India's Vulnerability: How Reciprocal Tariffs Threaten Key Industries
Table of Contents
India's burgeoning economy, fueled by globalization and ambitious growth targets, faces a significant challenge: the increasing threat of reciprocal tariffs. While the liberalization of global trade has undeniably propelled India's economic progress, escalating trade tensions and retaliatory tariffs pose a serious risk to several key Indian industries. This article explores the vulnerability of these sectors and analyzes the potential consequences of escalating trade wars, emphasizing the need for proactive mitigation strategies.
Impact on India's Export-Oriented Industries
Keywords: Export, Textiles, Pharmaceuticals, Agriculture, IT, Global Competitiveness, Market Access
Reciprocal tariffs directly hinder India's ability to export goods, impacting its global competitiveness and market access. The imposition of tariffs by other nations leads to reduced demand for Indian products, increased competition, and ultimately, a decrease in export revenue. This negatively affects several key export-oriented industries:
- Reduced demand for Indian textiles: Higher import duties in major markets like the US and EU significantly reduce the competitiveness of Indian textiles, impacting employment and revenue generation within this crucial sector.
- Increased competition for Indian pharmaceuticals: The imposition of tariffs makes Indian pharmaceuticals less price-competitive in international markets, potentially hindering growth and market share.
- Challenges for Indian agricultural exports: Higher import duties on agricultural products like rice, spices, and fruits restrict market access and limit the potential for growth in this vital sector.
- Potential loss of IT contracts: Protectionist measures in some countries could lead to a loss of IT contracts for Indian companies, affecting the country's burgeoning IT services sector.
- Impact on India's global competitiveness: The cumulative effect of reciprocal tariffs reduces India's overall global competitiveness, making it harder to attract foreign investment and compete on the world stage.
Case Study: The Textile Industry's Struggle
The Indian textile industry, a significant contributor to employment and exports, is particularly vulnerable to reciprocal tariffs. Increased import duties in key markets have led to a decline in exports, impacting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) disproportionately. Data from [Insert Source – e.g., Ministry of Commerce and Industry] shows a [Insert Percentage]% decline in textile exports to [Insert Country] following the imposition of tariffs in [Insert Year]. This decline has resulted in [Insert Number] job losses and a significant reduction in revenue for the industry.
Vulnerability of Specific Sectors
Keywords: Steel, Automobiles, Electronics, Supply Chains, Domestic Manufacturing
Beyond export-oriented industries, several other sectors are highly susceptible to the disruptive effects of reciprocal tariffs. The interconnectedness of global supply chains means that even industries focused on domestic consumption are affected by trade barriers.
- Increased costs for steel imports impacting the automobile industry: Higher steel import costs increase the production costs of automobiles, making them less competitive both domestically and internationally.
- Reduced competitiveness of Indian electronics manufacturers: Increased tariffs on imported components make Indian electronics less price-competitive, hindering their growth and market penetration.
- Disruption of supply chains due to tariff barriers: Tariffs disrupt the smooth flow of goods and components, leading to production delays, increased costs, and potential shortages.
- Impact on domestic manufacturing and job creation: The higher costs associated with tariffs reduce the profitability of domestic manufacturing, potentially leading to job losses and slower economic growth.
The Automobile Sector: A Critical Analysis
The Indian automobile industry, a significant contributor to the country’s GDP, is heavily reliant on imported components. The imposition of reciprocal tariffs on these components significantly increases production costs, impacting the competitiveness of Indian-made vehicles, both domestically and for export. This vulnerability highlights the need for policy interventions to promote domestic manufacturing of key auto components.
Economic Consequences and Mitigation Strategies
Keywords: GDP Growth, Inflation, Employment, Trade Agreements, Diversification, Policy Response
The cumulative effect of reciprocal tariffs can have significant macroeconomic consequences for India.
- Potential slowdown in GDP growth due to reduced exports and investment: Reduced export revenues and decreased foreign investment can lead to a slowdown in GDP growth.
- Increased inflation due to higher import costs: Higher import costs due to tariffs can lead to increased inflation, eroding consumer purchasing power.
- Job losses in affected industries: Reduced competitiveness and decreased demand can lead to job losses in various sectors.
Mitigation strategies are crucial to counter the negative effects of reciprocal tariffs:
- Negotiating favorable trade agreements: India needs to actively negotiate and strengthen trade agreements to secure preferential market access for its exports.
- Need for policy interventions to support vulnerable industries: Targeted government support, such as subsidies and tax breaks, can help vulnerable industries overcome the challenges posed by tariffs.
