025 -
 The Real Story Behind Leonardo Di Caprios Dating Habits
May 13, 2025
The Real Story Behind Leonardo Di Caprios Dating Habits
May 13, 2025
