US Measles Count At 1,046 Following End Of Indiana Outbreak
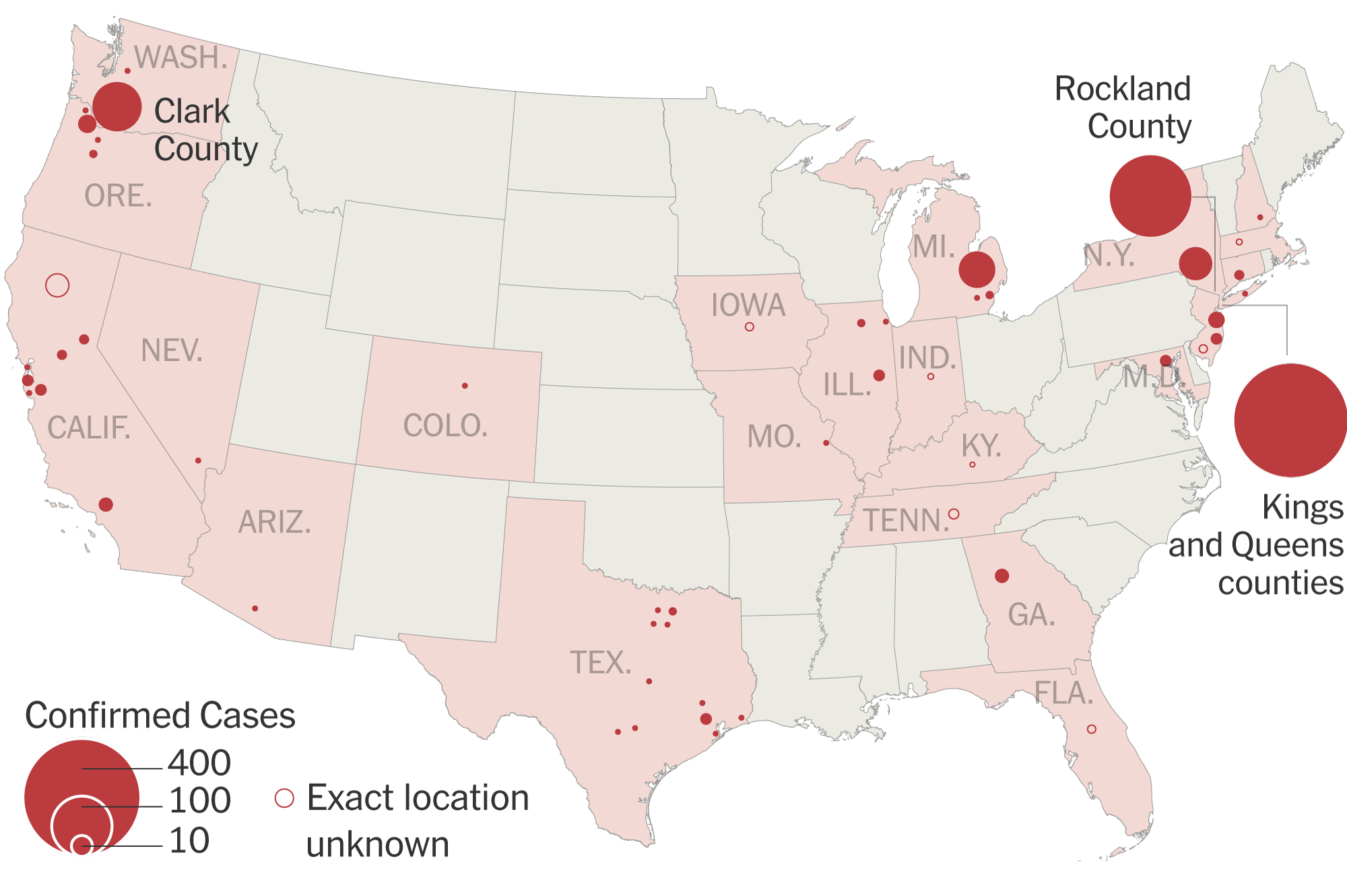
Table of Contents
The Indiana Outbreak: A Case Study
The Indiana measles outbreak serves as a stark warning about the rapid spread of this preventable disease. The outbreak, centered primarily in [Specific Indiana region/county if available], unfolded over a period of [Number] weeks, beginning in [Start date] and concluding in [End date]. A total of [Number] cases were reported, disproportionately affecting unvaccinated individuals and young children.
Contributing factors to the Indiana outbreak included:
- Low Vaccination Rates: Specific communities within the affected area demonstrated significantly lower-than-average MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccination rates.
