What Is Creatine? A Deep Dive Into The Popular Supplement

Table of Contents
What is Creatine and Where Does it Come From?
Creatine is a naturally occurring nitrogenous organic acid. It plays a vital role in your body's energy production system, specifically within your muscles. Think of it as a crucial component in the energy-transfer process that fuels high-intensity activities like weightlifting, sprinting, and even intense bursts of activity in everyday life. While your body naturally produces creatine in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas, and you can obtain small amounts from dietary sources like red meat and fish, creatine supplements provide a significantly higher concentration, making them a popular choice for boosting performance.
- Creatine is synthesized in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas. This natural production, however, often falls short of what's needed for optimal athletic performance.
- The body also obtains creatine from dietary sources. Red meat and fish are particularly good sources, but the amount obtained through diet alone is often insufficient for those looking to maximize its benefits.
- Creatine supplements are widely available in powder, capsule, and liquid forms. Choosing the right form often comes down to personal preference and convenience. Creatine monohydrate is the most researched and widely used form.
The Benefits of Creatine Supplementation
The popularity of creatine supplements stems from a wealth of research demonstrating its significant performance-enhancing effects. Let's explore some of the key benefits:
Improved Strength and Power
Creatine supplementation increases the storage of phosphocreatine in your muscles. Phosphocreatine is a crucial energy source for high-intensity, short-duration muscle contractions. By boosting phosphocreatine levels, creatine allows you to perform more reps, lift heavier weights, and generally experience a significant increase in strength and power output. Numerous studies have shown substantial improvements in strength and power gains in individuals supplementing with creatine.
Increased Muscle Mass
Creatine doesn't directly build muscle, but it plays a vital role in muscle protein synthesis, the process your body uses to build muscle tissue. By providing more energy for muscle contractions and potentially improving muscle hydration, creatine creates a more anabolic (muscle-building) environment, contributing to increased muscle mass when combined with a suitable training and nutrition program.
Enhanced Recovery
Intense workouts cause muscle damage and fatigue. Creatine can aid in the recovery process by reducing muscle damage and potentially speeding up the replenishment of energy stores. This can lead to faster recovery times between workouts and a reduced risk of overtraining.
- Improved athletic performance: across a range of disciplines requiring short bursts of intense activity.
- Increased muscle strength and power: leading to improved performance in weightlifting and other strength-based activities.
- Enhanced muscle growth: particularly when combined with resistance training and a proper diet.
- Faster recovery from workouts: reducing muscle soreness and fatigue.
- Potential cognitive benefits: Some studies suggest potential benefits for brain function and cognitive performance, though more research is needed in this area.
How to Use Creatine Effectively and Safely
To maximize the benefits of creatine and minimize any potential side effects, it's crucial to understand how to use it effectively and safely.
Dosage and Timing
The generally recommended daily dosage of creatine monohydrate is 3-5 grams. Many people use a "loading phase" initially, taking 20 grams per day for the first week to rapidly saturate the muscles with creatine, followed by a maintenance phase of 3-5 grams daily. The optimal timing is often post-workout, as this is when your muscles are most receptive to nutrient uptake. However, taking it at any time of the day is usually effective.
Cycling Creatine
Cycling creatine involves periods of supplementation followed by periods of rest. While some believe cycling can prevent potential side effects or maintain effectiveness, the evidence supporting this practice is limited. Continuous supplementation is generally considered safe and effective for most individuals.
Combining Creatine with other Supplements
Creatine can synergistically enhance the effects of other supplements, notably protein powder. Combining creatine with a high-protein diet supports muscle growth and recovery, amplifying the benefits of both.
- Always choose reputable brands. Look for third-party tested products to ensure quality and purity.
- Consult with a healthcare professional before starting creatine supplementation. This is especially important if you have pre-existing medical conditions.
- Stay well hydrated when taking creatine. Creatine draws water into the muscle cells, so adequate hydration is crucial.
- Be aware of potential side effects (discussed below).
Potential Side Effects of Creatine
While generally considered safe for healthy individuals, creatine can cause some side effects, most of which are mild and temporary.
- Water retention (weight gain): This is a common side effect, mainly due to creatine's ability to draw water into the muscles.
- Digestive upset (nausea, diarrhea): Some individuals may experience mild gastrointestinal discomfort, particularly when starting supplementation.
- Muscle cramps: Although rare, muscle cramps can occur due to changes in electrolyte balance.
- Dehydration (if not properly hydrated): This is why adequate fluid intake is crucial.
- Rare cases of kidney issues: These are typically associated with pre-existing kidney conditions and high doses.
Conclusion
Creatine, a naturally occurring compound and a popular supplement, significantly enhances athletic performance by increasing muscle phosphocreatine stores, supporting muscle growth, and improving recovery. While generally safe when used appropriately, potential side effects like water retention and digestive upset can occur. Remember to always choose high-quality creatine monohydrate, follow recommended dosages, and stay well-hydrated. Before starting any new supplement, including creatine supplementation, consult your doctor or a registered dietitian to discuss its suitability for your individual health needs and goals. Boost your performance with creatine – explore its power and potential today!

