India Detects New COVID Variants BA.1 And LF.7: INSACOG's Findings And Public Health Implications
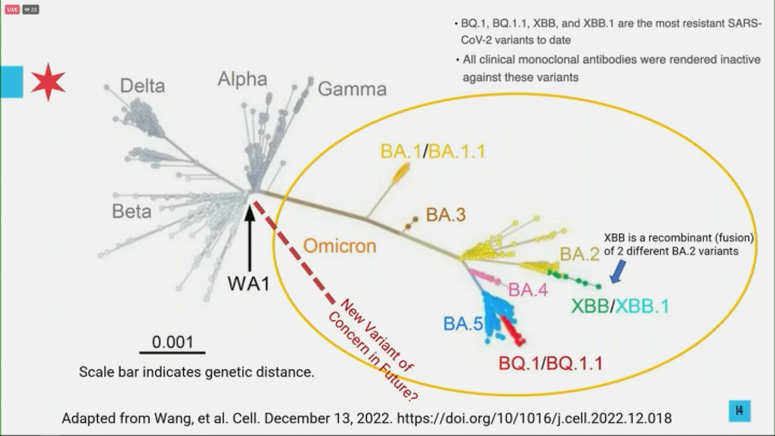
Table of Contents
INSACOG's Role in Variant Detection and Genomic Surveillance
INSACOG plays a pivotal role in India's fight against COVID-19. This consortium of laboratories across the country is responsible for conducting comprehensive genomic surveillance, allowing for the early identification and tracking of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Its network facilitates the rapid collection, sequencing, and analysis of viral samples, providing crucial data for informing public health strategies. This proactive approach to COVID-19 variant tracking has been instrumental in India's response to the pandemic.
- INSACOG's Network and Capabilities: INSACOG comprises a robust network of laboratories equipped with advanced whole-genome sequencing technology, enabling rapid analysis of viral genomes. This allows for swift identification of new variants and their characteristics.
- Whole-Genome Sequencing Methodology: The process involves extracting viral RNA from patient samples, converting it to DNA, and then sequencing the entire genome to identify genetic mutations.
- Previous Variant Detections: INSACOG's success in detecting and tracking previous variants, including Delta and Omicron sub-lineages, showcases its effectiveness in genomic surveillance. Early detection through whole-genome sequencing has been critical in tailoring public health responses.
- Importance of Early Detection: Early detection of new variants is critical for implementing timely and effective public health interventions, preventing widespread outbreaks, and minimizing the impact on the healthcare system.
Characteristics of the Newly Detected Variants BA.1 and LF.7
The newly detected variants, BA.1 and LF.7, represent further evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. While research is ongoing, preliminary findings are crucial for understanding their potential impact. Both variants exhibit specific mutations, which may affect their transmissibility, severity, and ability to evade existing immunity. Comparative analysis with other known variants is essential for assessing their threat level.
- Specific Mutations: Detailed analysis is underway to identify the specific mutations present in BA.1 and LF.7. These mutations are crucial for understanding their potential differences from previously circulating strains.
- Transmissibility Comparison: Studies are needed to determine if BA.1 and LF.7 exhibit higher transmissibility compared to previous variants like Omicron. This is a key factor in assessing their potential for widespread spread.
- Severity and Hospitalization Rates: The severity of illness caused by BA.1 and LF.7 requires further investigation. Data on hospitalization rates and severe disease outcomes will be crucial in determining their public health impact.
- Immune Escape Potential and Vaccine Efficacy: Determining the extent to which BA.1 and LF.7 can evade immunity provided by vaccination or prior infection is critical. This information will influence vaccination strategies and the need for booster shots.
Public Health Implications and Response Strategies
The detection of BA.1 and LF.7 highlights the continuing need for robust public health measures and a proactive response to new COVID-19 variants. Maintaining genomic surveillance, strengthening vaccination efforts, and promoting preventative measures are essential to mitigate the potential impact of these new variants.
- Continued Genomic Surveillance and Variant Tracking: Continuous monitoring of viral evolution through genomic surveillance remains crucial for early detection and rapid response to emerging variants.
- Vaccination Strategies and Boosters: Vaccination remains a cornerstone of COVID-19 prevention. Ongoing assessment of vaccine efficacy against BA.1 and LF.7 will inform booster strategies and vaccine development.
- Testing and Contact Tracing: Robust testing and contact tracing capacities remain essential for identifying cases, containing outbreaks, and preventing further spread.
- Public Health Messaging and Community Engagement: Clear and consistent public health messaging is vital for fostering community engagement and promoting preventative behaviors.
- International Collaboration: International collaboration and data sharing are critical for effective global pandemic management and response to emerging variants.
