Analyzing The Impact Of Reciprocal Tariffs On Key Indian Sectors

Table of Contents
Impact on the Indian Agricultural Sector
Reduced Exports and Increased Domestic Prices:
Reciprocal tariffs can severely curtail the competitiveness of Indian agricultural products in the global marketplace. This leads to decreased demand for exports, resulting in lower export volumes and, potentially, higher domestic prices for consumers. The implications are far-reaching:
- Reduced competitiveness in global markets: Indian farmers may struggle to compete with subsidized or tariff-protected producers in other countries.
- Potential for surplus production and price fluctuations: A decrease in export demand can lead to oversupply in the domestic market, causing price volatility and impacting farmers' incomes.
- Increased reliance on domestic consumption: With reduced export opportunities, India may become more reliant on internal consumption, which can present challenges if domestic demand does not rise proportionally.
- Need for government support and diversification strategies: The government needs to provide robust support mechanisms, including financial assistance, crop diversification programs, and market research initiatives, to help farmers navigate these challenges. This might involve exploring alternative crops better suited for the domestic market or exploring new export avenues.
Shift in Trade Partners and Market Diversification:
The imposition of reciprocal tariffs necessitates a strategic shift towards new trading partners and the exploration of alternative export markets. This requires a proactive and multifaceted approach:
- Exploration of new trade agreements and partnerships: India needs to actively pursue new trade agreements and strengthen existing partnerships with countries less affected by the tariff regime. This could involve negotiating preferential trade access or forming regional trade blocs.
- Investment in infrastructure to facilitate trade with new markets: Improved infrastructure, including efficient transportation networks and cold storage facilities, is crucial for accessing distant markets effectively.
- Development of new product lines catering to different market demands: Farmers and exporters need to adapt by diversifying their product offerings to meet the specific requirements of different international markets. This could include value-added products or specialized varieties of crops.
- Increased focus on regional trade blocs: Greater participation in regional trade agreements, such as the RCEP (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership), could provide access to new markets and potentially mitigate the impact of reciprocal tariffs.
Implications for the Indian Manufacturing Sector
Increased Input Costs and Reduced Profitability:
Tariffs on imported raw materials and components significantly increase production costs for Indian manufacturers. This directly impacts profit margins and overall competitiveness. This can lead to:
- Rising prices for essential inputs: Higher import costs translate to increased manufacturing expenses, making Indian products less price-competitive internationally.
- Reduced competitiveness against foreign manufacturers: Indian manufacturers might struggle to compete with foreign producers who may have access to cheaper raw materials.
- Potential for job losses and factory closures: Reduced profitability can lead to business closures, impacting employment and economic growth.
- Need for government incentives and subsidies: Targeted government support, such as subsidies or tax breaks, may be necessary to mitigate the impact of increased input costs and maintain the competitiveness of domestic manufacturers.
Opportunities for Domestic Substitution and Growth:
While challenging, reciprocal tariffs also present opportunities for domestic manufacturers. This can lead to:
- Investment in domestic production capacity: The increased cost of imports might stimulate investment in domestic production of previously imported goods.
- Development of import-substitution strategies: Manufacturers may focus on developing alternative domestic sources for raw materials and components.
- Potential for job creation and economic growth: Investment in domestic production can lead to job creation and overall economic growth.
- Focus on innovation and technological advancement: Domestic manufacturers might be forced to innovate and adopt more advanced technologies to become more efficient and competitive.
Effects on the Indian Service Sector
Challenges to the IT and ITES Industry:
Although less directly affected than manufacturing or agriculture, the Indian IT and ITES (Information Technology and Information Technology Enabled Services) sector faces indirect repercussions. A global economic slowdown triggered by reciprocal tariffs can lead to:
- Reduced global demand for IT services: A downturn in global economic activity can reduce demand for IT outsourcing and offshoring services.