- Spread within Close-Knit Communities: The virus spread rapidly within close-knit communities, such as schools and religious gatherings, where unvaccinated individuals were more likely to come into contact with infected persons.
- Delayed Diagnosis and Reporting: Initial delays in diagnosis and reporting hindered effective containment efforts.
Bullet Points:
- Timeline of Events: [Insert detailed timeline of the outbreak in Indiana]
- Cases by Age and Vaccination Status: [Insert data on age demographics and vaccination status of those infected]
- Outbreak Locations: [List specific locations where the outbreak was concentrated]
- Public Health Response: [Describe the public health measures implemented, including vaccination campaigns and contact tracing]
National Measles Statistics and Trends
The 1,046 measles cases reported across the US represent a significant increase compared to previous years. [Insert data comparing current numbers to previous years, citing sources]. This alarming rise underscores the need for renewed focus on measles prevention nationwide.
Several states beyond Indiana have also experienced significant outbreaks, including [List states with notable outbreaks]. The uneven distribution of cases across the US reflects variations in vaccination rates across different regions.
Bullet Points:
- National Measles Case Count by State: [Insert data on measles cases by state, if available, and cite source]
- Comparison to Previous Years: [Present a clear comparison of current numbers to previous years' data, emphasizing the increase]
- Vaccination Rates Across States: [Show a comparison of MMR vaccination rates across different states, correlating with outbreak severity if possible]
- Geographic Distribution: [Provide a map or visual representation of the geographic distribution of measles cases]
The Importance of Measles Vaccination
Measles is highly contagious, spreading easily through the air through coughing and sneezing. Complications from measles can be severe, including pneumonia, encephalitis (brain swelling), and even death. The MMR vaccine is highly effective in preventing measles infection. Studies have shown it to be [Percentage]% effective in preventing measles after two doses.
Addressing Common Misconceptions:
- Vaccine Safety: The MMR vaccine has undergone rigorous testing and has been proven safe and effective. [Cite credible sources debunking common vaccine myths].
- Herd Immunity: High vaccination rates create herd immunity, protecting even those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons.
Bullet Points:
- MMR Vaccine Mechanism: [Explain how the MMR vaccine works to build immunity]
- Vaccine Effectiveness Statistics: [Provide data on the effectiveness of the MMR vaccine in preventing infection and complications]
- Debunking Vaccine Myths: [Address common concerns and misinformation surrounding vaccine safety]
- Herd Immunity Importance: [Explain the concept of herd immunity and its role in protecting vulnerable populations]
Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy
Improving vaccination rates requires a multifaceted approach:
- Healthcare Provider Engagement: Healthcare providers play a critical role in educating patients about the benefits of vaccination and addressing concerns.
- Public Health Campaigns: Targeted public health campaigns using clear, evidence-based messaging can effectively counter misinformation and promote vaccine uptake.
- Community Outreach: Engaging community leaders and trusted figures to promote vaccination within specific communities is vital.
- Accessible Resources: Providing readily accessible information and resources to answer questions and address concerns is crucial.
Conclusion
The recent surge in the US measles outbreak, with 1,046 cases and counting, underscores the urgent need for increased MMR vaccination rates. Understanding the factors driving these outbreaks, including low vaccination rates and the spread of misinformation, is crucial. Implementing effective public health strategies, promoting vaccination, and addressing vaccine hesitancy are vital steps to protect communities nationwide. Let's work together to eliminate the threat of measles through widespread US measles vaccination. Contact your doctor or local health department today to learn more about protecting yourself and your loved ones.

Featured Posts
-
 Mlb Commissioner Rob Manfred Faces Ownership Challenges A Madden Style Analysis
May 30, 2025
Mlb Commissioner Rob Manfred Faces Ownership Challenges A Madden Style Analysis
May 30, 2025 -
 Tileoptiko Programma Kyriaki 4 And 5 Maioy
May 30, 2025
Tileoptiko Programma Kyriaki 4 And 5 Maioy
May 30, 2025 -
 Thnyt Alshykh Fysl Alhmwd Llardn Beyd Alastqlal Ma Zlt Asher Anny Byn Ahly
May 30, 2025
Thnyt Alshykh Fysl Alhmwd Llardn Beyd Alastqlal Ma Zlt Asher Anny Byn Ahly
May 30, 2025 -
 Nvidia Ceo Highlights The Formidable Rise Of Chinese Ai Competitors
May 30, 2025
Nvidia Ceo Highlights The Formidable Rise Of Chinese Ai Competitors
May 30, 2025 -
 Ti Na Deite Stin Tileorasi Kyriaki 4 5
May 30, 2025
Ti Na Deite Stin Tileorasi Kyriaki 4 5
May 30, 2025