Conclusion
The detection of new COVID-19 variants BA.1 and LF.7 in India by INSACOG emphasizes the ongoing need for vigilant genomic surveillance and a comprehensive public health response. Continued monitoring, proactive vaccination strategies, and adherence to preventative measures are crucial for mitigating the potential impact of these and future variants. Stay informed about new COVID-19 variants and INSACOG's updates to ensure the health and safety of yourself and your community. Continue practicing preventative measures to mitigate the spread of COVID-19 and its variants. Regularly check for updates on new COVID-19 variants from trusted sources like INSACOG and the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, India.

Featured Posts
-
 Recetas Faciles Y Rapidas Para Apagones Sin Luz Ni Gas
May 31, 2025
Recetas Faciles Y Rapidas Para Apagones Sin Luz Ni Gas
May 31, 2025 -
 Moroccan Childrens Charity Receives Boost From Duncan Bannatyne
May 31, 2025
Moroccan Childrens Charity Receives Boost From Duncan Bannatyne
May 31, 2025 -
 April 9th Nyt Mini Crossword Puzzle Clues And Solutions
May 31, 2025
April 9th Nyt Mini Crossword Puzzle Clues And Solutions
May 31, 2025 -
 Tsitsipas Defeats Berrettini Medvedev Moves On At Indian Wells
May 31, 2025
Tsitsipas Defeats Berrettini Medvedev Moves On At Indian Wells
May 31, 2025 -
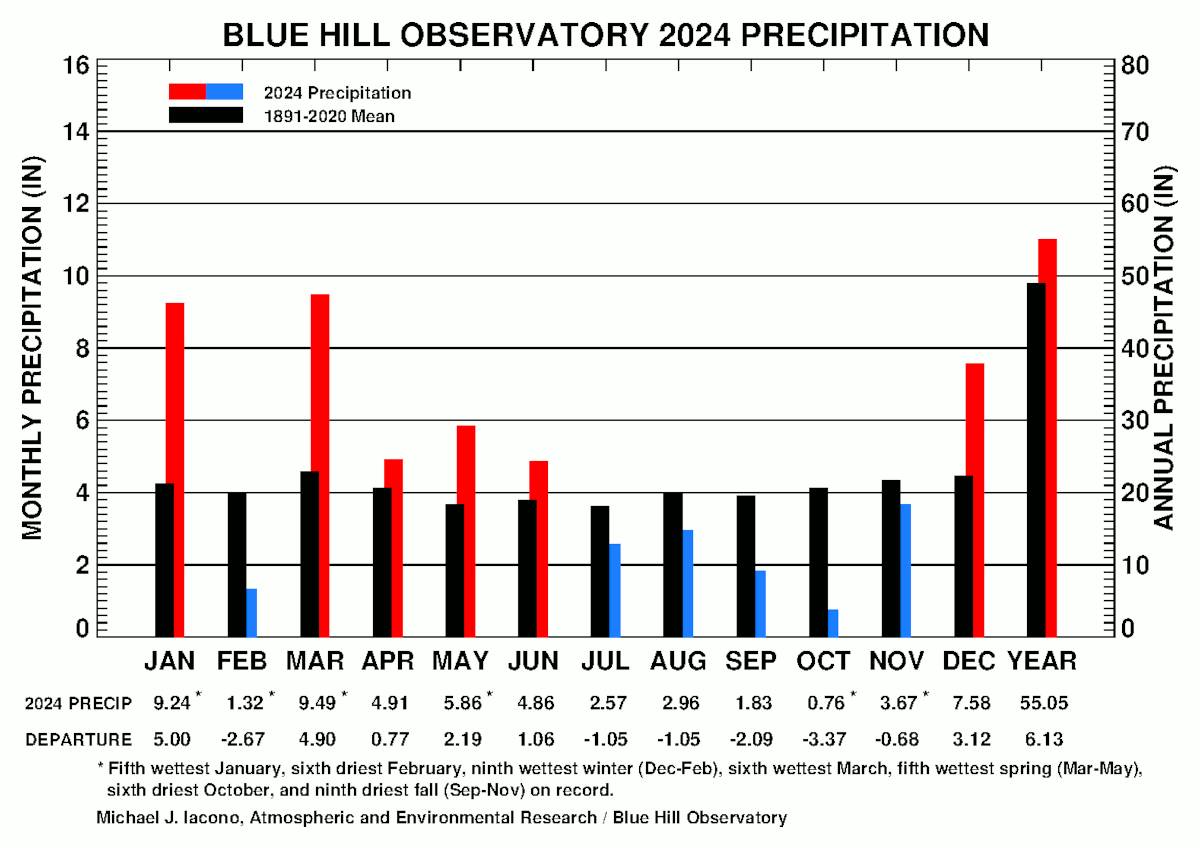 Aprils Rain Analyzing The Monthly Precipitation Totals
May 31, 2025
Aprils Rain Analyzing The Monthly Precipitation Totals
May 31, 2025
