Global Forest Destruction: A Record Year Fueled By Wildfires
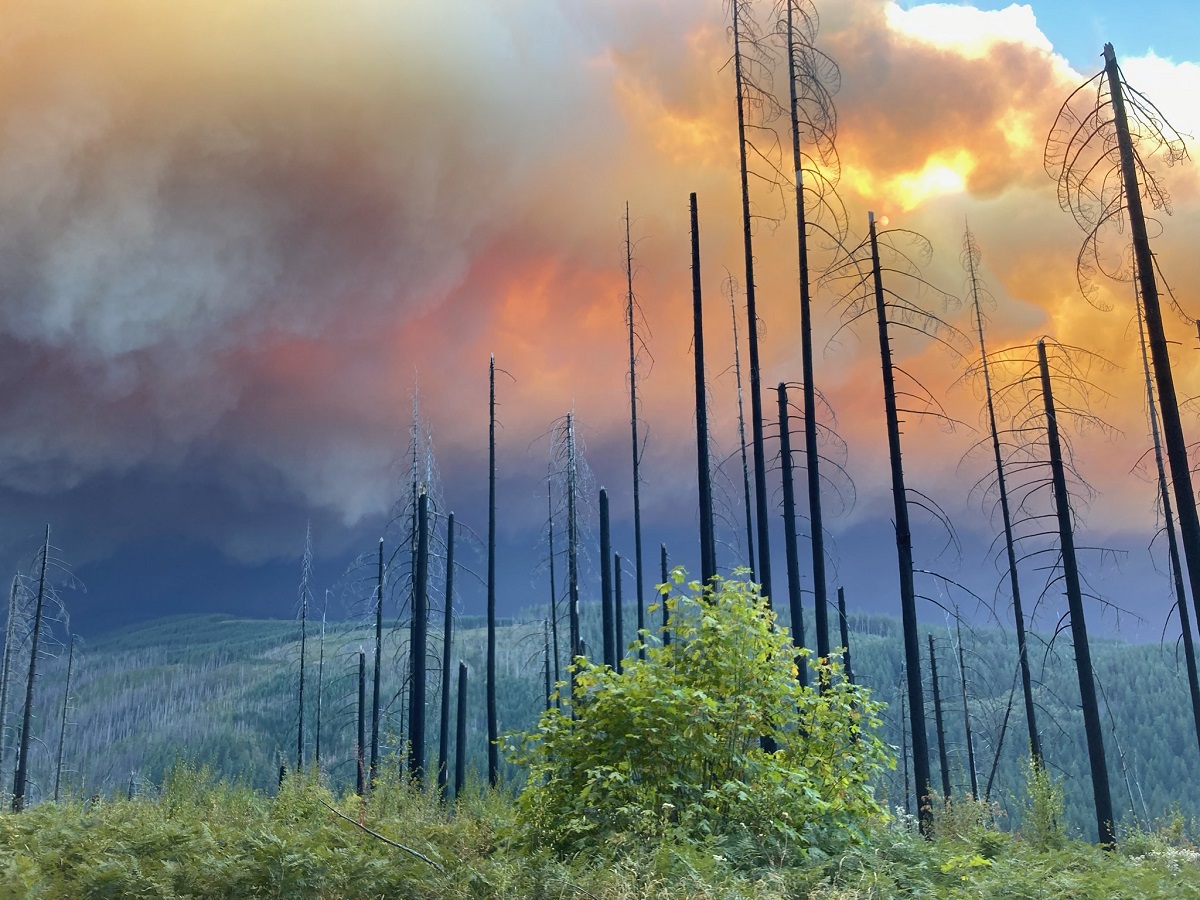

Table of Contents
The Role of Wildfires in Global Forest Destruction
Increased Frequency and Intensity of Wildfires
Climate change is undeniably a primary driver of increased wildfire frequency and intensity. Hotter, drier conditions create ideal fuel for wildfires, allowing them to ignite easily and spread rapidly across vast areas. This leads to longer fire seasons, resulting in more extensive damage and significantly longer recovery times for affected forests. The impact is devastating, leaving behind scarred landscapes and severely impacting biodiversity.
- Examples of major 2023 wildfire events contributing to global forest destruction:
- The Canadian wildfires of 2023 released an unprecedented amount of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, exceeding the total emissions from several countries.
- Extensive wildfires in Australia, Indonesia, and parts of the Amazon rainforest also contributed substantially to global forest destruction.
- Scale of forest area burned: Precise figures are still being compiled, but preliminary estimates indicate millions of hectares of forest were destroyed globally in 2023 due to wildfires.
Human-Induced Wildfires
While climate change intensifies the conditions, human actions remain significant contributors to wildfire outbreaks. Arson, accidental ignition from human activities, and inadequate forest management practices all play a role. Deforestation and land-clearing practices further increase the risk by creating more readily available fuel and fragmenting forest landscapes.
- Human impact on wildfire initiation and spread:
- Arson: Deliberately set fires account for a significant portion of wildfires, particularly in areas with weak law enforcement.
- Accidental fires: Negligently discarded cigarettes, campfires left unattended, and power line failures can all spark devastating wildfires.
- Deforestation: Clearing forests for agriculture or development creates fragmented landscapes, which serve as natural firebreaks. Removing these breaks accelerates wildfire spread.
- Lack of fire prevention: Insufficient investment in fire prevention and suppression technologies and strategies, especially in developing countries, exacerbates the problem.
