Deadly Fungi: The Emerging Superbug Crisis
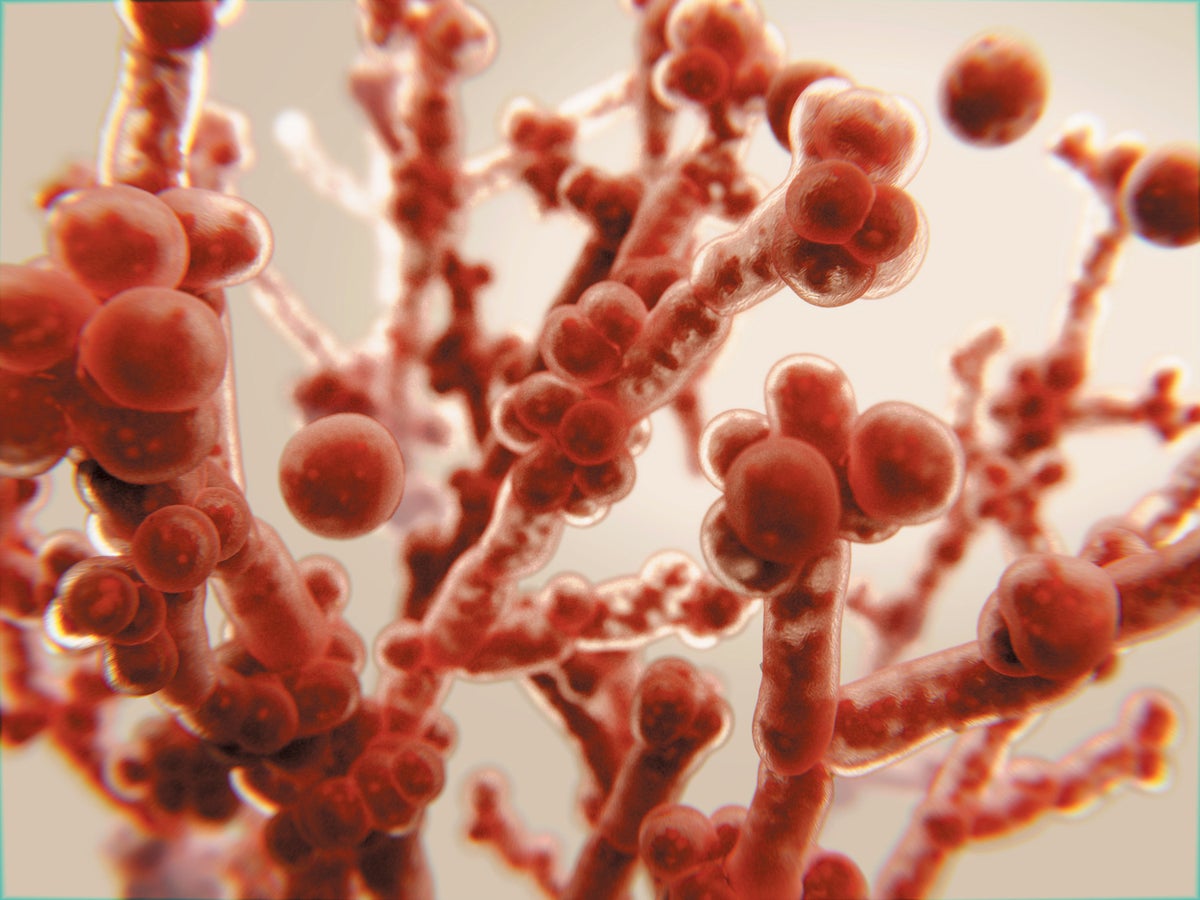
Table of Contents
The Rise of Antifungal Resistance
The overuse and misuse of antifungal medications are driving the evolution of resistant fungal strains. This is creating a serious public health challenge, especially for immunocompromised individuals. The development of antifungal resistance mirrors the trajectory of antibiotic resistance, highlighting the urgent need for proactive strategies. This escalating resistance means that infections once easily treatable are now becoming increasingly difficult, if not impossible, to cure.
-
Increased use of antifungals in agriculture and medicine: The widespread use of antifungals in agriculture to protect crops and in medicine to treat human and animal infections contributes significantly to the selection and spread of resistant strains. This overuse creates an environment where only the most resistant fungi survive and reproduce.
-
Lack of new antifungal drug development: The pharmaceutical industry has historically invested less in developing new antifungal drugs compared to antibacterial drugs. This shortage of new options limits our ability to effectively treat resistant fungal infections. The pipeline of novel antifungals is painfully slow, leaving us with fewer weapons to fight these deadly pathogens.
-
Improper use of antifungal medications leading to resistance: Incorrect dosages, incomplete treatment courses, and the use of antifungals for non-fungal infections all contribute to the selection and proliferation of resistant strains. Patient adherence to prescribed treatment regimens is crucial in preventing the emergence of resistance.