- Potential impact on project outsourcing and offshoring: Companies might postpone or cancel IT projects in response to economic uncertainty.
- Need for diversification and upskilling of the workforce: The sector needs to diversify its service offerings and invest in upskilling its workforce to adapt to evolving market demands.
- Focus on value-added services and innovation: Emphasis on high-value services, innovative solutions, and specialized expertise can help maintain competitiveness.
Implications for Tourism and Hospitality:
Reciprocal tariffs can indirectly impact the Indian tourism and hospitality sector through increased travel costs and potentially reduced visitor numbers.
- Impact on airline ticket prices and travel packages: Tariffs on imported goods and services used in the tourism sector might lead to increased prices.
- Potential for decreased tourism revenue: Higher travel costs could discourage international tourists from visiting India.
- Need for promotional strategies to attract tourists: The sector needs to develop creative marketing campaigns to attract tourists despite the increased costs.
- Focus on domestic tourism to mitigate losses: Boosting domestic tourism can partially compensate for the potential decline in international visitors.
Conclusion:
Reciprocal tariffs pose significant challenges and opportunities for key Indian sectors. The agricultural sector faces reduced export potential, while the manufacturing sector might experience increased costs. Even the service sector, while less directly affected, could feel the ripple effects of a global economic slowdown. However, these tariffs also present opportunities for domestic substitution, growth in certain sectors, and diversification of trade partners. Understanding the complex interplay of these factors is crucial for effective policy-making and business strategies. Further research and analysis of the reciprocal tariffs India impact is essential to mitigate negative consequences and leverage the potential benefits. Careful monitoring and proactive adaptation to this evolving global trade landscape will be vital for India's continued economic growth. Addressing the impact of reciprocal tariffs in India requires a holistic strategy.

