Congo's Cobalt Export Ban: Market Reaction And The Path Forward With A New Quota System
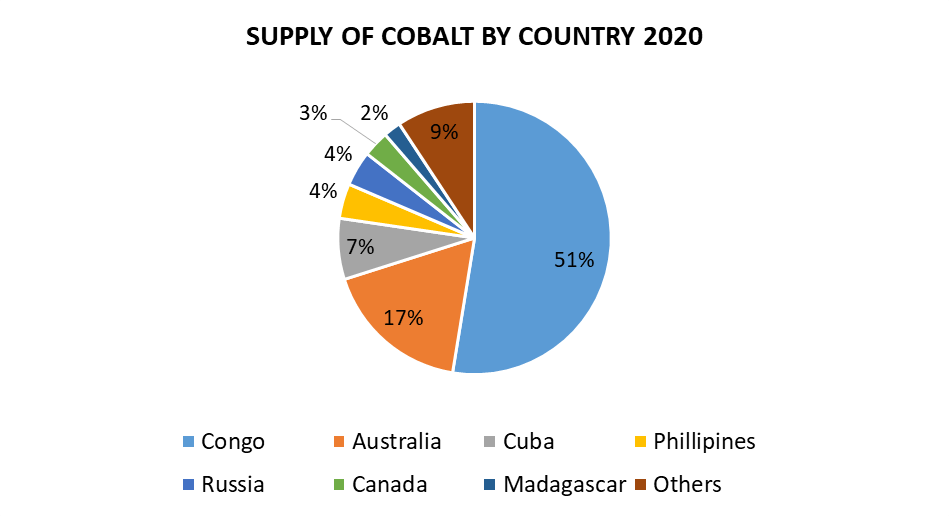
Table of Contents
Market Reaction to Potential Cobalt Export Restrictions
The prospect of Congo's cobalt export ban, or even a significantly restrictive quota system, has had a profound impact on global markets.
Price Volatility and Supply Chain Disruptions
Announcements regarding potential export limitations immediately triggered price volatility in the cobalt market. The price of cobalt, already subject to fluctuations due to supply and demand dynamics, experienced a sharp increase, creating significant supply chain disruptions. This ripple effect was felt across various industries reliant on cobalt, most notably the burgeoning EV battery sector. Companies like Tesla and other major battery manufacturers faced challenges securing sufficient cobalt supplies, leading to production delays and increased costs. This situation highlighted the critical dependence of the global economy on Congo's cobalt production and the vulnerability of supply chains to geopolitical events.
- Increased cobalt prices: The immediate impact was a surge in cobalt prices, impacting the profitability of manufacturers.
- Supply chain bottlenecks: Many companies experienced delays and shortages, hindering production.
- Increased demand for alternative battery technologies: The uncertainty spurred research and investment in alternative battery chemistries that require less or no cobalt.
- Geopolitical implications: The situation underscored the geopolitical risks associated with relying on a single source for critical minerals.
Investor Sentiment and Market Uncertainty
The news surrounding potential cobalt export restrictions significantly dampened investor confidence in cobalt mining companies and related industries. Stock prices of publicly listed cobalt mining companies experienced a downturn as investors reacted to the increased uncertainty and potential for reduced profitability. The risk of future cobalt supply shortages also impacted investment decisions, potentially hindering future project financing in the sector. This created a climate of uncertainty, impacting investment strategies and potentially diverting capital towards alternative resources.
- Decreased investor confidence: Uncertainty regarding future cobalt availability led to a drop in investor sentiment.
- Increased investment risk: The potential for export bans elevated the perceived risk associated with cobalt investments.
- Potential for capital flight: Investors may shift their capital to less risky ventures.
- Shift in investment towards alternative resources: The crisis accelerated interest in alternative battery technologies and materials.
Analyzing the New Cobalt Quota System in Congo
The Congolese government's implementation of a new cobalt quota system aims to address several issues, including revenue generation, environmental protection, and ethical sourcing. However, the system’s success hinges on transparent and effective implementation.
The Structure and Implementation of the Quota System
The specifics of Congo's new cobalt quota system are still unfolding. The criteria for allocating quotas will likely involve considerations of production capacity, environmental compliance, and adherence to ethical sourcing standards. However, concerns remain about the potential for corruption and the need for robust transparency mechanisms to ensure fair and equitable distribution of quotas. International oversight and collaborative efforts will be crucial to minimize corruption and maintain accountability.
- Quota allocation process: The method of allocating quotas needs to be clear, transparent, and demonstrably fair.
- Environmental considerations: The quota system should incentivize environmentally responsible mining practices.
- Social responsibility requirements: The system must incorporate measures to protect workers' rights and ensure fair labor practices.
- Transparency mechanisms: Open access to information regarding quota allocation and compliance is paramount.
Potential Impacts of the Quota System on DRC and Global Markets
The intended positive impacts of the quota system include increased government revenue for the DRC, improvements in working conditions within the mining sector, and enhanced environmental protection measures. However, potential negative consequences include supply limitations, higher cobalt prices, and the potential for increased black market activity. The long-term sustainability of the system depends on its ability to balance the needs of the DRC with the demands of the global market while promoting responsible and ethical mining practices.
