The Debate On Uterus Transplants And Transgender Women's Reproductive Rights
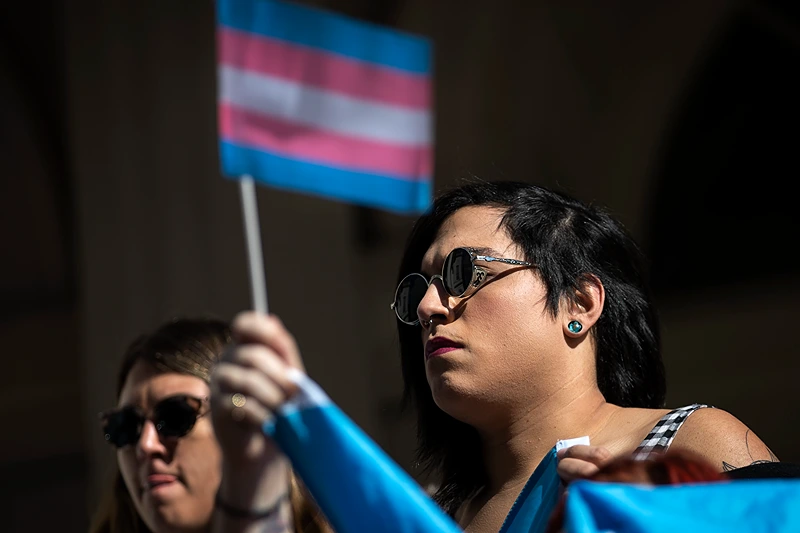
Table of Contents
The Medical Feasibility and Challenges of Uterus Transplants for Transgender Women
Uterus transplantation, while still a relatively new procedure, has shown some success in cisgender women. However, adapting this technology for transgender women presents unique medical challenges. The success rate of uterus transplants in cisgender women, while improving, is not yet universally high, with varying factors influencing outcomes. Translating this to the transgender population necessitates overcoming significant hurdles.
-
Hormonal Therapy: Transgender women undergoing uterus transplantation require meticulous hormonal management before and after the procedure to prepare the body for pregnancy and maintain the transplanted uterus's health. This involves careful monitoring and adjustments to hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
-
Surgical Complexities: The surgery itself is incredibly complex and carries significant risks, including infection, rejection, and potential complications related to blood vessels and the immune system. Adapting the procedure for transgender recipients requires further refinements and specialized surgical expertise.
-
Immunological Considerations: The recipient's immune system must be carefully managed to prevent rejection of the transplanted uterus. This often involves immunosuppressant drugs, which can have significant side effects. The immunological response in transgender women may differ from that of cisgender women, requiring tailored approaches.
-
Long-Term Health Implications: Both the recipient and the donor face potential long-term health consequences. Recipients may experience side effects from immunosuppressants, while donors face surgical risks and the emotional impact of the procedure. Ongoing research is crucial to understand and mitigate these risks.
Current research focuses on improving surgical techniques, refining immunosuppression protocols, and optimizing hormonal management to increase the safety and effectiveness of uterus transplantation in transgender women.
Ethical Considerations and Societal Implications
The ethical landscape surrounding uterus transplants for transgender women is fraught with complexities. The procedure raises significant questions about bodily autonomy, informed consent, and the potential for exploitation.
-
Informed Consent: Ensuring truly informed consent is paramount. Transgender women considering this procedure need comprehensive information about the risks, benefits, and alternatives, empowering them to make autonomous choices.
-
Donor-Recipient Relationship: The relationship between the donor and recipient requires careful consideration, guarding against coercion or exploitation. Strict ethical guidelines and oversight are crucial to prevent undue pressure on potential donors.
-
Commodification of Bodies: Concerns exist about the potential for the commodification of women's bodies, particularly in the context of organ donation. Ethical frameworks must prioritize the well-being and autonomy of both donors and recipients.
-
Societal Impact: The societal implications are profound. Successful uterus transplants could challenge existing gender norms and societal understandings of motherhood and reproduction, leading to shifts in social attitudes and policies.
Legal and Policy Ramifications
The legal and policy landscape surrounding uterus transplants for transgender women is largely uncharted territory. Existing laws related to reproductive rights and organ transplantation need significant adaptation to address the unique circumstances of this procedure.
-
Legal Status: The legal status of uterus transplantation varies across countries. Some jurisdictions may prohibit the procedure entirely, while others may have ambiguous or evolving regulations.