Featured Posts
-
 Hamer Bruins Moet Met Npo Toezichthouder Over Leeflang Praten
May 15, 2025
Hamer Bruins Moet Met Npo Toezichthouder Over Leeflang Praten
May 15, 2025 -
 Bruins Eist Spoedberaad Npo Over Leeflang Affaire
May 15, 2025
Bruins Eist Spoedberaad Npo Over Leeflang Affaire
May 15, 2025 -
 Npo Baas Beschuldigd Van Het Creeren Van Een Angstcultuur Door Tientallen Medewerkers
May 15, 2025
Npo Baas Beschuldigd Van Het Creeren Van Een Angstcultuur Door Tientallen Medewerkers
May 15, 2025 -
 Double Strike Cripples Hollywood Actors And Writers Demand Fair Treatment
May 15, 2025
Double Strike Cripples Hollywood Actors And Writers Demand Fair Treatment
May 15, 2025 -
 Herstel Van Vertrouwen College Van Omroepen En De Toekomst Van De Npo
May 15, 2025
Herstel Van Vertrouwen College Van Omroepen En De Toekomst Van De Npo
May 15, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Stock Market Valuation Concerns Bof As Perspective And Guidance For Investors
May 15, 2025
Stock Market Valuation Concerns Bof As Perspective And Guidance For Investors
May 15, 2025 -
 Xi Jinpings Calculated Move Expert Led Us Deal Negotiations
May 15, 2025
Xi Jinpings Calculated Move Expert Led Us Deal Negotiations
May 15, 2025 -
 The U S And Greenland The Untold Story Of A Hidden Nuclear Base
May 15, 2025
The U S And Greenland The Untold Story Of A Hidden Nuclear Base
May 15, 2025 -
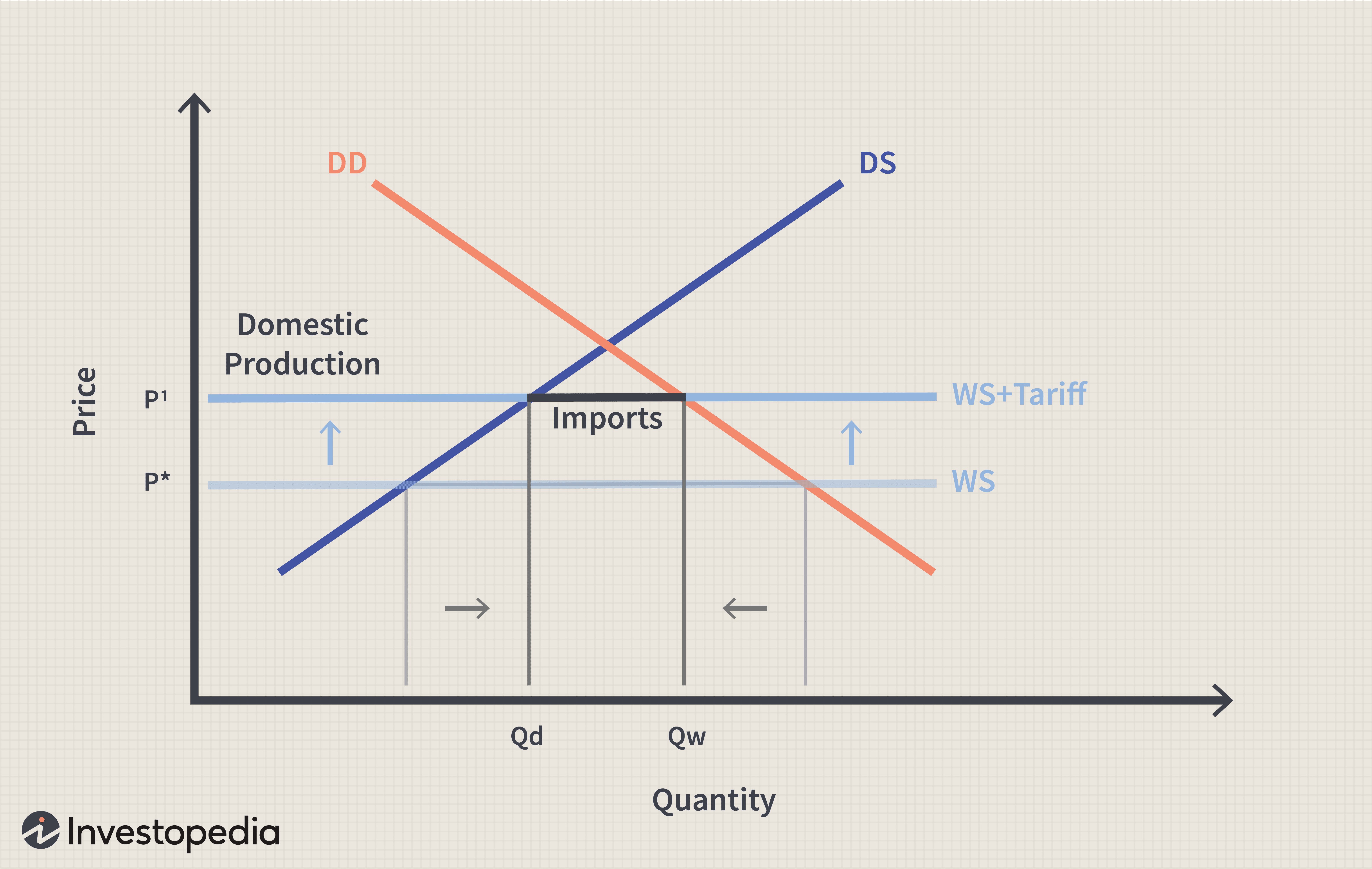 16 Billion At Stake How Trumps Tariffs Affect Californias Revenue
May 15, 2025
16 Billion At Stake How Trumps Tariffs Affect Californias Revenue
May 15, 2025 -
 Goldman Sachs Deciphers Trumps Preferred Oil Price Range
May 15, 2025
Goldman Sachs Deciphers Trumps Preferred Oil Price Range
May 15, 2025
