China's Growth Strategy: The Challenges Of Boosting Consumer Confidence

Table of Contents
The Weakening Foundation: Understanding the Factors Eroding Consumer Confidence
Several interconnected factors are eroding consumer confidence in China, creating a fragile foundation for future economic expansion. Understanding these underlying issues is crucial for developing effective strategies to address them.
Declining Income Growth and Rising Job Insecurity
Slowing wage growth, coupled with rising job insecurity, significantly impacts consumer spending. Technological advancements, while beneficial in the long run, are causing displacement in certain sectors, leading to anxieties about employment stability. The rising youth unemployment rate, particularly concerning, further dampens spending power among a crucial demographic. Income inequality, meanwhile, exacerbates the problem, creating a disparity between those with significant purchasing power and a large segment of the population with limited disposable income.
- Rising housing costs: Soaring property prices in major cities significantly reduce disposable income, limiting consumers' ability to spend on other goods and services.
- Uncertainty surrounding future job prospects: Fear of job losses or stagnant wages prevents consumers from making significant purchases or investing in the future.
- Reduced purchasing power due to inflation: The erosion of purchasing power due to inflation further reduces consumer confidence and spending.
The Shadow of Debt: High Household Leverage and its Impact
High levels of household debt cast a long shadow over consumer confidence. The burden of mortgages and loans significantly restricts disposable income, leaving less money for discretionary spending. The potential for widespread defaults poses a systemic risk to the economy, creating a climate of uncertainty and apprehension. While the government has implemented measures to manage household debt, the challenge remains significant.
The Burden of Mortgages and Loans
The increasing reliance on consumer credit, coupled with rising mortgage rates, has created a precarious financial situation for many households. The fear of defaults and the associated consequences—such as repossession of assets—contributes to a cautious and conservative spending approach.
- Rising mortgage rates impacting affordability: Higher interest rates make it more difficult for households to afford mortgages and other forms of debt, impacting their ability to spend.
- Increased reliance on consumer credit for daily expenses: The growing use of credit for everyday expenses indicates a lack of disposable income and potential future financial stress.
- Concerns about future repayment ability: The uncertainty surrounding future income and job security contributes to concerns about the ability to repay existing debt.
Geopolitical Uncertainty and its Effect on Consumer Sentiment
Geopolitical uncertainty adds another layer of complexity to the challenge of boosting consumer confidence. The global economic slowdown, trade tensions, and geopolitical risks create a climate of uncertainty that discourages spending and investment. Domestic policy changes also contribute to this volatility.
Global Economic Slowdown and Domestic Policy Changes
The interplay of global economic fluctuations and domestic policy adjustments directly influences consumer sentiment in China. Concerns about future economic stability, coupled with uncertainty surrounding government regulations and policies, lead consumers to adopt a wait-and-see approach, delaying major purchases.
- Impact of trade wars and sanctions: International trade disputes can negatively impact the Chinese economy, reducing consumer confidence and spending.
- Concerns about potential future economic instability: Uncertainty about the future economic outlook leads consumers to postpone major purchases and save more.
- Uncertainty surrounding government regulations and policies: Changes in government policies can create uncertainty and negatively impact consumer confidence.
Building Trust: Strategies to Reinvigorate Consumer Confidence
Addressing the challenges to consumer confidence requires a multi-pronged approach that involves both policy interventions and initiatives to promote financial literacy.
Policy Interventions to Boost Income and Employment
Government initiatives aimed at boosting income growth and job creation are essential for restoring consumer confidence. This requires a comprehensive strategy that encompasses various measures, including targeted subsidies, investments in infrastructure and green technologies, and enhanced social security programs.
- Targeted subsidies and tax breaks for low-income households: Direct financial assistance can significantly increase disposable income for low-income families.
- Investments in infrastructure and green technologies to create jobs: Investing in job-creating sectors can alleviate unemployment and boost consumer confidence.
- Enhanced social security programs and unemployment benefits: Strengthening social safety nets provides a crucial cushion for consumers facing job losses or financial hardship.
Addressing Debt Concerns and Promoting Financial Literacy
Strategies to manage household debt and promote financial literacy are equally important. This involves debt consolidation programs, financial literacy campaigns, and regulation of lending practices to prevent predatory lending.
- Debt consolidation programs: These programs can help households manage their debt more effectively, reducing financial stress and boosting confidence.
- Financial literacy campaigns: Educating consumers about responsible borrowing and financial management empowers them to make informed decisions.