-
Insurance Coverage: Access to uterus transplants is significantly hindered by the cost. Insurance coverage is often lacking, raising serious questions about equity and access to healthcare.
-
Legal Challenges: Potential legal battles may arise concerning issues of discrimination, bodily autonomy, and the definition of motherhood within the context of transgender women.
-
Advocacy Efforts: Advocacy groups are vital in shaping policy and advocating for legislative changes that ensure transgender women have equitable access to reproductive healthcare, including uterus transplantation where medically appropriate.
Alternative Reproductive Options and Technological Advancements
While uterus transplantation offers a potential pathway to parenthood, it's crucial to acknowledge other options available to transgender women.
-
Surrogacy: Surrogacy, while facing legal and ethical complexities depending on jurisdiction, offers an alternative route to parenthood. However, access can be limited by cost and legal restrictions.
-
Adoption: Adoption remains a viable and compassionate path to parenthood for transgender women, although the process can be lengthy and challenging.
-
Reproductive Technology Advancements: Ongoing advancements in reproductive technologies, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), offer potential future avenues for transgender women seeking to conceive. However, these techniques often face ethical and accessibility hurdles.
Each of these alternatives presents its own set of advantages and disadvantages that need careful consideration.
Conclusion
The debate surrounding uterus transplants and transgender women's reproductive rights is complex and multifaceted. It necessitates a careful weighing of medical feasibility, ethical implications, legal frameworks, and alternative reproductive choices. While the prospect of uterus transplants holds potential, significant challenges remain regarding safety, accessibility, and ethical considerations. Ongoing dialogue, further research, and appropriate legislative action are crucial to ensure that all individuals, including transgender women, have access to safe, ethical, and appropriate reproductive healthcare options. We must advocate for policies that support transgender rights and promote reproductive autonomy for all. Support organizations fighting for LGBTQ+ rights and reproductive justice to advance this vital conversation and work towards a future where all individuals can exercise their reproductive rights.
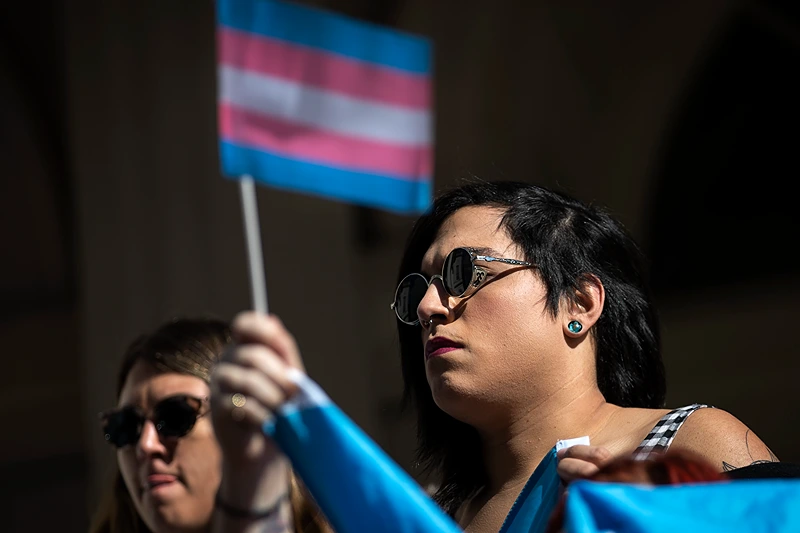
Featured Posts
-
 2 000 Guest Capacity Unveiling The New Look Of The Queen Elizabeth 2 Cruise Ship
May 10, 2025
2 000 Guest Capacity Unveiling The New Look Of The Queen Elizabeth 2 Cruise Ship
May 10, 2025 -
 Three Actions To Show Allyship On International Transgender Day Of Visibility
May 10, 2025
Three Actions To Show Allyship On International Transgender Day Of Visibility
May 10, 2025 -
 Slovenska Dvojnicka Dakoty Johnson
May 10, 2025
Slovenska Dvojnicka Dakoty Johnson
May 10, 2025 -
 High Potential A Legacy Of Psych Spiritual Success After 11 Years
May 10, 2025
High Potential A Legacy Of Psych Spiritual Success After 11 Years
May 10, 2025 -
 U S Federal Reserve Holds Steady Rate Hike Pause Amidst Economic Pressures
May 10, 2025
U S Federal Reserve Holds Steady Rate Hike Pause Amidst Economic Pressures
May 10, 2025
