Global COVID-19 Case Rise: A New Variant's Potential Role, Says WHO

Table of Contents
Rising COVID-19 Infection Rates Globally
The world is witnessing a renewed surge in COVID-19 infections. While precise global figures fluctuate daily, reports from reliable sources like the WHO and Johns Hopkins University consistently indicate a significant increase in reported cases compared to previous months. This isn't uniformly distributed; some regions are experiencing far more dramatic increases than others.
- Specific Regions Experiencing Significant Increases: Data indicates substantial increases in case numbers in parts of Asia, Europe, and the Americas. Specific countries within these regions may experience larger or smaller increases depending on factors like vaccination rates and public health measures.
- Percentage Increase Compared to Previous Periods: The percentage increase varies widely by region, but many areas are seeing double-digit or even triple-digit percentage increases in COVID-19 cases compared to the previous month or quarter. (Note: Specific data would be inserted here if available from reliable sources and would be presented visually in a chart or graph.)
- Data Visualization: Visual representations of the data (e.g., interactive maps, line graphs showcasing infection rates over time) would provide a more impactful understanding of the global situation. These visualizations would clearly illustrate the variations in case numbers across different countries and regions.
The variations in case numbers aren't solely attributable to a new variant. Other factors are undoubtedly at play, including:
- Seasonal Factors: Changes in weather patterns can influence virus transmission rates.
- Reduced Testing: Decreased testing capacity in some regions may lead to underreporting of actual case numbers.
- Waning Immunity: The effectiveness of initial vaccinations and prior infections may wane over time, making individuals more susceptible to reinfection.
The Potential Role of New COVID-19 Variants
The emergence of new COVID-19 variants remains a significant concern. These variants, through mutations, can exhibit changes in transmissibility, severity, and vaccine effectiveness. While specific variant names (like XBB.1.5 or future variants) will be identified as they emerge, the general impact remains consistent.
- Characteristics of Concerning New Variants: New variants often exhibit increased transmissibility, allowing for faster spread within populations. Furthermore, some variants demonstrate immune evasion capabilities, meaning they can circumvent the immunity conferred by previous infections or vaccinations.
- Severity of Illness: While some variants might be more transmissible, the severity of illness they cause can vary. Data on hospitalizations and deaths related to new variants is crucial for assessing their public health impact. This data needs careful analysis to differentiate between increased transmission and increased virulence.
- Vaccine Effectiveness: The effectiveness of current vaccines in protecting against infection, severe illness, and death from new variants is continuously monitored and updated by health organizations. Booster shots are often recommended to maintain protection against emerging variants.
Understanding variant evolution is challenging. Predicting their future behavior requires ongoing genomic surveillance and analysis by experts in virology and epidemiology. Statements from the WHO and other leading virologists offer valuable insights into the current understanding and potential future trajectories of these variants.
Public Health Responses and Mitigation Strategies
Global health organizations and individual countries are implementing various measures to control the rising COVID-19 cases. These strategies focus on preventing transmission, managing severe cases, and minimizing the overall impact of the pandemic.
- Vaccination Campaigns and Booster Shots: Mass vaccination campaigns, including booster shots, remain a cornerstone of mitigation strategies. These campaigns aim to maximize population immunity and reduce severe outcomes.
- Testing and Surveillance Strategies: Robust testing and genomic surveillance systems are critical for early detection and tracking of new variants. This rapid identification enables prompt public health responses.
- Public Health Messaging and Guidelines: Clear communication through public health campaigns emphasizing the importance of preventative measures like mask-wearing, social distancing, and hand hygiene remains crucial.
- International Collaboration and Data Sharing: International cooperation is essential for effective pandemic management. Sharing data, resources, and best practices is critical for a global response to this global health crisis.
The effectiveness of these strategies varies across different settings, influenced by factors like access to resources, compliance with guidelines, and the specific characteristics of the circulating variants. Equitable access to vaccines and testing is paramount for ensuring a global, effective response.
The Importance of Continued Surveillance and Research
The continued emergence of new variants necessitates ongoing genomic surveillance. This critical process allows for:
- Rapid Detection and Characterization of New Variants: Early detection of new variants is essential for enabling timely responses, such as adapting vaccines and public health measures.
- Continued Research on Vaccine Development and Antiviral Treatments: Investment in research and development of new vaccines and antiviral treatments is crucial for maintaining a strong defense against emerging variants.
- Data Sharing and International Collaboration: The sharing of genomic data and research findings across international borders enables a more comprehensive and rapid response to emerging threats.
The long-term implications of the pandemic highlight the importance of preparedness for future outbreaks. Investing in global health infrastructure, surveillance systems, and research capabilities is vital for mitigating the risk of future pandemics.
Conclusion
The global rise in COVID-19 cases, fueled by the potential impact of new variants, underscores the ongoing need for vigilance. This article highlighted the importance of understanding the factors contributing to the surge in infections and the crucial role of public health responses. Continued surveillance, research, and adherence to preventative measures remain crucial for managing this evolving global health crisis. Stay informed about the latest developments concerning global COVID-19 cases, follow public health guidelines, and get vaccinated/boosted to protect yourself and help mitigate the spread of the virus and new variants. The fight against rising COVID-19 infection rates is an ongoing battle requiring our collective effort.