-
Spread of resistant strains through healthcare settings: Hospitals and other healthcare facilities are breeding grounds for the transmission of resistant fungal pathogens. These settings often house immunocompromised individuals who are particularly vulnerable to severe infections. Improved infection control practices are critical in limiting this spread.
High-Risk Populations and Deadly Fungi Infections
Certain populations are at a significantly higher risk of developing severe fungal infections. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. These individuals often have weakened immune systems, making them particularly susceptible to opportunistic fungal infections.
-
Immunocompromised individuals (e.g., HIV/AIDS patients, organ transplant recipients, cancer patients): Individuals with compromised immune systems are unable to effectively fight off fungal infections, leading to potentially life-threatening consequences.
-
Patients receiving prolonged antibiotic treatment: Antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms in the body, creating an opportunity for fungi to thrive and cause infection. This is a significant concern, especially in hospital settings.
-
Individuals with underlying health conditions (e.g., diabetes, chronic lung disease): These conditions can further weaken the immune system and increase susceptibility to fungal infections. Managing these underlying conditions is essential in reducing the risk of fungal disease.
-
Premature infants and newborns: Newborns and premature infants have immature immune systems, making them highly susceptible to invasive fungal infections. Prophylactic measures and close monitoring are essential in these vulnerable populations.
Types of Deadly Fungi and Their Impact
Several species of fungi pose a significant threat, each with unique characteristics and challenges in treatment. The emergence of multi-drug resistant strains is particularly alarming, creating a critical need for novel therapeutic strategies.
-
Candida auris: This highly drug-resistant yeast is a major concern in healthcare settings, causing bloodstream infections and other severe illnesses. Its resistance to multiple antifungal agents makes treatment extremely challenging.
-
Aspergillus fumigatus: A common mold, Aspergillus fumigatus can cause invasive aspergillosis, a life-threatening condition, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems or lung disease. This fungus poses a significant threat to transplant recipients and those with chronic lung conditions.
-
Cryptococcus neoformans: This fungus primarily causes meningitis, particularly in individuals with HIV/AIDS. Its ability to spread through the bloodstream and infect the central nervous system makes it a particularly dangerous pathogen.
-
Emerging fungal pathogens and their increasing resistance: New and emerging fungal pathogens are constantly evolving, with some exhibiting resistance to even the most potent antifungal drugs. This underscores the dynamic and evolving nature of this public health threat.
Combating the Deadly Fungi Crisis: Prevention and Treatment Strategies
A multi-pronged approach is necessary to effectively combat this growing threat. This requires a concerted effort from healthcare professionals, researchers, and public health officials.
-
Strict infection control protocols in healthcare settings: Implementing robust infection control measures, including hand hygiene, environmental cleaning, and appropriate isolation procedures, is crucial in preventing the spread of resistant fungal pathogens.
-
Responsible use of antifungal medications: Promoting the judicious use of antifungals through antifungal stewardship programs can help slow the development of resistance. This involves optimizing treatment regimens, avoiding unnecessary use, and encouraging adherence to prescribed treatments.
-
Development of new antifungal drugs and treatment strategies: Increased investment in research and development of new antifungal drugs and alternative treatment strategies is urgently needed to combat drug-resistant fungi.
-
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment of fungal infections: Rapid and accurate diagnosis of fungal infections is critical to initiate timely treatment and improve patient outcomes. This requires improved diagnostic tools and greater awareness among healthcare providers.
-
Public health surveillance and monitoring of resistant strains: Robust surveillance systems are essential to track the emergence and spread of resistant fungal strains, allowing for targeted interventions and informed public health strategies.
Conclusion
The rise of deadly fungi presents a significant and growing threat to global health. The increasing resistance to antifungal drugs, coupled with the vulnerability of high-risk populations, necessitates urgent action. By implementing stricter infection control measures, promoting responsible antifungal use, and investing in research and development of new treatments, we can mitigate the impact of this emerging superbug crisis. Let's work together to prevent the spread of deadly fungi and protect vulnerable populations. Learn more about the dangers of deadly fungi and how you can contribute to prevention efforts.

Featured Posts
-
 Historical Universal Credit Payments Are You Missing Out
May 08, 2025
Historical Universal Credit Payments Are You Missing Out
May 08, 2025 -
 Alshmrany Rayh Fy Antqal Jysws Lflamnghw Fydyw W Tfasyl
May 08, 2025
Alshmrany Rayh Fy Antqal Jysws Lflamnghw Fydyw W Tfasyl
May 08, 2025 -
 Billionaires Favorite Etf Predicted 110 Surge In 2025
May 08, 2025
Billionaires Favorite Etf Predicted 110 Surge In 2025
May 08, 2025 -
 Breaking Bread With Scholars Navigating Academic Conversations And Networking
May 08, 2025
Breaking Bread With Scholars Navigating Academic Conversations And Networking
May 08, 2025 -
 Sufian Commends Gcci President For Successful Expo 2025 Organization
May 08, 2025
Sufian Commends Gcci President For Successful Expo 2025 Organization
May 08, 2025
