Superbug Alert: The Danger Of Drug-Resistant Fungi
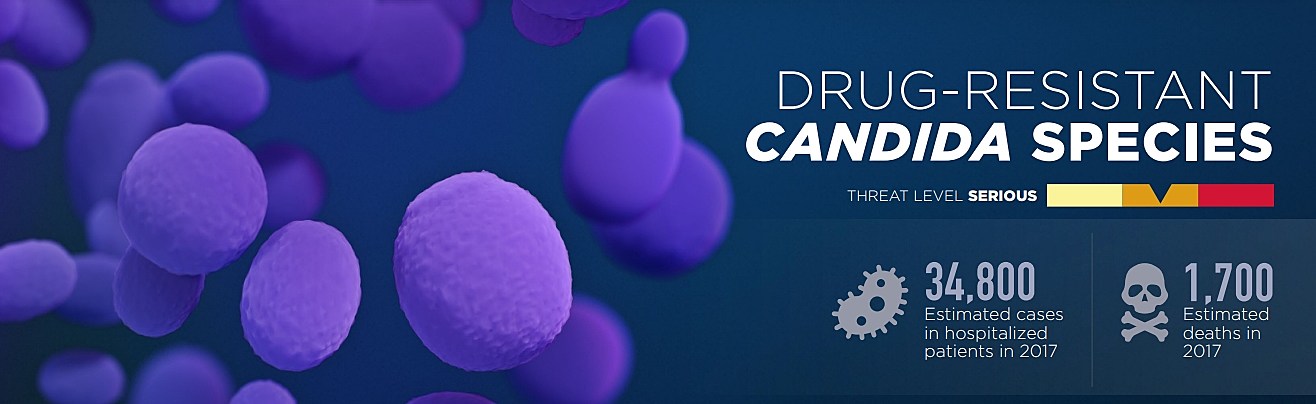
Table of Contents
The Rise of Antifungal Resistance
Understanding Antifungal Resistance
Antifungal resistance occurs when fungi develop mechanisms to survive exposure to antifungal drugs, rendering these treatments ineffective. This resistance develops through various methods:
- Target modification: Fungi alter the drug's target site, preventing the drug from binding and exerting its effect. This is common with azoles, a major class of antifungal drugs.
- Efflux pumps: Fungi develop pumps that actively expel antifungal drugs from their cells, reducing the drug's intracellular concentration.
- Reduced drug permeability: Fungi modify their cell walls or membranes to make them less permeable to antifungal drugs, limiting drug entry.
Several fungi are particularly notorious for developing resistance, including Candida auris, a highly drug-resistant yeast causing serious bloodstream infections, and Aspergillus fumigatus, a mold that can cause invasive aspergillosis, particularly dangerous for immunocompromised individuals. The rise of these drug-resistant fungi highlights the urgent need for effective strategies to combat antifungal resistance.
Contributing Factors to Antifungal Resistance
Several factors contribute to the escalating problem of antifungal resistance:
- Overuse and misuse of antifungals: The widespread and often unnecessary use of antifungal medications in both human healthcare and agriculture contributes significantly to the selection and proliferation of resistant strains. Improper use, such as incomplete treatment courses, further accelerates resistance development.
- Lack of new antifungal drug development: The antifungal drug pipeline is significantly less robust than that for antibacterial drugs. This shortage of new drugs limits treatment options for resistant infections.
- Globalization and travel: Increased global travel and trade facilitate the rapid spread of drug-resistant fungal strains across continents, making containment challenging.
These interconnected factors emphasize the complexity of the challenge and the need for a multi-pronged approach to address the issue.
The Impact of Drug-Resistant Fungi on Human Health
High-Risk Populations
Drug-resistant fungal infections pose a significant threat to several high-risk populations:
- Immunocompromised individuals: Patients with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy, organ transplantation recipients, or individuals with HIV/AIDS, are particularly vulnerable to severe fungal infections.