- Regulation of lending practices to prevent predatory lending: Stricter regulations protect consumers from unfair lending practices and promote responsible borrowing.
Conclusion: A Path Towards Sustainable Growth: Rebuilding Consumer Confidence in China
The challenges to boosting consumer confidence in China are multifaceted and require a comprehensive approach. Addressing declining income growth, managing high household debt, and mitigating geopolitical uncertainty are crucial for achieving sustainable economic growth. The strategies discussed—including policy interventions to boost income and employment, coupled with initiatives to address debt concerns and promote financial literacy—are essential steps towards rebuilding consumer confidence. Further research and discussion on effective strategies for bolstering "China's Growth Strategy: Boosting Consumer Confidence" are vital. A concerted effort, involving both government policies and private sector initiatives, is necessary to restore consumer confidence and achieve sustainable economic growth in China.

Featured Posts
-
 Persemian Gerakan Bali Bersih Sampah Strategi Menuju Pulau Bali Yang Lebih Bersih
May 28, 2025
Persemian Gerakan Bali Bersih Sampah Strategi Menuju Pulau Bali Yang Lebih Bersih
May 28, 2025 -
 Tyrese Haliburtons Father Pacers End Suspension
May 28, 2025
Tyrese Haliburtons Father Pacers End Suspension
May 28, 2025 -
 Clear Skies Ahead Metro Detroit Weather Update For Monday
May 28, 2025
Clear Skies Ahead Metro Detroit Weather Update For Monday
May 28, 2025 -
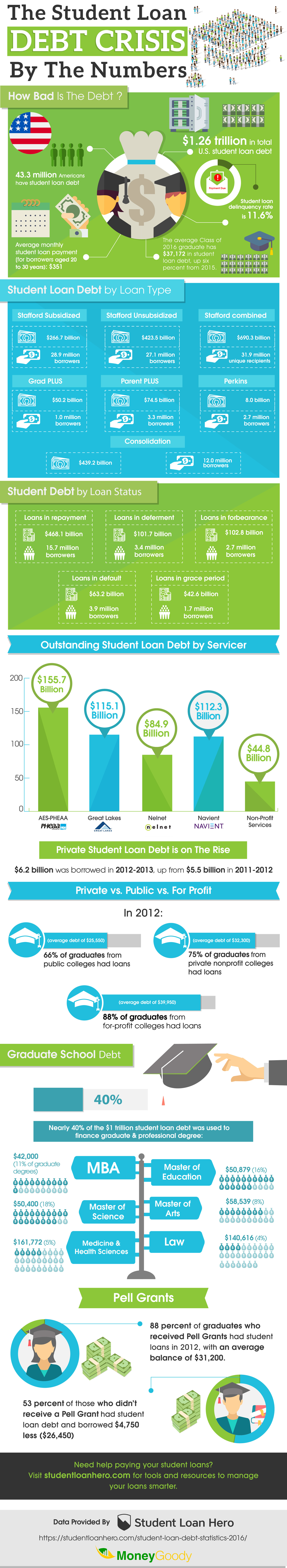 The Student Loan Crisis And Its Economic Ramifications
May 28, 2025
The Student Loan Crisis And Its Economic Ramifications
May 28, 2025 -
 Prakiraan Cuaca Jawa Tengah 23 April Hujan Lebat Di Beberapa Daerah
May 28, 2025
Prakiraan Cuaca Jawa Tengah 23 April Hujan Lebat Di Beberapa Daerah
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Crispr Gene Editing A Breakthrough In Precision And Efficacy
May 30, 2025
Crispr Gene Editing A Breakthrough In Precision And Efficacy
May 30, 2025 -
 Evan Longoria Officially Retires As A Tampa Bay Ray
May 30, 2025
Evan Longoria Officially Retires As A Tampa Bay Ray
May 30, 2025 -
 Advanced Crispr System For Precise Whole Gene Integration
May 30, 2025
Advanced Crispr System For Precise Whole Gene Integration
May 30, 2025 -
 Madden And Mlb Analyzing Rob Manfreds Ownership Troubles
May 30, 2025
Madden And Mlb Analyzing Rob Manfreds Ownership Troubles
May 30, 2025 -
 Longorias Retirement The End Of An Era For The Tampa Bay Rays
May 30, 2025
Longorias Retirement The End Of An Era For The Tampa Bay Rays
May 30, 2025