- Strategies for economic diversification: Reducing reliance on specific export markets and diversifying into new industries can reduce vulnerability to trade shocks.
Conclusion
India's vulnerability to reciprocal tariffs is a significant concern, impacting key export-oriented industries such as textiles and pharmaceuticals, as well as sectors like automobiles and electronics that rely on imported components. The potential consequences, including reduced GDP growth, higher inflation, and job losses, highlight the urgency of addressing this challenge. Proactive strategies, including diversification of export markets, strengthening domestic manufacturing capabilities, and engaging in effective trade diplomacy, are vital to mitigate the potential damage and ensure the continued growth of the Indian economy. Further research into the impact of reciprocal tariffs and the development of robust mitigation strategies are essential to safeguard India's economic future. Ignoring the threat of reciprocal tariffs will only exacerbate India’s economic vulnerability. A proactive and comprehensive approach is essential to navigate this challenge and ensure continued economic prosperity.

Featured Posts
-
 Hamer Bruins Moet Met Npo Toezichthouder Over Leeflang Praten
May 15, 2025
Hamer Bruins Moet Met Npo Toezichthouder Over Leeflang Praten
May 15, 2025 -
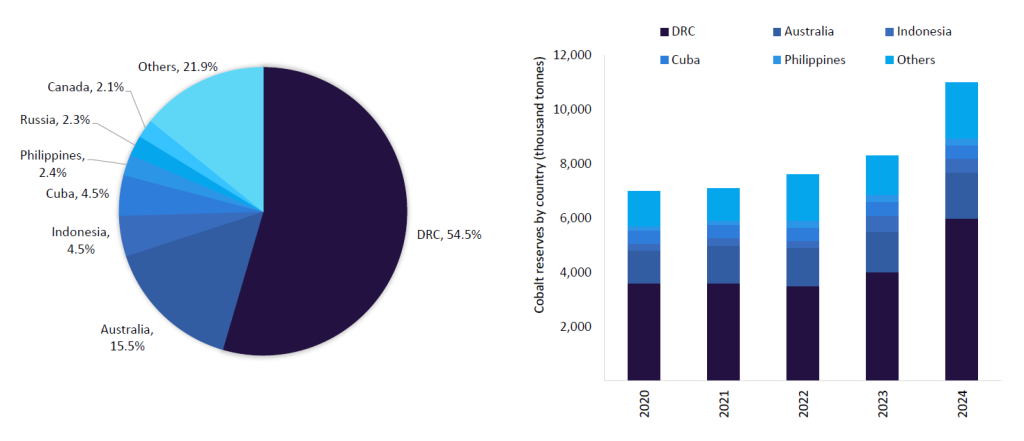 Cobalt Market Outlook Assessing The Impact Of Congos Export Ban And Future Quotas
May 15, 2025
Cobalt Market Outlook Assessing The Impact Of Congos Export Ban And Future Quotas
May 15, 2025 -
 Buduschee Turetskogo Voennogo Kontingenta Na Kipre Obsuzhdenie Na Haqqin Az
May 15, 2025
Buduschee Turetskogo Voennogo Kontingenta Na Kipre Obsuzhdenie Na Haqqin Az
May 15, 2025 -
 Trump Supporter Ray Epps Defamation Case Against Fox News The January 6th Allegations
May 15, 2025
Trump Supporter Ray Epps Defamation Case Against Fox News The January 6th Allegations
May 15, 2025 -
 Hamer Bruins En Npo Toezichthouder Moeten Over Leeflang Praten
May 15, 2025
Hamer Bruins En Npo Toezichthouder Moeten Over Leeflang Praten
May 15, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Stock Market Valuation Concerns Bof As Perspective And Guidance For Investors
May 15, 2025
Stock Market Valuation Concerns Bof As Perspective And Guidance For Investors
May 15, 2025 -
 Xi Jinpings Calculated Move Expert Led Us Deal Negotiations
May 15, 2025
Xi Jinpings Calculated Move Expert Led Us Deal Negotiations
May 15, 2025 -
 The U S And Greenland The Untold Story Of A Hidden Nuclear Base
May 15, 2025
The U S And Greenland The Untold Story Of A Hidden Nuclear Base
May 15, 2025 -
 16 Billion At Stake How Trumps Tariffs Affect Californias Revenue
May 15, 2025
16 Billion At Stake How Trumps Tariffs Affect Californias Revenue
May 15, 2025 -
 Goldman Sachs Deciphers Trumps Preferred Oil Price Range
May 15, 2025
Goldman Sachs Deciphers Trumps Preferred Oil Price Range
May 15, 2025