Deforestation Beyond Wildfires: Other Key Drivers of Global Forest Loss
Beyond wildfires, several other factors contribute significantly to global forest destruction. These interconnected issues require a multifaceted approach to effective forest conservation.
Illegal Logging and Timber Trade
The illegal logging industry remains a significant driver of deforestation, particularly in tropical rainforests. Weak law enforcement, corruption, and high demand for timber products fuel this unsustainable practice. The illegal timber trade deprives nations of valuable resources and undermines efforts towards sustainable forestry.
- Scale of illegal logging and its impact: Illegal logging contributes to habitat loss, biodiversity reduction, and carbon emissions. It often targets high-value timber species, further depleting forest resources. Millions of cubic meters of timber are illegally harvested annually.
Agricultural Expansion and Land Conversion
The conversion of forests to agricultural land, driven by the increasing global demand for food and biofuels, is a primary cause of deforestation. Palm oil plantations, cattle ranching, and soybean farming are particularly damaging. Unsustainable agricultural practices further degrade remaining forest ecosystems.
- Impact of agriculture on forest loss: Large-scale monoculture agriculture replaces diverse forest ecosystems, resulting in biodiversity loss and soil degradation. Deforestation for agriculture is a leading contributor to greenhouse gas emissions.
Mining and Infrastructure Development
Mining operations and the construction of roads, dams, and other infrastructure projects frequently lead to widespread deforestation and habitat fragmentation. A lack of stringent environmental regulations and inadequate impact assessments exacerbate the problem.
- Impact of mining and infrastructure: Mining activities often involve clearing large areas of forest for access roads, extraction sites, and waste disposal. Infrastructure projects can fragment habitats, isolating populations and hindering natural regeneration.
The Impact of Global Forest Destruction
The consequences of global forest destruction are far-reaching and deeply impactful.
Biodiversity Loss
Deforestation leads to habitat loss and fragmentation, pushing countless plant and animal species towards extinction. Unique ecosystems are destroyed, leading to an irreversible loss of biodiversity.
- Specific species affected: Many endangered species, including orangutans, tigers, and numerous bird species, are directly threatened by habitat loss due to deforestation.
Climate Change Exacerbation
Forests play a crucial role in carbon sequestration, absorbing atmospheric CO2. Their destruction releases vast amounts of stored carbon, accelerating climate change.
- Relationship between forest loss and rising temperatures: Deforestation contributes significantly to the increase in greenhouse gases, leading to rising global temperatures and more extreme weather events.
Economic and Social Consequences
Deforestation has severe economic and social consequences. Indigenous communities who rely on forests for their livelihoods are often displaced and deprived of their traditional way of life. The loss of forests increases the risk of natural disasters like floods and landslides.
- Socio-economic impacts: Deforestation leads to reduced ecosystem services, including clean water, fertile soil, and climate regulation, impacting human well-being and economic stability.
Conclusion
The record levels of global forest destruction in 2023 demand immediate and decisive action. Wildfires, driven by climate change and human activities, are a major factor, but illegal logging, agricultural expansion, and infrastructure development also play crucial roles. The consequences – biodiversity loss, climate change exacerbation, and socioeconomic disruption – are devastating. To prevent further catastrophic global forest destruction, we must implement stricter policies to combat deforestation, invest heavily in sustainable forestry practices, actively promote reforestation efforts, and urgently address climate change. Let's work together to protect our forests and secure a sustainable future.

Featured Posts
-
 Sabalenkas Rome Run Ends Zheng Qinwen To Play Gauff
May 26, 2025
Sabalenkas Rome Run Ends Zheng Qinwen To Play Gauff
May 26, 2025 -
 Millions Stolen Inside The Office365 Executive Hack
May 26, 2025
Millions Stolen Inside The Office365 Executive Hack
May 26, 2025 -
 Paris Roubaix Spectator Who Threw Bottle At Van Der Poel Turns Himself In
May 26, 2025
Paris Roubaix Spectator Who Threw Bottle At Van Der Poel Turns Himself In
May 26, 2025 -
 Largest English Language Yom Ha Zikaron Ceremony Hosted By Masa Israel
May 26, 2025
Largest English Language Yom Ha Zikaron Ceremony Hosted By Masa Israel
May 26, 2025 -
 Prenez Le Depart Avec La Rtbf Gerez Votre Equipe Cycliste Pour Le Tour De France
May 26, 2025
Prenez Le Depart Avec La Rtbf Gerez Votre Equipe Cycliste Pour Le Tour De France
May 26, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Comparatif Samsung Galaxy S25 256 Go Vs Concurrents 775 E
May 28, 2025
Comparatif Samsung Galaxy S25 256 Go Vs Concurrents 775 E
May 28, 2025 -
 Bon Plan Samsung Galaxy S25 128 Go 5 Etoiles A 814 22 E
May 28, 2025
Bon Plan Samsung Galaxy S25 128 Go 5 Etoiles A 814 22 E
May 28, 2025 -
 Samsung Galaxy S25 256 Go Test Et Avis Complet 775 E
May 28, 2025
Samsung Galaxy S25 256 Go Test Et Avis Complet 775 E
May 28, 2025 -
 Samsung Galaxy S25 256 Go Le Top Produit A 775 E Notre Avis
May 28, 2025
Samsung Galaxy S25 256 Go Le Top Produit A 775 E Notre Avis
May 28, 2025 -
 Personal Loan Interest Rates Your Guide To Finding The Best Deal Today
May 28, 2025
Personal Loan Interest Rates Your Guide To Finding The Best Deal Today
May 28, 2025