- Patients with underlying medical conditions: Individuals with chronic illnesses like diabetes, cancer, or cystic fibrosis are at increased risk due to their compromised immune function.
- Premature infants: These vulnerable newborns are particularly susceptible to invasive fungal infections due to their underdeveloped immune systems.
Serious infections caused by drug-resistant fungi, such as invasive candidiasis and aspergillosis, can lead to significant morbidity and mortality.
Mortality and Morbidity Rates
Drug-resistant fungal infections are associated with high mortality and morbidity rates, placing a considerable burden on healthcare systems:
- Increased mortality: Mortality rates for invasive fungal infections caused by drug-resistant strains are significantly higher compared to those caused by susceptible strains.
- Increased length of hospital stays: Treatment of drug-resistant fungal infections often requires prolonged hospitalization, increasing healthcare costs.
- Higher treatment costs: The need for more expensive and often less effective treatment options for resistant infections dramatically increases healthcare expenditure.
Combating the Threat of Drug-Resistant Fungi
Prevention Strategies
Implementing effective prevention strategies is crucial in minimizing the risk of fungal infections and the development of resistance:
- Improved infection control practices: Strict adherence to infection control protocols in healthcare settings is paramount, including proper hand hygiene, environmental cleaning, and the appropriate use of personal protective equipment.
- Judicious use of antifungals: Healthcare professionals should prescribe antifungals only when necessary and ensure appropriate dosages and treatment durations to minimize the risk of resistance development. This includes implementing antifungal stewardship programs to optimize antifungal use.
- Development and implementation of antifungal stewardship programs: These programs promote the responsible use of antifungals to prevent the emergence and spread of resistance.
The Need for New Antifungal Drugs and Therapies
The development of new antifungal drugs and alternative therapies is crucial to combating drug-resistant fungi:
- New antifungal targets: Research focuses on identifying novel targets within fungi to develop new classes of antifungal drugs that circumvent existing resistance mechanisms.
- Innovative treatment approaches: Alternative therapies, such as phage therapy (using bacteriophages to target fungi) and immunotherapy, are being explored to enhance treatment options for drug-resistant fungal infections.
- Increased funding for antifungal research: Government and pharmaceutical company investment in antifungal drug discovery and development is essential to address the urgent need for effective treatments.
Conclusion
The threat of drug-resistant fungi is a significant and growing public health concern. The high mortality rates, increased healthcare costs, and lack of effective treatment options highlight the urgency of the situation. The rise of antifungal resistance is driven by multiple factors, including the overuse of antifungals, a shortage of new drugs, and the global spread of resistant strains. Combating this threat requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing improved infection control, judicious antifungal use, and substantial investment in the research and development of new antifungal drugs and alternative therapies. The threat of drug-resistant fungi is real and growing. Let's work together to prevent the spread of these deadly superbugs before it's too late. Learn more about drug-resistant fungi and how you can help.

Featured Posts
-
 Ma Qalh Alshmrany En Antqal Jysws Almhtml Lflamnghw
May 08, 2025
Ma Qalh Alshmrany En Antqal Jysws Almhtml Lflamnghw
May 08, 2025 -
 20 Surprising Facts About The Making Of Saving Private Ryan
May 08, 2025
20 Surprising Facts About The Making Of Saving Private Ryan
May 08, 2025 -
 Jwayy Dstawyzat Awr Gdagry Tyn Khwatyn Grftar
May 08, 2025
Jwayy Dstawyzat Awr Gdagry Tyn Khwatyn Grftar
May 08, 2025 -
 No More Cash Uber Auto Payment Options Explained Upi And More
May 08, 2025
No More Cash Uber Auto Payment Options Explained Upi And More
May 08, 2025 -
 Wall Street Ten Kripto Paraya Artan Ilgi Yatirim Stratejileri Ve Riskler
May 08, 2025
Wall Street Ten Kripto Paraya Artan Ilgi Yatirim Stratejileri Ve Riskler
May 08, 2025