Featured Posts
-
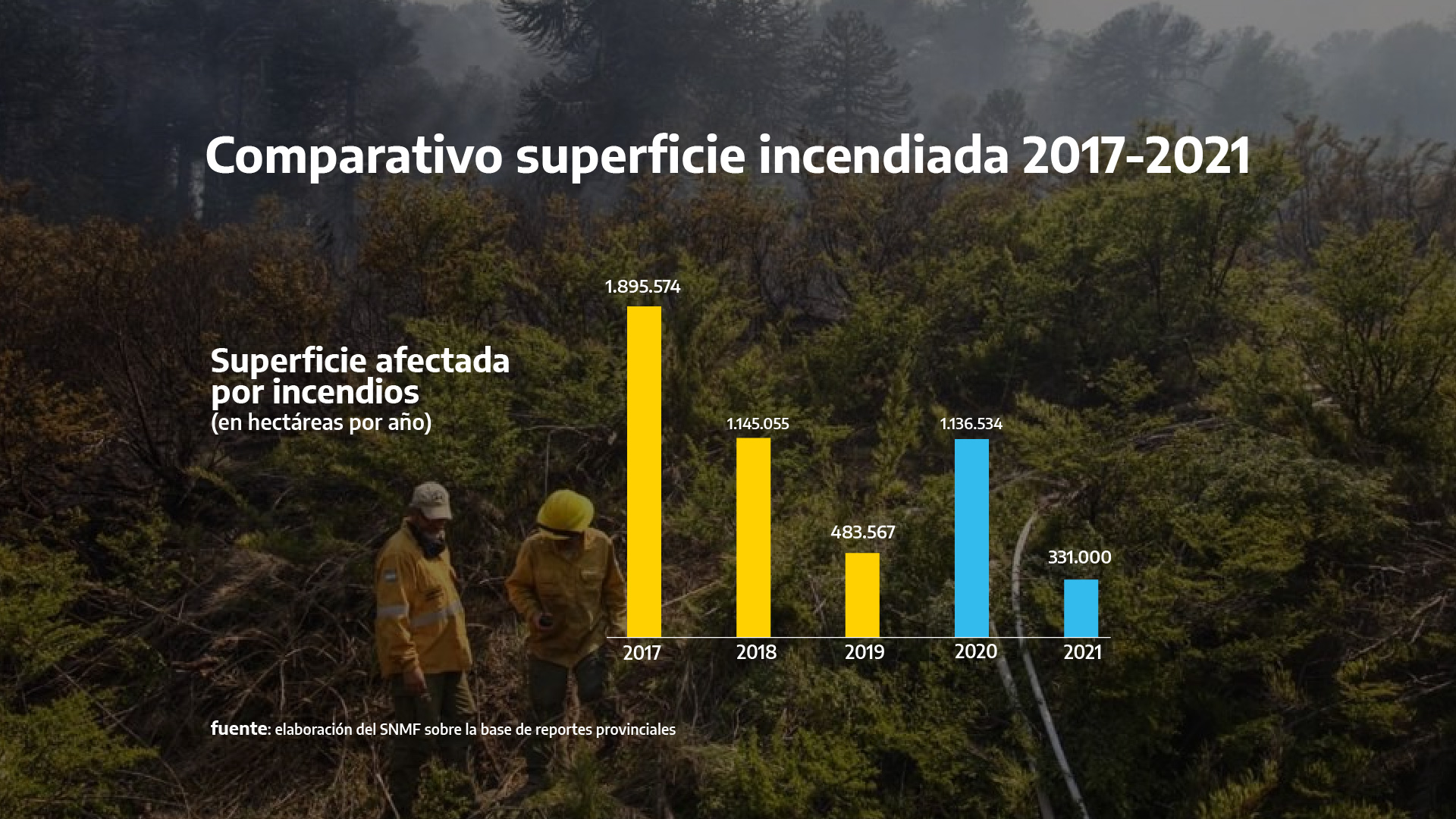 Constanza Afectada Por Incendio Bomberos Forestales En Accion
May 31, 2025
Constanza Afectada Por Incendio Bomberos Forestales En Accion
May 31, 2025 -
 Hot Girl Cau Long Thuy Linh Doi Thu Dang Gom Tai Vong 1 Thuy Si Mo Rong 2025
May 31, 2025
Hot Girl Cau Long Thuy Linh Doi Thu Dang Gom Tai Vong 1 Thuy Si Mo Rong 2025
May 31, 2025 -
 Orange County High School Sports Friday May 23rd Game Results And Player Statistics
May 31, 2025
Orange County High School Sports Friday May 23rd Game Results And Player Statistics
May 31, 2025 -
 La Receta De Carcamusas Un Plato Tradicional Toledano Rico En Proteinas
May 31, 2025
La Receta De Carcamusas Un Plato Tradicional Toledano Rico En Proteinas
May 31, 2025 -
 Decouvrir La Vie Et L Uvre D Arnarulunguaq Une Pionniere Inuit
May 31, 2025
Decouvrir La Vie Et L Uvre D Arnarulunguaq Une Pionniere Inuit
May 31, 2025
