Western Massachusetts Rainfall: The Climate Change Connection
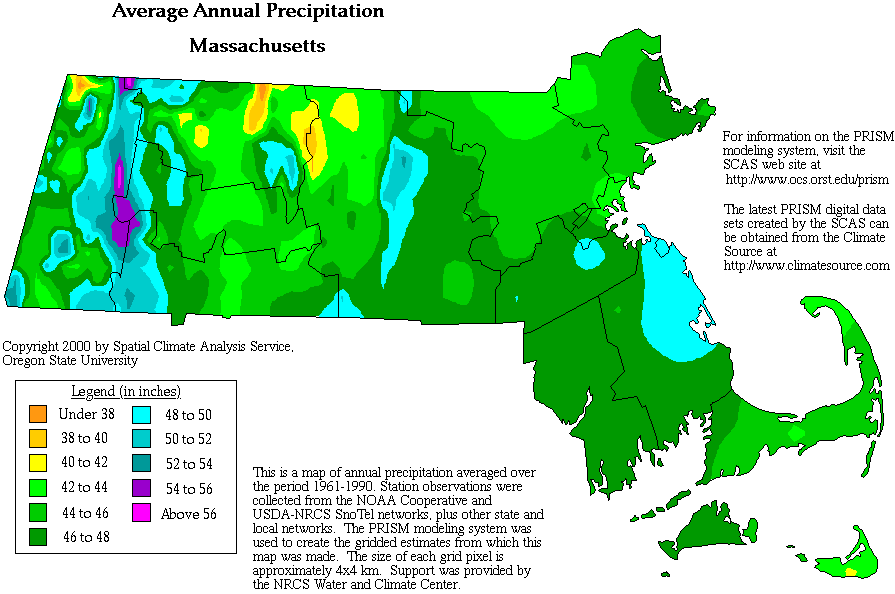
Table of Contents
Observed Changes in Western Massachusetts Rainfall
Western Massachusetts is experiencing a noticeable alteration in its historical rainfall patterns, marked by both increased intensity and altered seasonal distribution. This section details these observable changes, providing a foundation for understanding the broader climate change implications.
Increased Frequency of Intense Rainfall Events
The region has witnessed a troubling rise in the frequency and intensity of heavy downpours. These extreme rainfall events pose significant risks:
- Higher intensity storms: Data from the National Weather Service indicates a clear upward trend in the amount of rainfall recorded during individual storm events in Western Massachusetts over the past few decades.
- Increased risk of flash flooding: Overwhelmed drainage systems, common in older infrastructure, lead to increased instances of flash flooding, damaging property and disrupting daily life. The Connecticut River Valley, in particular, is highly vulnerable.
- Overwhelmed drainage systems: Existing drainage infrastructure, designed for historical rainfall patterns, is struggling to cope with the increased volume and intensity of modern storms.
- Damage to infrastructure: Roads, bridges, and buildings sustain damage from both flooding and the erosive power of intense rainfall.
Shifting Seasonal Precipitation Patterns
The distribution of rainfall throughout the year is also changing. This includes:
- Changes in snowfall amounts: While some winters still see substantial snowfall, overall, the amount of snowfall has decreased, with a trend towards more rain and less snow.
- Earlier spring snowmelt: The earlier melting of snowpack contributes to increased spring runoff and potential flooding, affecting water resource management.
- Altered growing seasons: Changes in precipitation timing impact agricultural practices, potentially disrupting planting and harvest cycles.
- Impact on agriculture: Farmers are facing increased challenges due to unpredictable rainfall patterns, affecting crop yields and livestock production.
- Increased risk of droughts in certain periods: While intense rainfall events are increasing, there are also periods of extended drought, creating a challenging paradox for water resource management.
Longer Periods of Drought
Periods of prolonged drought are becoming more frequent and intense in Western Massachusetts. This leads to:
- Impact on water resources: Droughts strain water supplies, impacting both municipal water systems and agricultural irrigation.
- Agriculture and forestry: Drought conditions negatively impact crop yields and forest health, increasing vulnerability to wildfires.
- Increased risk of wildfires: Dry conditions create a heightened risk of wildfires, posing a threat to property and natural ecosystems. Recent years have witnessed several significant wildfires in the region, linked to prolonged dry spells.
The Climate Change Link
The observed changes in Western Massachusetts rainfall are strongly linked to the broader phenomenon of climate change.