- Economic benefits for the DRC: Increased government revenue can fuel economic development and social programs.
- Environmental sustainability improvements: The quota system can promote responsible mining practices and reduce environmental damage.
- Social and ethical implications: Improved worker conditions and ethical sourcing are vital components of a successful system.
- Global market stability: The quota system, if well-managed, could contribute to greater stability in the cobalt market.
Pathways Forward: Mitigation Strategies and Long-Term Solutions
Addressing the challenges posed by Congo's cobalt production requires a multi-faceted approach involving diversification of sources, sustainable mining practices, and international cooperation.
Diversification of Cobalt Sources
Reducing reliance on the DRC as the primary source of cobalt is crucial. This necessitates exploring alternative cobalt sources worldwide, including countries with potential for cobalt production, such as Australia, Canada, and others. However, diversifying cobalt sources faces challenges, including geological limitations, political instability in some regions, and the time needed to develop new mining operations. Technological advancements in cobalt recycling also hold significant promise for reducing dependence on primary mining.
- Exploration of new cobalt deposits: Investing in exploration and development of new cobalt sources is crucial for diversification.
- Technological advancements in cobalt recycling: Recycling can significantly increase cobalt supply and reduce reliance on mining.
- Development of alternative battery technologies: Research into battery technologies that use less or no cobalt is essential for long-term security.
- International collaboration: Cooperative efforts between countries can facilitate the development of responsible cobalt mining and supply chains.
Sustainable and Ethical Cobalt Mining Practices
Sustainable and ethical cobalt mining practices in the DRC are paramount. This includes improving working conditions, ensuring fair wages, and reducing environmental damage. International organizations and certification schemes play a vital role in promoting responsible sourcing and traceability throughout the cobalt supply chain. Transparency and accountability are key to ensuring that the cobalt used in global products is ethically sourced.
- Improved worker safety and fair wages: Implementing robust labor standards and ensuring fair compensation for workers is essential.
- Environmental remediation efforts: Addressing past environmental damage and preventing future harm is crucial.
- Implementation of international standards: Adherence to internationally recognized standards for responsible mining is necessary.
- Traceability and transparency in the supply chain: Clear and transparent tracking of cobalt from mine to end-product is vital.
Conclusion: Congo's Cobalt Export Ban: Looking Ahead
The potential for a Congo cobalt export ban, coupled with the implementation of a new quota system, presents both challenges and opportunities. The market reaction has shown the critical dependence of global industries on Congo's cobalt production and the vulnerability of supply chains to geopolitical factors. The success of the new quota system hinges on transparent implementation and a commitment to sustainable and ethical mining practices. Collaboration between governments, industry players, and civil society is essential to navigate the complexities of the cobalt market and build a more responsible and resilient supply chain. Stay updated on the latest developments regarding Congo's cobalt export policies and contribute to a more sustainable future by supporting responsibly sourced cobalt.

Featured Posts
-
 Butlers Big Game Golden State Warriors Defeat Houston Rockets
May 15, 2025
Butlers Big Game Golden State Warriors Defeat Houston Rockets
May 15, 2025 -
 Trump Officials Push Back Against Rfk Jr S Pesticide Criticism
May 15, 2025
Trump Officials Push Back Against Rfk Jr S Pesticide Criticism
May 15, 2025 -
 Stock Market Valuation Concerns Bof As Perspective And Guidance For Investors
May 15, 2025
Stock Market Valuation Concerns Bof As Perspective And Guidance For Investors
May 15, 2025 -
 Stocks Surge On Bse Sensex Rally And Top Performers
May 15, 2025
Stocks Surge On Bse Sensex Rally And Top Performers
May 15, 2025 -
 Indias Vulnerability How Reciprocal Tariffs Threaten Key Industries
May 15, 2025
Indias Vulnerability How Reciprocal Tariffs Threaten Key Industries
May 15, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Warriors Expect Jimmy Butler To Play In Game 3
May 15, 2025
Warriors Expect Jimmy Butler To Play In Game 3
May 15, 2025 -
 Warriors Defeat Jimmy Butler Suffers Pelvic Contusion Future Games In Jeopardy
May 15, 2025
Warriors Defeat Jimmy Butler Suffers Pelvic Contusion Future Games In Jeopardy
May 15, 2025 -
 Padres Vs Dodgers Will The Padres Thwart The Dodgers Strategy
May 15, 2025
Padres Vs Dodgers Will The Padres Thwart The Dodgers Strategy
May 15, 2025 -
 Padres Resistance To Dodgers Master Plan A Season Of Rivalry
May 15, 2025
Padres Resistance To Dodgers Master Plan A Season Of Rivalry
May 15, 2025 -
 Jimmy Butlers Pelvic Contusion Game Status Uncertain After Warriors Loss
May 15, 2025
Jimmy Butlers Pelvic Contusion Game Status Uncertain After Warriors Loss
May 15, 2025