Featured Posts
-
 Pelvic Contusion Sidelines Jimmy Butler Impact On Miami Heats Season
May 15, 2025
Pelvic Contusion Sidelines Jimmy Butler Impact On Miami Heats Season
May 15, 2025 -
 Building Voice Assistants Made Easy Open Ais 2024 Developer Tools
May 15, 2025
Building Voice Assistants Made Easy Open Ais 2024 Developer Tools
May 15, 2025 -
 Drc Cobalt Export Ban Aftermath Analyzing The Markets Response And Quota Expectations
May 15, 2025
Drc Cobalt Export Ban Aftermath Analyzing The Markets Response And Quota Expectations
May 15, 2025 -
 Max Muncy Ditches Torpedo Bat After 3 At Bats Connects For Game Tying Hit
May 15, 2025
Max Muncy Ditches Torpedo Bat After 3 At Bats Connects For Game Tying Hit
May 15, 2025 -
 Los Angeles Wildfires Fuel A Disturbing Betting Trend
May 15, 2025
Los Angeles Wildfires Fuel A Disturbing Betting Trend
May 15, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Anthony Edwards Paternity Case Resolved Custody Decision Announced
May 15, 2025
Anthony Edwards Paternity Case Resolved Custody Decision Announced
May 15, 2025 -
 The Latest On Anthony Edwards Baby Mama Drama A Twitter Analysis
May 15, 2025
The Latest On Anthony Edwards Baby Mama Drama A Twitter Analysis
May 15, 2025 -
 The Anthony Edwards Baby Mama Saga Unfolding Online
May 15, 2025
The Anthony Edwards Baby Mama Saga Unfolding Online
May 15, 2025 -
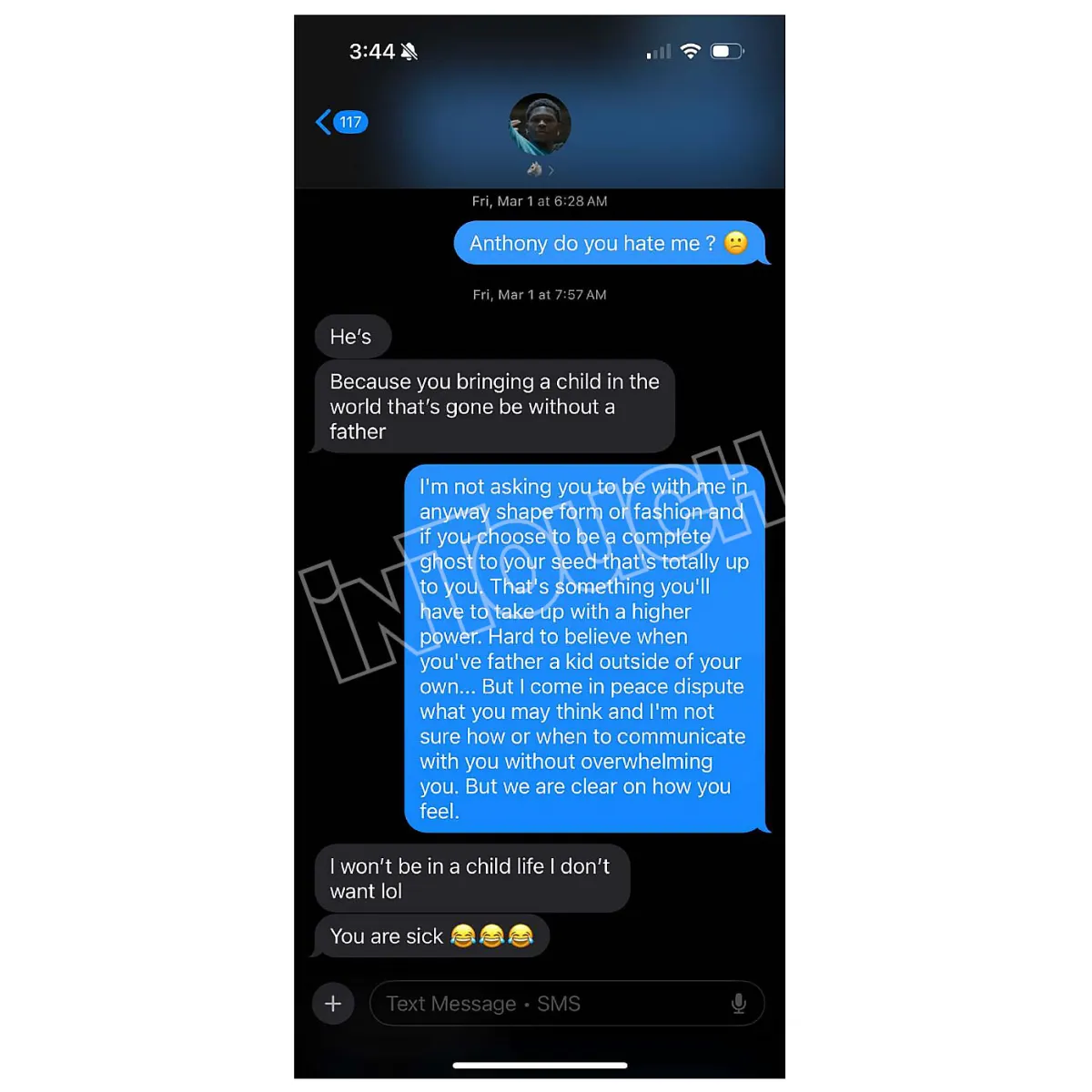 Court Awards Ayesha Howard Custody After Anthony Edwards Paternity Dispute
May 15, 2025
Court Awards Ayesha Howard Custody After Anthony Edwards Paternity Dispute
May 15, 2025 -
 Twitter Explodes Over Anthony Edwards Baby Mama Drama
May 15, 2025
Twitter Explodes Over Anthony Edwards Baby Mama Drama
May 15, 2025