Scientific Evidence of a Warming Climate
The scientific consensus overwhelmingly supports the reality of anthropogenic (human-caused) climate change. This is evidenced by:
- Greenhouse gas emissions: The burning of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases, trapping heat in the atmosphere and driving global warming.
- Rising global temperatures: Global average temperatures are rising, with observable effects on weather patterns worldwide.
- Changes in atmospheric circulation: Warmer temperatures disrupt atmospheric circulation patterns, leading to changes in precipitation distribution.
- Increased water vapor in the atmosphere: A warmer atmosphere holds more water vapor, leading to more intense rainfall events when conditions are right. Studies from the IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) support these findings.
Projected Future Rainfall Changes for Western Massachusetts
Climate models project continued changes in precipitation patterns for Western Massachusetts, with implications for:
- Increased variability in rainfall: Expect even greater swings between periods of intense rainfall and prolonged drought.
- More frequent extreme weather events: The frequency and intensity of both floods and droughts are projected to increase.
- Potential for both severe droughts and intense flooding: This creates a significant challenge for water resource management and infrastructure planning. Specific predictions for Western Massachusetts from reputable climate models, such as those used by the NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration), point towards this troubling trend.
Impacts and Mitigation Strategies
The altered rainfall patterns in Western Massachusetts have far-reaching consequences.
Environmental Consequences
Changes in rainfall profoundly impact the region's ecosystems:
- Impacts on forests, wetlands, rivers, and lakes: Altered water levels and increased flooding affect the health and biodiversity of these ecosystems.
- Changes in plant and animal life: Species adapted to existing climate conditions may struggle to survive under altered rainfall patterns.
Socioeconomic Impacts
The changes affect human communities in several ways:
- Damage to infrastructure: Flooding and extreme weather events damage roads, bridges, and other critical infrastructure.
- Impact on agriculture and tourism: Unpredictable rainfall patterns negatively affect agricultural production and tourism, key sectors of the regional economy.
- Increased insurance costs: Increased risk of damage from flooding and extreme weather leads to higher insurance premiums.
- Water resource management challenges: Managing water supplies becomes increasingly complex under conditions of both intense rainfall and drought.
Mitigation and Adaptation Measures
Addressing the challenges requires a multifaceted approach:
- Investing in renewable energy: Transitioning to renewable energy sources reduces greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating climate change.
- Improving water management practices: Investing in better water storage, conservation, and distribution systems is crucial.
- Developing flood control measures: Improving drainage systems and implementing flood control measures can protect communities from flooding.
- Promoting sustainable land use practices: Sustainable land management practices, such as reforestation and soil conservation, can enhance resilience to extreme weather events.
- Community resilience planning: Community-level planning is essential to prepare for and respond to the impacts of altered rainfall patterns.
Conclusion
Western Massachusetts is experiencing significant and concerning changes in its rainfall patterns, directly linked to climate change. The increased frequency of intense rainfall events, shifting seasonal precipitation, and longer periods of drought pose serious environmental and socioeconomic challenges. Understanding the connection between Western Massachusetts rainfall and climate change is crucial for implementing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies. Learn more about the specific impacts on your community and get involved in local efforts to address climate change. Participate in initiatives promoting sustainable practices and advocate for policies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance community resilience to extreme weather events. Take action to protect Western Massachusetts from the effects of changing rainfall patterns.

Featured Posts
-
 Zverev Shelton And Cerundolo Battle For Munich Semifinal Spots
May 31, 2025
Zverev Shelton And Cerundolo Battle For Munich Semifinal Spots
May 31, 2025 -
 Impact Des Travaux D Ingenierie Castor Sur Deux Cours D Eau De La Drome
May 31, 2025
Impact Des Travaux D Ingenierie Castor Sur Deux Cours D Eau De La Drome
May 31, 2025 -
 High Fentanyl Levels Confirmed In Princes Death March 26th
May 31, 2025
High Fentanyl Levels Confirmed In Princes Death March 26th
May 31, 2025 -
 Etude De L Ingenierie Castor Dans Deux Cours D Eau De La Drome
May 31, 2025
Etude De L Ingenierie Castor Dans Deux Cours D Eau De La Drome
May 31, 2025 -
 Historic Meeting Pope Leo Xiv Greets Giro D Italia Peloton
May 31, 2025
Historic Meeting Pope Leo Xiv Greets Giro D Italia Peloton
May 31, 2025
